
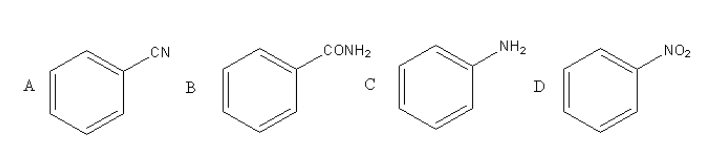
A given nitrogen containing aromatic compound A reacts with \[{\text{Sn/HCl}}\], followed by \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] to give an unstable compound B. B, on treatment with phenol, forms a beautiful coloured compound C with molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_{{\text{12}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{10}}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]. The structure of compound A is:

Answer
573k+ views
Hint: \[{\text{Sn/HCl}}\] will reduce the compound A. Nitric acid \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] cause the formation of diazonium ions. The diazonium ion will give the substitution reaction with phenol. The formed product will be a diazo compound.
Complete step by step solution:
\[{\text{Sn/HCl}}\] is a reducing agent, so it will reduce the compound A. \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] is known as nitric acid. The nitric acid is used for nitration. Nitric acid forms the diazonium ion with the amine functional group.
Amine forms by the reduction of the nitro functional group. So, compound A should be a nitro compound.
Compound A has a cyanide functional group so, option (A) is incorrect.
Compound B has an amide functional group so, option (B) is incorrect.
Compound C has an amine functional group so, option (C) is incorrect.
Compound D has a nitro functional group so, option (D) is correct.
The reaction of nitrobenzene with \[{\text{Sn/HCl}}\] and then with \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] is as follows:
The nitrobenzene gets reduced in presence of \[{\text{Sn/HCl}}\] and forms aniline. Aniline reacts with nitric acid and forms diazonium ion.
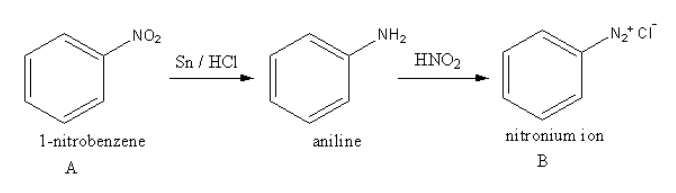
So, the unstable compound B is nitronium ion.
The compound B reacts with phenol to give para-hydroxy azobenzene.
The reaction of compound B with phenol is as follows:
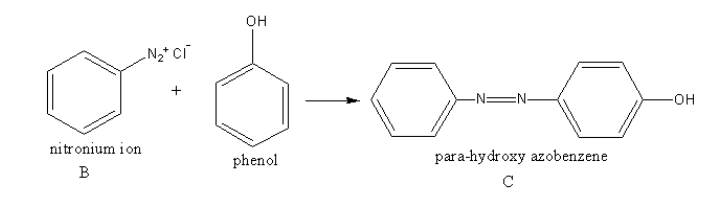
So, the compound A is $1 - $nitrobenzene.
Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Note: The ${\text{Sn + }}\,{\text{HCl}}$ is a reducing agent. The mixture of ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\,{\text{ + }}\,{\text{HCl}}$ at high temperature is used for the preparation of nitric acid which gives diazonium chloride. The diazonium chloride gives an electrophile. The electrophile attacks on the para position of the phenol and replaces the proton forming the final product.
Complete step by step solution:
\[{\text{Sn/HCl}}\] is a reducing agent, so it will reduce the compound A. \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] is known as nitric acid. The nitric acid is used for nitration. Nitric acid forms the diazonium ion with the amine functional group.
Amine forms by the reduction of the nitro functional group. So, compound A should be a nitro compound.
Compound A has a cyanide functional group so, option (A) is incorrect.
Compound B has an amide functional group so, option (B) is incorrect.
Compound C has an amine functional group so, option (C) is incorrect.
Compound D has a nitro functional group so, option (D) is correct.
The reaction of nitrobenzene with \[{\text{Sn/HCl}}\] and then with \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] is as follows:
The nitrobenzene gets reduced in presence of \[{\text{Sn/HCl}}\] and forms aniline. Aniline reacts with nitric acid and forms diazonium ion.

So, the unstable compound B is nitronium ion.
The compound B reacts with phenol to give para-hydroxy azobenzene.
The reaction of compound B with phenol is as follows:

So, the compound A is $1 - $nitrobenzene.
Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Note: The ${\text{Sn + }}\,{\text{HCl}}$ is a reducing agent. The mixture of ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\,{\text{ + }}\,{\text{HCl}}$ at high temperature is used for the preparation of nitric acid which gives diazonium chloride. The diazonium chloride gives an electrophile. The electrophile attacks on the para position of the phenol and replaces the proton forming the final product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




