
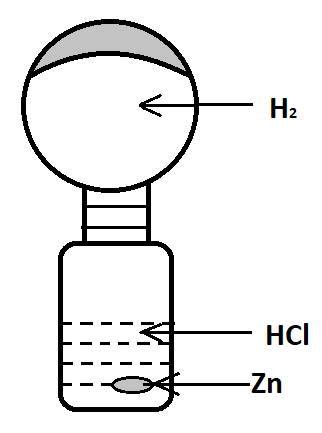
A group of students prepare a hydrogen balloon in the laboratory as shown in the picture below:
(A)What will be the observation if this “setup” is taken from the laboratory and placed in sunlight for one hour?
(B)Name the gas law associated with the above observation.
(C)The volume of ${H_2}$ gas at constant pressure is 500 ml at 300K. Calculate the temperature at which the volume is reduced at 400 ml at the same pressure.

Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The volume of a gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas provided the pressure remains constant. When the balloon is taken out of the lab then temperature increases and pressure becomes constant.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s look at the answer of the part (a)
If the set-up is placed in sunlight for an hour then the volume of the gas will increase as temperature will increase. So, the balloon will inflate more. This is in accordance with Charles law. The sunlight increases the temperature and atmospheric pressure is constant.
Let’s look at the answer of part (b)
The law associated with the above observation is Charles Law. The law states that “The volume of a gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas provided the pressure remains constant.”
Now, volume is directly proportional to temperature at constant pressure.
V α T: at constant pressure.
Let’s look at the answer of part (c)
According to Charles law, ‘V’ is directly proportional to temperature.
V α T
Now, it is given in the question that the initial volume (${V_1}$) is 500mL and the final volume (${V_2}$) is 400ml and the initial temperature (${T_1}$) is 300K.
${V_1}$ = 500ml
${V_2}$ = 400ml
${T_1}$ = 300K
Now, we will calculate the new temperature. From Charles law, we can derive the relation between initial and final temperatures and volume of a gas. The ratio of initial volume and temperature of the gas will be equal to a constant and the ratio of final volume and temperature of the gas will also be equal to the same constant. Hence, we conclude that the ratio of initial temperature and volume of a gas is equal to the ratio of final volume and temperature of the gas.
$\dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_2}}}$
From the above equation: ${T_2} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{V_1}}} \times {T_1}$
${T_2} = \dfrac{{400}}{{500}} \times 300$ = 240K
The new temperature is lower than the previous temperature.
Note: Charles law is applicable to ideal gases and ideal solutions. The application of Charles law is immense in nature. It is widely used in hot air balloons. The tyres of vehicles burst in summer on account of Charles law.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s look at the answer of the part (a)
If the set-up is placed in sunlight for an hour then the volume of the gas will increase as temperature will increase. So, the balloon will inflate more. This is in accordance with Charles law. The sunlight increases the temperature and atmospheric pressure is constant.
Let’s look at the answer of part (b)
The law associated with the above observation is Charles Law. The law states that “The volume of a gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas provided the pressure remains constant.”
Now, volume is directly proportional to temperature at constant pressure.
V α T: at constant pressure.
Let’s look at the answer of part (c)
According to Charles law, ‘V’ is directly proportional to temperature.
V α T
Now, it is given in the question that the initial volume (${V_1}$) is 500mL and the final volume (${V_2}$) is 400ml and the initial temperature (${T_1}$) is 300K.
${V_1}$ = 500ml
${V_2}$ = 400ml
${T_1}$ = 300K
Now, we will calculate the new temperature. From Charles law, we can derive the relation between initial and final temperatures and volume of a gas. The ratio of initial volume and temperature of the gas will be equal to a constant and the ratio of final volume and temperature of the gas will also be equal to the same constant. Hence, we conclude that the ratio of initial temperature and volume of a gas is equal to the ratio of final volume and temperature of the gas.
$\dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_2}}}$
From the above equation: ${T_2} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{V_1}}} \times {T_1}$
${T_2} = \dfrac{{400}}{{500}} \times 300$ = 240K
The new temperature is lower than the previous temperature.
Note: Charles law is applicable to ideal gases and ideal solutions. The application of Charles law is immense in nature. It is widely used in hot air balloons. The tyres of vehicles burst in summer on account of Charles law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




