
a) Illustrate the following name reactions giving suitable example in each case:
i) Clemmensen reduction
ii) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction
b) How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) Ethyl cyanide to ethanoic acid
(ii) Butan-1-ol to butanoic acid
(iii)Benzoic acid to m-bromobenzoic acid
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: As we know clemmensen reduction is based on the reduction of ketones, or aldehydes, and the reaction Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction is related to the alpha position addition in the carboxylic acid. If we talk about the conversions, then these conversions will be done with the help of bromine, or potassium permanganate.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, we will talk about all the reactions step by step.
First, we will discuss part (a).
The first (i) reaction is Clemmensen reduction.
As mentioned this reaction includes the reduction of aldehydes or ketones using hydrochloric acid, and zinc amalgam, and it is reduced to the alkanes. So, let us take an example of acetophenone.
The chemical reaction is
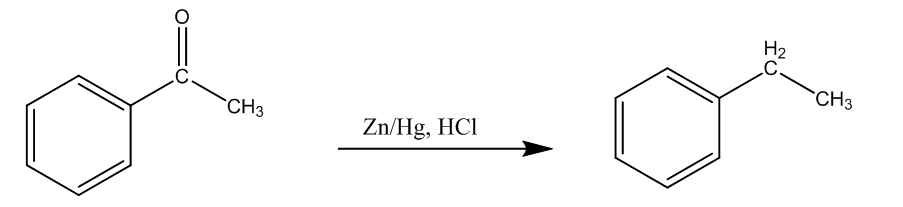
Here, we can see acetophenone is reduced to the Ethyl benzene, or 1-Phenyl Ethane
Now, the second (ii) reaction is Hell- Volhard-Zelinsky, it involves the halogenation of carboxylic acids at the alpha carbon position. This reaction is carried out with the catalytic amount of phosphorus tribromide, and the addition of diatomic bromine.
The chemical reaction is
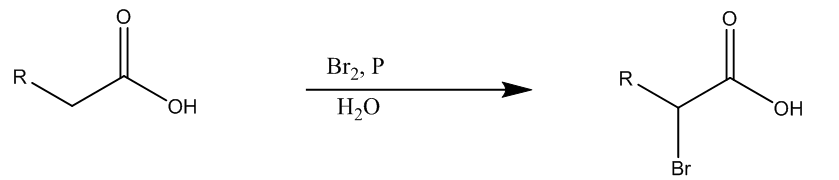
Here we can see the general carboxylic addition forms alpha-bromo carboxylic acid.
Now, we will discuss the part (b).
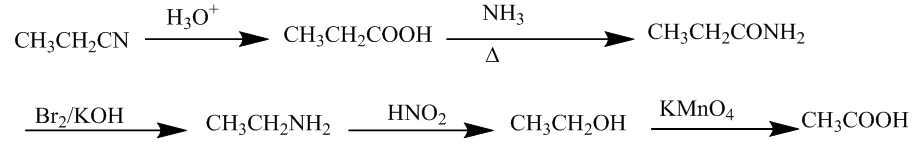
The first (i) is the conversion of Ethyl cyanide to ethanoic acid.
The conversion will take place thru hydrolysis, then diatomic bromine, and potassium permanganate. The chemical reaction is
Now, the second (ii) is the conversion of butan -1- ol to butanoic acid. It is done by the use of potassium permanganate. The chemical reaction is
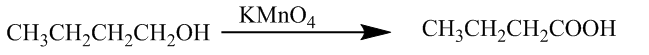
The third (iii) is the conversion of benzoic acid to m-bromobenzoic acid. It takes place through the bromination of benzoic acid. The chemical reaction is
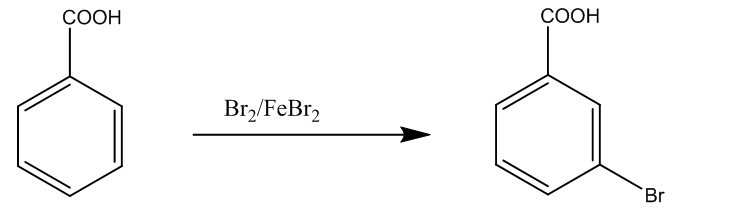
Now, in the end we can conclude that in part (a) (i) the product is alkane, and in (ii) the product is alpha – bromo carboxylic acid. In the part (b) we have shown the conversion reactions.
Note: It is important to know that in the Hell-Volhard- Zelinsky reaction, there is no fluorination, and iodination of carboxylic acids. So, we just consider the bromination of carboxylic acids.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, we will talk about all the reactions step by step.
First, we will discuss part (a).
The first (i) reaction is Clemmensen reduction.
As mentioned this reaction includes the reduction of aldehydes or ketones using hydrochloric acid, and zinc amalgam, and it is reduced to the alkanes. So, let us take an example of acetophenone.
The chemical reaction is

Here, we can see acetophenone is reduced to the Ethyl benzene, or 1-Phenyl Ethane
Now, the second (ii) reaction is Hell- Volhard-Zelinsky, it involves the halogenation of carboxylic acids at the alpha carbon position. This reaction is carried out with the catalytic amount of phosphorus tribromide, and the addition of diatomic bromine.
The chemical reaction is

Here we can see the general carboxylic addition forms alpha-bromo carboxylic acid.
Now, we will discuss the part (b).
The first (i) is the conversion of Ethyl cyanide to ethanoic acid.
The conversion will take place thru hydrolysis, then diatomic bromine, and potassium permanganate. The chemical reaction is

Now, the second (ii) is the conversion of butan -1- ol to butanoic acid. It is done by the use of potassium permanganate. The chemical reaction is
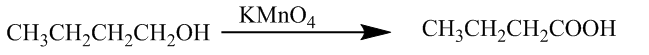
The third (iii) is the conversion of benzoic acid to m-bromobenzoic acid. It takes place through the bromination of benzoic acid. The chemical reaction is

Now, in the end we can conclude that in part (a) (i) the product is alkane, and in (ii) the product is alpha – bromo carboxylic acid. In the part (b) we have shown the conversion reactions.
Note: It is important to know that in the Hell-Volhard- Zelinsky reaction, there is no fluorination, and iodination of carboxylic acids. So, we just consider the bromination of carboxylic acids.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




