
A lipid is a polymer made up of
(a) Modified glucose molecules
(b) Amino acids
(c) Nucleotides
(d) Fatty acids and glycerol
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: In humans and other animals lipids are the main constituents of body fat, as well as vegetable fat. The primary feature all lipid molecules share is they don't dissolve in water.
Complete answer:
A lipid is a polymer composed of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule. Lipids produce a special polymer form which is considered to be a key component of cell membranes and hormones. Lipids help to store energy, provide cushion, protect tissues, separate the body, and form membranes of cells.
- Glucose molecules are the monomers that constitute the polysaccharides.
- Amino acids are the polypeptide chain or protein monomer. 20 amino acids make up the various protein types.
- Nucleotides are the nucleic acid monomers e.g. DNA and RNA.
Fatty acids are lipid monomers formed by a hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group attached at the end. This is the simplest form of polymer in lipids. A carboxyl group consists of a carbon atom that forms a double bond with a single atom of oxygen and a single bond with an atom of oxygen bound to another atom of carbon. These chains make up the saturated and unsaturated fats in animals and plants.
Glycerol is a simple alcohol composed of three atoms of oxygen and three atoms of carbon that bind eight times with hydrogen atoms. When each single- bonded oxygen molecule binds to a carbon that is part of a glycerol molecule, fatty acids form more complex lipid polymers called triglycerides, triacylglycerols, or triacylglycerides. Triglycerides, especially make up animal products.
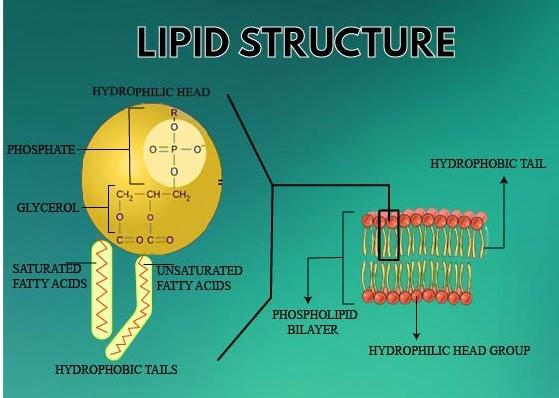
So, the correct answer is, ‘Fatty acids and glycerol’.
Note: Lipids are substances that are water- insoluble and can be categorized as fats, phospholipids, waxes, and steroids. This makes lipids essential to building structures, such as cell membranes, that have to retain their shape when surrounded by liquid. Its tight molecular bonds make lipids ideal for long-term storage of energy. The insolubility of lipid molecules is given because they form with ester bonds, compounds formed from an alcohol and acid by removing a hydrogen atom in a water molecule.
Complete answer:
A lipid is a polymer composed of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule. Lipids produce a special polymer form which is considered to be a key component of cell membranes and hormones. Lipids help to store energy, provide cushion, protect tissues, separate the body, and form membranes of cells.
- Glucose molecules are the monomers that constitute the polysaccharides.
- Amino acids are the polypeptide chain or protein monomer. 20 amino acids make up the various protein types.
- Nucleotides are the nucleic acid monomers e.g. DNA and RNA.
Fatty acids are lipid monomers formed by a hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group attached at the end. This is the simplest form of polymer in lipids. A carboxyl group consists of a carbon atom that forms a double bond with a single atom of oxygen and a single bond with an atom of oxygen bound to another atom of carbon. These chains make up the saturated and unsaturated fats in animals and plants.
Glycerol is a simple alcohol composed of three atoms of oxygen and three atoms of carbon that bind eight times with hydrogen atoms. When each single- bonded oxygen molecule binds to a carbon that is part of a glycerol molecule, fatty acids form more complex lipid polymers called triglycerides, triacylglycerols, or triacylglycerides. Triglycerides, especially make up animal products.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Fatty acids and glycerol’.
Note: Lipids are substances that are water- insoluble and can be categorized as fats, phospholipids, waxes, and steroids. This makes lipids essential to building structures, such as cell membranes, that have to retain their shape when surrounded by liquid. Its tight molecular bonds make lipids ideal for long-term storage of energy. The insolubility of lipid molecules is given because they form with ester bonds, compounds formed from an alcohol and acid by removing a hydrogen atom in a water molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




