
A ladder 5 m long is leaning against a wall. The bottom of the ladder is pulled along the ground away from the wall, at the rate of 2 m/s. How fast is its height on the wall decreasing when the foot of the ladder is 4 m away from the wall?
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: In this question use the concept of Pythagoras theorem which is given as; $ {\left( {hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {perpendicular} \right)^2} + {\left( {base} \right)^2} $ and also remember that $ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = 2m/s $ , use this information to approach the solution of the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
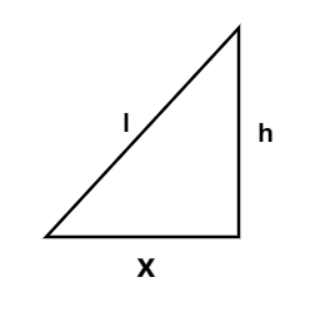
According to the given information we have length of ladder (l) = 5 m
Let x be the distance between the bottom of the ladder and the wall at any instant and h be the height of the wall between the top of the ladder and the wall at any instant
Also, the rate at which the foot of the ladder is pulled along the ground away from the wall i.e. $ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = 2m/s $ (it is positive because x is increasing with time)
Since, at any instant according to Pythagoras theorem $ {l^2} = {x^2} + {h^2} $
Substituting the values in the above equation we get
$ {\left( 5 \right)^2} = {x^2} + {h^2} $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ 25 = {x^2} + {h^2} $ (equation 1)
Differentiating equation (1) with respect to time, we get
$ \dfrac{d}{{dt}}\left( {25} \right) = \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}\left( {{x^2}} \right) + \dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}}\left( {{h^2}} \right) $
As we know that \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( C \right) = 0\]here C is the constant and \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^n}} \right) = n{x^{n - 1}}\]
Therefore, $ 0 = 2x\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} + 2h\dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ h\dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} = - x\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ \dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} = \left( {\dfrac{{ - x}}{h}} \right)\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} $ (equation 2)
At the instant when foot of the ladder is 4 m away from the wall i.e. when x = 4m using equation 1 we can say
$ {\left( 4 \right)^2} + {h^2} - 25 $
$ \Rightarrow 8 + {h^2} = 25 $
$\Rightarrow {h^2} = 25 - 16 $
$\Rightarrow {h^2} = 9 $
$\Rightarrow h = \sqrt 9 = \pm 3 $
Since height h is always a positive quantity so h = - 3 is rejected
Therefore h = 3 m
Now, put x = 4 m and h = 3 m and $ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = 2m/s $ in equation 2 we get
$ \dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} = \left( {\dfrac{{ - 4}}{3}} \right) \times 2 $
$ \Rightarrow\dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} = - 2.67m/s $
Here negative sign shows that height of the wall is decreasing with respect to time
Therefore, the height on the wall is decreasing at a rate of 2.67 m/s when the foot of the ladder is 4 m away from the wall.
Note: In these types of problems, a relation between various variables are obtained using the Pythagoras theorem since using the given information we formed a right-angle triangle and then by differentiating it we get the relation between the rate of change of these variables and hence finally the unknown rate of change of variable is computed with the help of given data.
Complete step-by-step answer:
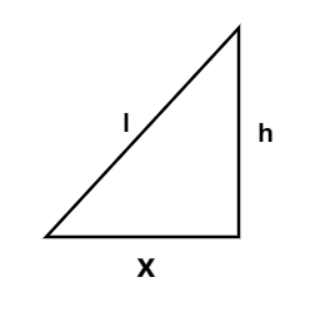
According to the given information we have length of ladder (l) = 5 m
Let x be the distance between the bottom of the ladder and the wall at any instant and h be the height of the wall between the top of the ladder and the wall at any instant
Also, the rate at which the foot of the ladder is pulled along the ground away from the wall i.e. $ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = 2m/s $ (it is positive because x is increasing with time)
Since, at any instant according to Pythagoras theorem $ {l^2} = {x^2} + {h^2} $
Substituting the values in the above equation we get
$ {\left( 5 \right)^2} = {x^2} + {h^2} $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ 25 = {x^2} + {h^2} $ (equation 1)
Differentiating equation (1) with respect to time, we get
$ \dfrac{d}{{dt}}\left( {25} \right) = \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}\left( {{x^2}} \right) + \dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}}\left( {{h^2}} \right) $
As we know that \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( C \right) = 0\]here C is the constant and \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^n}} \right) = n{x^{n - 1}}\]
Therefore, $ 0 = 2x\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} + 2h\dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ h\dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} = - x\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ \dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} = \left( {\dfrac{{ - x}}{h}} \right)\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} $ (equation 2)
At the instant when foot of the ladder is 4 m away from the wall i.e. when x = 4m using equation 1 we can say
$ {\left( 4 \right)^2} + {h^2} - 25 $
$ \Rightarrow 8 + {h^2} = 25 $
$\Rightarrow {h^2} = 25 - 16 $
$\Rightarrow {h^2} = 9 $
$\Rightarrow h = \sqrt 9 = \pm 3 $
Since height h is always a positive quantity so h = - 3 is rejected
Therefore h = 3 m
Now, put x = 4 m and h = 3 m and $ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = 2m/s $ in equation 2 we get
$ \dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} = \left( {\dfrac{{ - 4}}{3}} \right) \times 2 $
$ \Rightarrow\dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} = - 2.67m/s $
Here negative sign shows that height of the wall is decreasing with respect to time
Therefore, the height on the wall is decreasing at a rate of 2.67 m/s when the foot of the ladder is 4 m away from the wall.
Note: In these types of problems, a relation between various variables are obtained using the Pythagoras theorem since using the given information we formed a right-angle triangle and then by differentiating it we get the relation between the rate of change of these variables and hence finally the unknown rate of change of variable is computed with the help of given data.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




