
A hot liquid in a big room. The logarithm of the numerical value of the temperature difference between the liquid and the room is plotted against time. The plot will be very nearly
A) a straight line
B) a circular arc
C) a parabola
D) an ellipse
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: The hot liquid kept in a big room loses its temperature with time. The rate at which the liquid cools is directly proportional to the temperature difference between the liquid and the surroundings of the room. This is known as Newton’s law of cooling.
Complete step by step solution:
When a hot liquid is kept in a big room, the liquid will begin to lose its temperature with time and the surrounding walls of the room will gain the thermal energy of the liquid. Since the room is big, we can assume that the energy dissipated by the liquid will not change the temperature of the surroundings. According to Newton’s law of cooling, the rate of cooling of the hot liquid is directly proportional to the temperature difference between the liquid and the surroundings of the room. If T is the temperature of the hot liquid and ${{T}_{S}}$ is the temperature of the surroundings of the room, then according to Newton’s cooling law
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dT}{dt}\propto (T-{{T}_{S}}) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dT}{dt}=k(T-{{T}_{S}}) \\
\end{align}$
Where, k is a constant of proportionality. Now we bring the $(T-{{T}_{S}})$ term on the LHS and $dt$on the RHS, we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dT}{(T-{{T}_{S}})}=k\,dt$
Performing integration on both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \int{\dfrac{dT}{(T-{{T}_{S}})}=\int{k\,dt}} \\
& \Rightarrow \ln (T-{{T}_{S}})=kt+C \\
\end{align}$
Where, C is the constant. From the above equation, we can say that
$\Rightarrow \ln (T-{{T}_{S}})\propto \,t$
From the above relation, if a graph is plotted between $\ln(T-T_S)$ and $t$, then it will be a straight line as shown below.
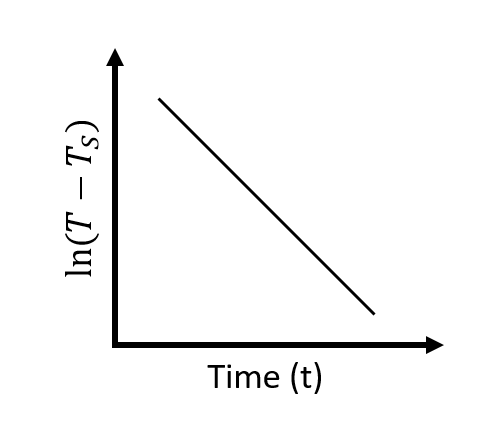
$\therefore$ The plot will be very nearly a straight line. Hence option (A) is correct.
Note:
Newton’s law of cooling is only applicable to small temperature differences. So if the room would have been small the temperature difference would be large and hence, Newton’s law would not be applicable. In such cases, Stefan’s law is to be used.
Complete step by step solution:
When a hot liquid is kept in a big room, the liquid will begin to lose its temperature with time and the surrounding walls of the room will gain the thermal energy of the liquid. Since the room is big, we can assume that the energy dissipated by the liquid will not change the temperature of the surroundings. According to Newton’s law of cooling, the rate of cooling of the hot liquid is directly proportional to the temperature difference between the liquid and the surroundings of the room. If T is the temperature of the hot liquid and ${{T}_{S}}$ is the temperature of the surroundings of the room, then according to Newton’s cooling law
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dT}{dt}\propto (T-{{T}_{S}}) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dT}{dt}=k(T-{{T}_{S}}) \\
\end{align}$
Where, k is a constant of proportionality. Now we bring the $(T-{{T}_{S}})$ term on the LHS and $dt$on the RHS, we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dT}{(T-{{T}_{S}})}=k\,dt$
Performing integration on both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \int{\dfrac{dT}{(T-{{T}_{S}})}=\int{k\,dt}} \\
& \Rightarrow \ln (T-{{T}_{S}})=kt+C \\
\end{align}$
Where, C is the constant. From the above equation, we can say that
$\Rightarrow \ln (T-{{T}_{S}})\propto \,t$
From the above relation, if a graph is plotted between $\ln(T-T_S)$ and $t$, then it will be a straight line as shown below.

$\therefore$ The plot will be very nearly a straight line. Hence option (A) is correct.
Note:
Newton’s law of cooling is only applicable to small temperature differences. So if the room would have been small the temperature difference would be large and hence, Newton’s law would not be applicable. In such cases, Stefan’s law is to be used.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




