
A man is moving downward on an inclined plane ($\theta=37^\circ$) with velocity ${{v}_{0}}$ and rain drops appear to him moving in horizontal direction with velocity $2{{v}_{0}}$ towards him. If man increases his velocity to $2{{v}_{0}}$ then what is the velocity of rain drops as observed by man?
A. $\sqrt{\dfrac{41}{5}}{{v}_{0}}$
B. $\sqrt{39}{{v}_{0}}$
C. $7{{v}_{0}}$
D. $6{{v}_{0}}$

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Velocity of an object is the rate of change of position. It is a vector quantity and thus, has both magnitude and direction.
The velocity of man and relative velocity of rain is given. The relative velocity of the object A with respect to B is defined as the velocity of object A in the rest frame of object B.
First, resolve the velocity of man and relative velocity of rain in its vector components, obtain velocity of rain with respect to ground. Then, after man increases his velocity, obtain relative velocity of rain.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Velocity of an object is defined as its displacement per unit time. It is a vector.
Relative velocity of the object A with respect to B tells us the velocity of object A in the rest frame of object B.
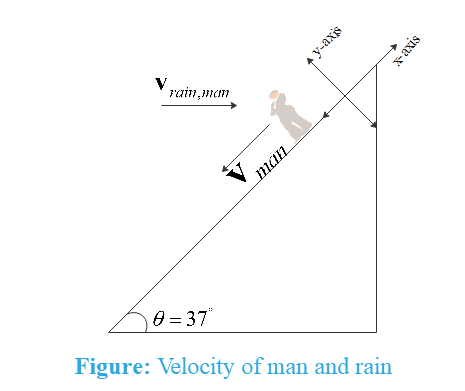
The observer is moving with velocity ${{v}_{0}}$ downward the inclined plane as shown. We resolve the velocity of man in direction of motion and perpendicular to direction of motion as shown in figure and assume that x-axis lies along inclined plane and y-axis lies perpendicular to it. The velocity vector of man can be written as
${{\mathbf{v}}_{man}}=-{{v}_{0}}\,\hat{i}$
The relative velocity of rain with respect to man is $2{{v}_{0}}$ towards the man horizontally. Therefore, velocity vector of rain with respect to man can be written as
${{\mathbf{v}}_{rain,man}}=2{{v}_{0}}\cos \theta \,\,\hat{i}-2{{v}_{0}}\sin \theta \,\,\hat{j}$
$\because {{\mathbf{v}}_{rain,man}}={{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}}-{{\mathbf{v}}_{man}}\Rightarrow {{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}}={{\mathbf{v}}_{man}}+{{\mathbf{v}}_{rain,man}}$${{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}}=-3{{v}_{0}}\cos \theta \,\,\hat{i}-3{{v}_{0}}\sin \theta \,\,\hat{j}$
We get velocity of rain with respect to ground as
${{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}}=\left( 2{{v}_{0}}\cos \theta \,\,\hat{i}-2{{v}_{0}}\sin \theta \,\,\hat{j} \right)+\left( -{{v}_{0}}\,\,\hat{i} \right)$
${{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}}=(2{{v}_{0}}\cos \theta \,-{{v}_{0}})\hat{i}-2{{v}_{0}}\sin \theta \,\,\hat{j}$
If man increases his velocity to $2{{v}_{0}}$, his velocity becomes
$\mathbf{v}{{'}_{man}}=-2{{v}_{0}}\,\,\hat{i}$
The velocity of rain drops as observed by man after increasing his speed is the relative velocity i.e.
$\mathbf{v}{{'}_{rain,man}}=\mathbf{v}{{'}_{rain}}-\mathbf{v}{{'}_{man}}$
$\Rightarrow \mathbf{v}{{'}_{rain,man}}=[(2{{v}_{0}}\cos \theta \,-{{v}_{0}})\hat{i}-2{{v}_{0}}\sin \theta \,\hat{j}]-(-2{{v}_{0}}\,\,\hat{i})$
$\Rightarrow \mathbf{v}{{'}_{rain,man}}={{v}_{0}}[(2\cos \theta +1)\hat{i}-2\sin \theta \,\,\hat{j}$
Magnitude of velocity of rain is
$\left| {{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}} \right|=\sqrt{{{v}_{0}}^{2}[{{(2\cos \theta +1)}^{2}}+{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }$
Since, we have $\theta=37^\circ$, $\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5}$ and $\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}$. We substitute these values and get
$\left| {{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}} \right|={{v}_{0}}\sqrt{{{\left( 2\times \dfrac{4}{5}+1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right)}^{2}}}={{v}_{0}}\sqrt{\dfrac{41}{5}}$
Hence, option A is correct.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Velocity is a vector quantity and has both magnitude and direction.
The relative velocity of an object A with respect to B is defined as its velocity in the rest frame of object B.
Vector sum of any two quantities is the sum of their corresponding components.
The velocity of man and relative velocity of rain is given. The relative velocity of the object A with respect to B is defined as the velocity of object A in the rest frame of object B.
First, resolve the velocity of man and relative velocity of rain in its vector components, obtain velocity of rain with respect to ground. Then, after man increases his velocity, obtain relative velocity of rain.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Velocity of an object is defined as its displacement per unit time. It is a vector.
Relative velocity of the object A with respect to B tells us the velocity of object A in the rest frame of object B.

The observer is moving with velocity ${{v}_{0}}$ downward the inclined plane as shown. We resolve the velocity of man in direction of motion and perpendicular to direction of motion as shown in figure and assume that x-axis lies along inclined plane and y-axis lies perpendicular to it. The velocity vector of man can be written as
${{\mathbf{v}}_{man}}=-{{v}_{0}}\,\hat{i}$
The relative velocity of rain with respect to man is $2{{v}_{0}}$ towards the man horizontally. Therefore, velocity vector of rain with respect to man can be written as
${{\mathbf{v}}_{rain,man}}=2{{v}_{0}}\cos \theta \,\,\hat{i}-2{{v}_{0}}\sin \theta \,\,\hat{j}$
$\because {{\mathbf{v}}_{rain,man}}={{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}}-{{\mathbf{v}}_{man}}\Rightarrow {{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}}={{\mathbf{v}}_{man}}+{{\mathbf{v}}_{rain,man}}$${{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}}=-3{{v}_{0}}\cos \theta \,\,\hat{i}-3{{v}_{0}}\sin \theta \,\,\hat{j}$
We get velocity of rain with respect to ground as
${{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}}=\left( 2{{v}_{0}}\cos \theta \,\,\hat{i}-2{{v}_{0}}\sin \theta \,\,\hat{j} \right)+\left( -{{v}_{0}}\,\,\hat{i} \right)$
${{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}}=(2{{v}_{0}}\cos \theta \,-{{v}_{0}})\hat{i}-2{{v}_{0}}\sin \theta \,\,\hat{j}$
If man increases his velocity to $2{{v}_{0}}$, his velocity becomes
$\mathbf{v}{{'}_{man}}=-2{{v}_{0}}\,\,\hat{i}$
The velocity of rain drops as observed by man after increasing his speed is the relative velocity i.e.
$\mathbf{v}{{'}_{rain,man}}=\mathbf{v}{{'}_{rain}}-\mathbf{v}{{'}_{man}}$
$\Rightarrow \mathbf{v}{{'}_{rain,man}}=[(2{{v}_{0}}\cos \theta \,-{{v}_{0}})\hat{i}-2{{v}_{0}}\sin \theta \,\hat{j}]-(-2{{v}_{0}}\,\,\hat{i})$
$\Rightarrow \mathbf{v}{{'}_{rain,man}}={{v}_{0}}[(2\cos \theta +1)\hat{i}-2\sin \theta \,\,\hat{j}$
Magnitude of velocity of rain is
$\left| {{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}} \right|=\sqrt{{{v}_{0}}^{2}[{{(2\cos \theta +1)}^{2}}+{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }$
Since, we have $\theta=37^\circ$, $\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5}$ and $\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}$. We substitute these values and get
$\left| {{\mathbf{v}}_{rain}} \right|={{v}_{0}}\sqrt{{{\left( 2\times \dfrac{4}{5}+1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right)}^{2}}}={{v}_{0}}\sqrt{\dfrac{41}{5}}$
Hence, option A is correct.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Velocity is a vector quantity and has both magnitude and direction.
The relative velocity of an object A with respect to B is defined as its velocity in the rest frame of object B.
Vector sum of any two quantities is the sum of their corresponding components.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




