
A layer of ice of thickness y is on the surface of a lake. The air is at constant temperature \[ - \theta \]°\[C\] and the ice water interface is at \[0^\circ \]. Then that the rate at which the thickness increases is given by.
\[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{k\theta }}{{L\rho y}}\]
Where k is the thermal conductivity of the ice, \[L\] is the latent heat of fusion and \[\rho \] is the density of the ice. Type 1 for true and 0 for false.
Answer
572.4k+ views
Hint: As in the question thickness of layer of ice is given and also air at constant temperature and ice water interface is also given. Temperature of water is more than the ice, so heat will be there that is going from water to air through ice. By considering this, we can easily find the rate at which the thickness will be increased.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider one lake and it is having a layer of ice on its surface as shown. The thickness of the ice is y and the air is at constant temperature \[ - \theta \]°\[C\] and the ice water interface is at \[0^\circ \].
Rate at which the thickness increases, \[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{k\theta }}{{L\rho y}}\]
Where k is the thermal conductivity of the ice, \[L\] is the latent heat of fusion and \[\rho \] is the density of the ice.
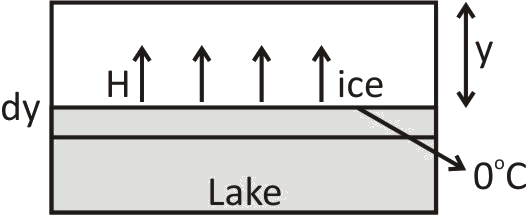
As heat will be going from water to air through ice, so
\[H = \dfrac{{\Delta T}}{R}\]
\[\dfrac{{0 - \left( \theta \right)}}{R} = \dfrac{\theta }{R}\] ----- (1)
We know,
\[H = \dfrac{{dQ}}{{dt}}\] ------ (2)
Compare equation (1) and (2), we get-
\[dQ = \dfrac{\theta }{R}.dt\] ---- (3)
Also, \[R = \dfrac{t}{{kA}}\]
Here t is thickness, A is area and K is thermal conductivity.
\[R = \dfrac{y}{{kA}}\]
Substitute the value of R in equation (3), we get-
\[dQ = \dfrac{{\theta kA}}{y}.dt\]
This \[dQ\] is the heat that is going from water to air through ice. Using this much amount of heat, ice formed and \[dy\] layer of ice is increased (as shown)
If Q heat is used then, \[Q = m \times L\]
Here L is the latent heat of the fusion.
We know, \[m = v \times \rho \] (mass= volume× density)
\[ = A \times dy \times \rho \times L\]
\[dQ = \dfrac{{\theta kA}}{y}.dt\]
\[Ady.L.\rho = \dfrac{{\theta kA}}{y}.dt\]
So, \[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{\theta kA}}{{y.A.L.\rho }}\]
\[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = \] \[\dfrac{{\theta k}}{{L\rho y}}\]
So, this is true.
Note:
The latent heat of fusion is the amount of heat that is gained by solid substance to convert into liquid without any other increase in temperature.
Or we can also solve directly by rate of loss of heat = \[L.A\rho \dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}}\] =\[\dfrac{{K\theta A}}{y}\]
By comparing equations, we will get the \[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}}\]
Complete step by step solution:
Consider one lake and it is having a layer of ice on its surface as shown. The thickness of the ice is y and the air is at constant temperature \[ - \theta \]°\[C\] and the ice water interface is at \[0^\circ \].
Rate at which the thickness increases, \[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{k\theta }}{{L\rho y}}\]
Where k is the thermal conductivity of the ice, \[L\] is the latent heat of fusion and \[\rho \] is the density of the ice.

As heat will be going from water to air through ice, so
\[H = \dfrac{{\Delta T}}{R}\]
\[\dfrac{{0 - \left( \theta \right)}}{R} = \dfrac{\theta }{R}\] ----- (1)
We know,
\[H = \dfrac{{dQ}}{{dt}}\] ------ (2)
Compare equation (1) and (2), we get-
\[dQ = \dfrac{\theta }{R}.dt\] ---- (3)
Also, \[R = \dfrac{t}{{kA}}\]
Here t is thickness, A is area and K is thermal conductivity.
\[R = \dfrac{y}{{kA}}\]
Substitute the value of R in equation (3), we get-
\[dQ = \dfrac{{\theta kA}}{y}.dt\]
This \[dQ\] is the heat that is going from water to air through ice. Using this much amount of heat, ice formed and \[dy\] layer of ice is increased (as shown)
If Q heat is used then, \[Q = m \times L\]
Here L is the latent heat of the fusion.
We know, \[m = v \times \rho \] (mass= volume× density)
\[ = A \times dy \times \rho \times L\]
\[dQ = \dfrac{{\theta kA}}{y}.dt\]
\[Ady.L.\rho = \dfrac{{\theta kA}}{y}.dt\]
So, \[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{\theta kA}}{{y.A.L.\rho }}\]
\[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = \] \[\dfrac{{\theta k}}{{L\rho y}}\]
So, this is true.
Note:
The latent heat of fusion is the amount of heat that is gained by solid substance to convert into liquid without any other increase in temperature.
Or we can also solve directly by rate of loss of heat = \[L.A\rho \dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}}\] =\[\dfrac{{K\theta A}}{y}\]
By comparing equations, we will get the \[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




