
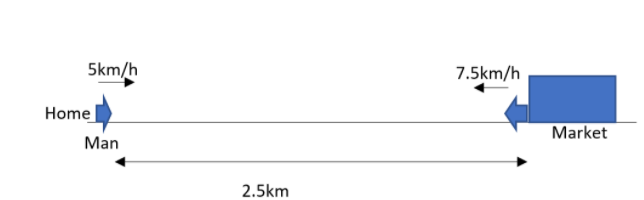
A man is on a journey on a straight road from his home to a market $2.5km$ away with a speed of $5km{{h}^{-1}}$. It has been found that when the market closes, he instantly turns and walks back home with a speed of $7.5km{{h}^{-1}}$.
(a) What will be the magnitude of average velocity?
(b) What will be the average speed of the man over the interval of time?
$\begin{align}
& \left( 1 \right)0\text{ to 30min} \\
& \left( 2 \right)0\text{ to 50min} \\
& \left( 3 \right)0\text{ to 40min} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: First of all find the average velocity and average speed on the journey to the market and the comeback. Calculate the total time taken for the travel. When the person comes back home, the displacement will be zero. Calculate the same in each interval of time mentioned in the question. This all will help you in answering the question.
Complete step by step answer:
The time taken to reach market will be,
${{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{2.5}{5}=0.5h=30\min $
The time taken to get back to home will be calculated as,
${{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{2.5}{7.5}=0.33h=20\min $
The average velocity for the interval $\left( 0-30 \right)\min $ will be,
$v=\dfrac{2.5}{0.5}=5km{{h}^{-1}}$
Average speed for the interval $\left( 0-30 \right)\min $ will be,
$s=\dfrac{2.5}{0.5}=5km{{h}^{-1}}$
Total time taken for the travel will be,
$t=30+20=50\min =\dfrac{5}{6}h$
We can see that when he reached back then net displacement will be zero
Therefore in the case of $\left( 0-50 \right)\min $, the average velocity will be,
$v=\dfrac{0}{\dfrac{5}{6}}=0km{{h}^{-1}}$
Total distance he covered when he arrive back will be,
$2.5+2.5=5km$
Therefore the average speed will be given as,
$s=\dfrac{5}{\dfrac{5}{6}}=6km{{h}^{-1}}$
Distance travelled in the first $30\min $is given as $2.5km$. While returning, the distance travelled in $10\min $,
$d=7.5\times \dfrac{1}{6}=1.25km$
The total time taken will be,
$t=40\min =\dfrac{2}{3}h$
Hence the displacement in $0-40\min $will be,
$2.5-1.25=1.25km$
The average velocity for the interval $0-40\min $is,
$v=\dfrac{1.25}{\dfrac{2}{3}}=1.875km{{h}^{-1}}$
The average speed in this interval is given as,
$s=\dfrac{3.75}{\dfrac{2}{3}}=5.625km{{h}^{-1}}$
Note: The velocity is the time rate of variation of the displacement. Distance covered is the total length of the path traversed by a body. The displacement will be the shortest distance between the initial and final locations of the body. Time rate of variation of distance is known as speed.
Complete step by step answer:
The time taken to reach market will be,
${{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{2.5}{5}=0.5h=30\min $
The time taken to get back to home will be calculated as,
${{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{2.5}{7.5}=0.33h=20\min $
The average velocity for the interval $\left( 0-30 \right)\min $ will be,
$v=\dfrac{2.5}{0.5}=5km{{h}^{-1}}$
Average speed for the interval $\left( 0-30 \right)\min $ will be,
$s=\dfrac{2.5}{0.5}=5km{{h}^{-1}}$
Total time taken for the travel will be,
$t=30+20=50\min =\dfrac{5}{6}h$
We can see that when he reached back then net displacement will be zero
Therefore in the case of $\left( 0-50 \right)\min $, the average velocity will be,
$v=\dfrac{0}{\dfrac{5}{6}}=0km{{h}^{-1}}$
Total distance he covered when he arrive back will be,
$2.5+2.5=5km$
Therefore the average speed will be given as,
$s=\dfrac{5}{\dfrac{5}{6}}=6km{{h}^{-1}}$
Distance travelled in the first $30\min $is given as $2.5km$. While returning, the distance travelled in $10\min $,
$d=7.5\times \dfrac{1}{6}=1.25km$
The total time taken will be,
$t=40\min =\dfrac{2}{3}h$
Hence the displacement in $0-40\min $will be,
$2.5-1.25=1.25km$
The average velocity for the interval $0-40\min $is,
$v=\dfrac{1.25}{\dfrac{2}{3}}=1.875km{{h}^{-1}}$
The average speed in this interval is given as,
$s=\dfrac{3.75}{\dfrac{2}{3}}=5.625km{{h}^{-1}}$

Note: The velocity is the time rate of variation of the displacement. Distance covered is the total length of the path traversed by a body. The displacement will be the shortest distance between the initial and final locations of the body. Time rate of variation of distance is known as speed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




