
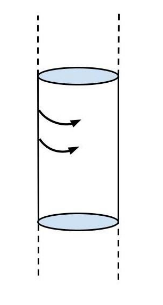
A hollow cylinder having infinite length and carrying uniform current per unit length \[\lambda \]along the circumference as shown. Magnetic field inside the cylinder is:
A. $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}\lambda }}{2}$
B. ${\mu _0}\lambda $
C. $2{\mu _0}\lambda $
D. None

Answer
497.4k+ views
Hint:To answer this question, which is based on Biot-Savart's formula, we must first understand it in general. In physics, specifically electromagnetic, the Biot-Savart law describes the magnetic field generated by a continuous electric current. It connects the magnitude, direction, length, and proximity of the electric current to the magnetic field.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that there is current flowing around its circumference.We already know that there will be a magnetic field inside the cylinder is,
$\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{2I'}}{{r'}}$
Where \[I'\] denotes the direction of flow of current and \[r'\] denotes the distance from the centre.
$\lambda $ is the current length per unit, thus;
\[\lambda {\text{ }} = \;\dfrac{I}{{2\pi r\;}}\;\]
Therefore, from here we will deduce equation for $I$
\[ \Rightarrow I = \;\lambda 2\pi r\]
At $r'$ distance from the center, the current inside the cylinder is: \[{\text{I' = }}\lambda {\text{2}}\pi r{\text{'}}\]
We've now inserted the value into the equation.
\[{{\text{B}}_{{\text{(inside) }}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{2I'}}{{r'}} \\
\Rightarrow {{\text{B}}_{{\text{(inside) }}}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\left( {2 \times \lambda \times \dfrac{{2\pi r'}}{{r'}}} \right) \\
\therefore {{\text{B}}_{{\text{(inside) }}}} = \lambda {\mu _0} \]
Therefore, magnetic field inside the cylinder is \[\lambda {\mu _0}\]
So, the correct option is B.
Additional Information: Biot-Savart Law's Importance;
The following are some of the advantages of the Biot-Savart law:
1. In electrostatics, the Biot-Savart law is comparable to Coulomb's law.
2. The law also applies to very small current-carrying conductors.
3. The law applies to current distributions that are symmetrical.
Note:It's important to understand that the Biot–Savart law is vital to magnetostatics, serving in a similar way to Coulomb's law in electrostatics. When magnetostatics is not applicable, Jefimenko's equations should be used instead of the Biot–Savart law. The law is consistent with both Ampère's circuital law and Gauss's law for magnetism in the magnetostatic approximation.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that there is current flowing around its circumference.We already know that there will be a magnetic field inside the cylinder is,
$\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{2I'}}{{r'}}$
Where \[I'\] denotes the direction of flow of current and \[r'\] denotes the distance from the centre.
$\lambda $ is the current length per unit, thus;
\[\lambda {\text{ }} = \;\dfrac{I}{{2\pi r\;}}\;\]
Therefore, from here we will deduce equation for $I$
\[ \Rightarrow I = \;\lambda 2\pi r\]
At $r'$ distance from the center, the current inside the cylinder is: \[{\text{I' = }}\lambda {\text{2}}\pi r{\text{'}}\]
We've now inserted the value into the equation.
\[{{\text{B}}_{{\text{(inside) }}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{2I'}}{{r'}} \\
\Rightarrow {{\text{B}}_{{\text{(inside) }}}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\left( {2 \times \lambda \times \dfrac{{2\pi r'}}{{r'}}} \right) \\
\therefore {{\text{B}}_{{\text{(inside) }}}} = \lambda {\mu _0} \]
Therefore, magnetic field inside the cylinder is \[\lambda {\mu _0}\]
So, the correct option is B.
Additional Information: Biot-Savart Law's Importance;
The following are some of the advantages of the Biot-Savart law:
1. In electrostatics, the Biot-Savart law is comparable to Coulomb's law.
2. The law also applies to very small current-carrying conductors.
3. The law applies to current distributions that are symmetrical.
Note:It's important to understand that the Biot–Savart law is vital to magnetostatics, serving in a similar way to Coulomb's law in electrostatics. When magnetostatics is not applicable, Jefimenko's equations should be used instead of the Biot–Savart law. The law is consistent with both Ampère's circuital law and Gauss's law for magnetism in the magnetostatic approximation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




