
A man places a chain of mass m and length l on the table slowly. Initially, the lower end of the chain just touches the table. The man drops the chain when half of the chain is in the vertical position. Then work done by the man in his process is?
(A). $-\dfrac{mgl}{2}$
(B). $-\dfrac{mgl}{4}$
(C). $-\dfrac{3mgl}{8}$
(D). $-\dfrac{mgl}{8}$
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Begin by first calculating the initial and final potential energies possessed by the chain when it is just touching the table surface and when it is just dropped respectively. Calculate the change in potential energy. This change is equivalent to the work done on the chain by gravity.
Then, by using the work energy theorem, equate the work done by the man and work done by gravity to the change in kinetic energy of the system, which is zero, since the chain is at rest in its initial and final positions. From here, just rearranging the equation should give you the required relation.
Formula Used :
Gravitational potential energy $U = mgh$
Work Energy theorem: $W_{all\;forces} = \Delta KE$
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that gravitational potential energy is the energy an object possesses by virtue of its position in a gravitational field. This can be quantified as:
$U_{gravity} = mgh$, where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the centre of mass of the object.
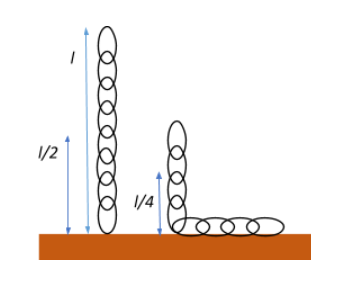
Now, for the first case when the lower end of the chain just touches the table, the centre of mass of the chain lies at $\dfrac{l}{2}$, therefore, the potential energy possessed by the chain can be given as:
$U_{initial} = mg\dfrac{l}{2} = \dfrac{mgl}{2}$
Now, when half the chain is in the vertical position, the mass of the chain becomes $\dfrac{m}{2}$, which is centred at a length $\dfrac{l}{4}$ of the chain. Therefore, the potential energy possessed by the chain can be given as:
$U_{final} = \dfrac{m}{2}g\dfrac{l}{4} = \dfrac{mgl}{8}$
Thus, the change in potential energy or the net potential energy possessed by the chain will be:
$\Delta U = U_{initial} – U_{final} = \dfrac{mgl}{2} - \dfrac{mgl}{8} = \dfrac{3mgl}{8}$.
According to the work-energy theorem. The net work done by the forces in a system is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the system.
$\Rightarrow W_{man} + W_{gravity} = \Delta KE$
Since the chain is at rest initially and finally, the $\Delta KE = 0$
$\Rightarrow W_{man} +W_{gravity} = 0$
Now, the work done by gravity is stored as the net potential energy in the chain.
$\Rightarrow W_{man} + \dfrac{3mgl}{8} = 0 \Rightarrow W_{man} = -\dfrac{3mgl}{8}$
Therefore, the correct option is: C. $-\dfrac{3mgl}{8}$
Note: Always remember that for an object held at some height from the surface, take the distance between the surface and the point at which all the mass of the body seems to be concentrated (which is the centre of mass) as the height at which the body is held. This will give an accurate representation of the gravitational potential energy experienced by the body, since for rigid and symmetric bodies, the centre of mass and centre of gravity coincide with each other.
Then, by using the work energy theorem, equate the work done by the man and work done by gravity to the change in kinetic energy of the system, which is zero, since the chain is at rest in its initial and final positions. From here, just rearranging the equation should give you the required relation.
Formula Used :
Gravitational potential energy $U = mgh$
Work Energy theorem: $W_{all\;forces} = \Delta KE$
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that gravitational potential energy is the energy an object possesses by virtue of its position in a gravitational field. This can be quantified as:
$U_{gravity} = mgh$, where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the centre of mass of the object.
Now, for the first case when the lower end of the chain just touches the table, the centre of mass of the chain lies at $\dfrac{l}{2}$, therefore, the potential energy possessed by the chain can be given as:
$U_{initial} = mg\dfrac{l}{2} = \dfrac{mgl}{2}$
Now, when half the chain is in the vertical position, the mass of the chain becomes $\dfrac{m}{2}$, which is centred at a length $\dfrac{l}{4}$ of the chain. Therefore, the potential energy possessed by the chain can be given as:
$U_{final} = \dfrac{m}{2}g\dfrac{l}{4} = \dfrac{mgl}{8}$
Thus, the change in potential energy or the net potential energy possessed by the chain will be:
$\Delta U = U_{initial} – U_{final} = \dfrac{mgl}{2} - \dfrac{mgl}{8} = \dfrac{3mgl}{8}$.

According to the work-energy theorem. The net work done by the forces in a system is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the system.
$\Rightarrow W_{man} + W_{gravity} = \Delta KE$
Since the chain is at rest initially and finally, the $\Delta KE = 0$
$\Rightarrow W_{man} +W_{gravity} = 0$
Now, the work done by gravity is stored as the net potential energy in the chain.
$\Rightarrow W_{man} + \dfrac{3mgl}{8} = 0 \Rightarrow W_{man} = -\dfrac{3mgl}{8}$
Therefore, the correct option is: C. $-\dfrac{3mgl}{8}$
Note: Always remember that for an object held at some height from the surface, take the distance between the surface and the point at which all the mass of the body seems to be concentrated (which is the centre of mass) as the height at which the body is held. This will give an accurate representation of the gravitational potential energy experienced by the body, since for rigid and symmetric bodies, the centre of mass and centre of gravity coincide with each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




