
What is a line spectrum? How it differs from the band spectrum.
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: when a light is passed through a prism it spreads into a series called as spectra. There are two types of spectrum emission and absorption spectra. The spectrum of radiation emitted by a substance that has absorbed energy is called the emission spectrum, while the absorption spectrum is considered as the photographic negative of the emission spectrum.
Complete answer:
When any substance absorbs energy and then this energy is radiated, it occurs in the form of a spectrum, like a band of light dispersed by a prism. Emission spectrum consists of atoms and molecules having absorbed energy by the heat that is provided to them, and then they become excited and emit energy. The absorption spectrum is the negative of the emission spectrum.
These emission and absorption spectra, when they do not emit light in a continuous manner, that is they emit light at only specific wavelengths, then the spectra is termed as a line spectra. This is often observed for atoms and called atomic spectra. It contains lines on various frequencies or energies.
Line spectrum differs from band spectrum as band spectrum consists of continuous radiation of light emitted by the substance that absorbs some wavelengths while some wavelength is missing, creating dark bands of almost similar frequencies, therefore called band spectrum.
Line spectrum looks like
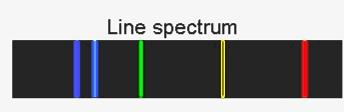
And band spectrum looks like
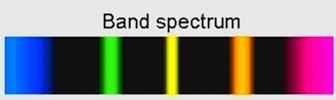
Hence, line spectrum is for atoms having radiations at particular wavelengths, while band spectrum has continuous radiations creating dark bands.
Note:
The atomic spectrum is unique for elements as each element has a different atomic spectrum like a fingerprint. This is used to identify elements. This technique that uses the study of emission and absorption spectrum is called spectroscopy and is used to identify elements like radium, gallium, thallium, etc.
Complete answer:
When any substance absorbs energy and then this energy is radiated, it occurs in the form of a spectrum, like a band of light dispersed by a prism. Emission spectrum consists of atoms and molecules having absorbed energy by the heat that is provided to them, and then they become excited and emit energy. The absorption spectrum is the negative of the emission spectrum.
These emission and absorption spectra, when they do not emit light in a continuous manner, that is they emit light at only specific wavelengths, then the spectra is termed as a line spectra. This is often observed for atoms and called atomic spectra. It contains lines on various frequencies or energies.
Line spectrum differs from band spectrum as band spectrum consists of continuous radiation of light emitted by the substance that absorbs some wavelengths while some wavelength is missing, creating dark bands of almost similar frequencies, therefore called band spectrum.
Line spectrum looks like

And band spectrum looks like

Hence, line spectrum is for atoms having radiations at particular wavelengths, while band spectrum has continuous radiations creating dark bands.
Note:
The atomic spectrum is unique for elements as each element has a different atomic spectrum like a fingerprint. This is used to identify elements. This technique that uses the study of emission and absorption spectrum is called spectroscopy and is used to identify elements like radium, gallium, thallium, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




