
What is a Lever? State its principle.
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: Lever comes under an easy machine and it's defined as a lever may be a rigid, straight or bent bar which is capable of turning a few fixed axes. A lever works on the principle of moments, the principle of moment states that, when a system or a body is in equilibrium the sum of the clockwise moments will be suitable to the sum of the anticlockwise moments on the system or the thing.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A lever may be a machine made from a rigid beam and a fulcrum. The effort (input force) and cargo (output force) are applied to either end of the beam. The fulcrum is the point on which the beam pivots. When an attempt is applied to at least one end of the lever, a load is applied at the opposite end of the lever.
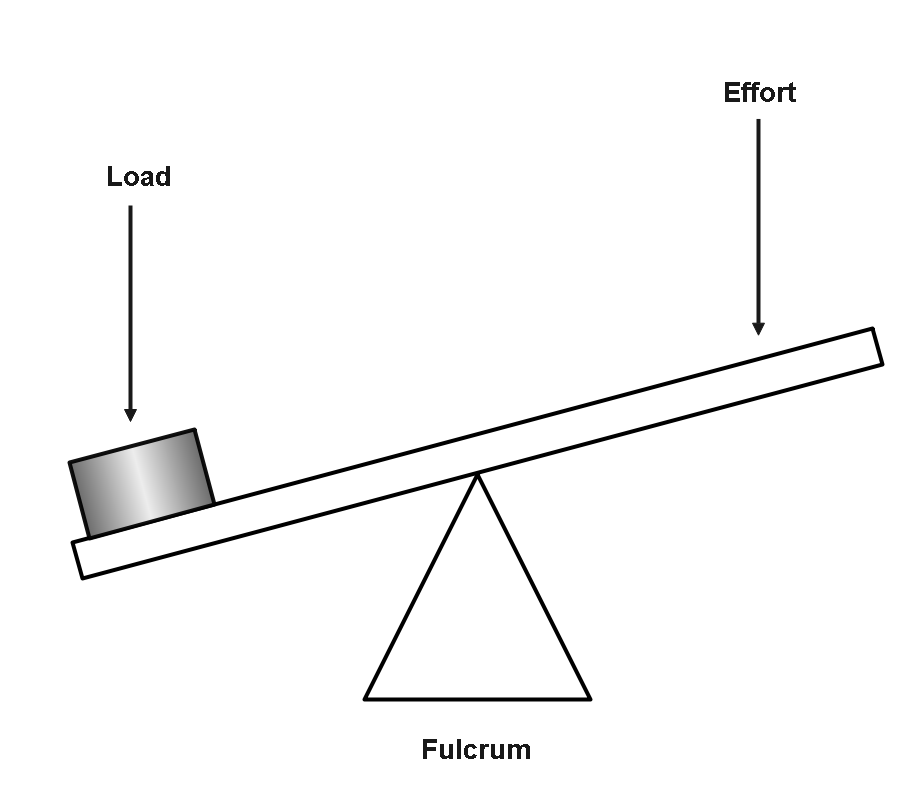
There are three parts to all levers:
Fulcrum: A resistive force that is to be overcome by a machine is called the Load. S.I. The unit is Newton (N).
Input force: (also called the effort) An external force applied to a simple machine to overcome a load is called the Effort. S.I. The unit is Newton (N).
Output force: (also called the load) The point on which something turns or is supported.
Mechanical advantage: ratio may be a measure of the force amplification achieved by employing a tool, robot or machine system. The device trades off input forces against movement to get a desired amplification within the output force. The model for this is often the law of the lever.
Principle: Now we will understand the principle of lever.
The lever may be a movable bar that pivots on a fulcrum attached to a hard and fast point. The lever works by putting forces at different distances from the or a pivot. As the lever rotates around the pivot point or fulcrum the distant part moves faster than the closer point.
Therefore, we can say that the force applied to the far point from the fulcrum must be less than the force located at a closer point, because power is the product of force and velocity.
A principle that applies to a system of balanced forces a few fulcrum or pivot, during which the entire anticlockwise moment is adequate to the entire clockwise moment. Therefore, a lever will balance or turn regularly about the purpose of support when the range of the force and force arm equals the range of the resistance and resistance arm.
Note: Generally, the lever system is employed to lift loads using the principle of moments. When heavy loads must be lifted, they are put on the load end and then, the fulcrum is pushed close to the load. Hence, the load arm distance is reduced and energy arm distance is increased. Hence using the principle of moments, the load is often lifted employing a lower amount of effort force, since the products of load and cargo arm are going to be equal to the effort and effort arm.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A lever may be a machine made from a rigid beam and a fulcrum. The effort (input force) and cargo (output force) are applied to either end of the beam. The fulcrum is the point on which the beam pivots. When an attempt is applied to at least one end of the lever, a load is applied at the opposite end of the lever.

There are three parts to all levers:
Fulcrum: A resistive force that is to be overcome by a machine is called the Load. S.I. The unit is Newton (N).
Input force: (also called the effort) An external force applied to a simple machine to overcome a load is called the Effort. S.I. The unit is Newton (N).
Output force: (also called the load) The point on which something turns or is supported.
Mechanical advantage: ratio may be a measure of the force amplification achieved by employing a tool, robot or machine system. The device trades off input forces against movement to get a desired amplification within the output force. The model for this is often the law of the lever.
Principle: Now we will understand the principle of lever.
The lever may be a movable bar that pivots on a fulcrum attached to a hard and fast point. The lever works by putting forces at different distances from the or a pivot. As the lever rotates around the pivot point or fulcrum the distant part moves faster than the closer point.
Therefore, we can say that the force applied to the far point from the fulcrum must be less than the force located at a closer point, because power is the product of force and velocity.
A principle that applies to a system of balanced forces a few fulcrum or pivot, during which the entire anticlockwise moment is adequate to the entire clockwise moment. Therefore, a lever will balance or turn regularly about the purpose of support when the range of the force and force arm equals the range of the resistance and resistance arm.
Note: Generally, the lever system is employed to lift loads using the principle of moments. When heavy loads must be lifted, they are put on the load end and then, the fulcrum is pushed close to the load. Hence, the load arm distance is reduced and energy arm distance is increased. Hence using the principle of moments, the load is often lifted employing a lower amount of effort force, since the products of load and cargo arm are going to be equal to the effort and effort arm.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




