
A mass of 0.2kg is attached to the lower end of a massless spring of force-constant 200N/m, the upper end of which is fixed to a rigid support. Which of the following statements is/ are true? (This question has multiple correct options.)
A. In equilibrium, the spring will be stretched by 1cm.
B. If the mass is raised till the spring is in an unstretched state and then released, it will go down by 2cm before moving upwards.
C. The frequency of oscillation will be nearly 5Hz.
D. If the system is taken to the moon, the frequency of oscillation will be the same as on the Earth.
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: We know that, at equilibrium, spring force is equal to its weight, since net force is zero at equilibrium. From there, we get how long the spring is stretched at equilibrium. Also, by law of conservation of energy, initial energy and final energy are the same, this gives the length at which the spring will go down. If you know the frequency of this system, you will know whether it depends on gravity or not. With all the above known facts, check which all options are true.
Formula used:
Hooke’s law,
${{F}_{s}}=-kx$
Expression for frequency of the given system,
$\nu =\dfrac{1}{2\pi }\sqrt{\dfrac{k}{m}}$
Complete answer:
So, we have a spring mass system hung vertically on a rigid support.
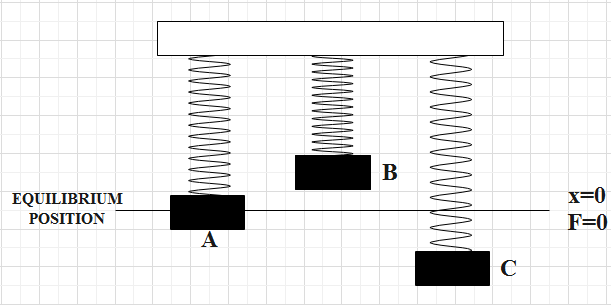
In the figure, position A represents equilibrium position of the system, B represents unstretched position and C represents stretched spring.
For A, the spring mass system is said to be in equilibrium position, that is, the net force acting at this position is zero.
$\sum{F}=0$
We know the forces that are acting on the body. They are: the restoring force of the spring and the gravity.
By Hooke’s law, we have,
Spring force ${{F}_{s}}$ is directly proportional to its displacement from the equilibrium position. That is,
${{F}_{s}}=-kx$ ………………. (1)
Where, k (spring constant) is the constant of proportionality.
Force due to gravity is its weight,
${{F}_{g}}=mg$ ……………….. (2)
At equilibrium, the sum of (1) and (2) is zero.
${{F}_{s}}+{{F}_{g}}=0$
$\Rightarrow mg+(-kx)=0$
$\Rightarrow mg=kx$ ……………….. (3)
We are given,
$m=0.2kg$
$k=200N{{m}^{-1}}$
$g=9.8m{{s}^{-2}}$
Substituting we get,
$x=\dfrac{0.2\times 9.8}{200}m$
$x=0.01m=1cm$
So, option A is true.
For the mass to be raised to the unstretched position work done is given by,
$W=mgx=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$ ………… (4)
Now the body is released, by law of conservation of energy, the total work now becomes,
$mgd=mgx+\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$
Where d is the distance at which it goes down when released.
From (4),
$mgd=2mgx$
$d=2x=2\times 1cm=2cm$
So, option B is also true.
Frequency of this system is given by,
$\nu =\dfrac{1}{2\pi }\sqrt{\dfrac{k}{m}}$ ……………… (5)
$\nu =\dfrac{1}{2\pi }\sqrt{\dfrac{200}{0.2}}$
$\nu =5.03Hz\sim 5Hz$
So, option C is also true.
Equation (4) clearly shows that, the frequency is independent of g, the acceleration due to gravity. So, the system will have the same frequency of oscillation if we take it to the moon. Hence option D is also true.
So, the correct answer is “Option A,B,C and D”.
Note:
We are given the question that there are multiple options that are true. So we should consider each and every option being true. Also, try to draw a free body diagram mentioning all the forces acting on the body in questions like this, so as to make it easier for you to solve the question.
Formula used:
Hooke’s law,
${{F}_{s}}=-kx$
Expression for frequency of the given system,
$\nu =\dfrac{1}{2\pi }\sqrt{\dfrac{k}{m}}$
Complete answer:
So, we have a spring mass system hung vertically on a rigid support.

In the figure, position A represents equilibrium position of the system, B represents unstretched position and C represents stretched spring.
For A, the spring mass system is said to be in equilibrium position, that is, the net force acting at this position is zero.
$\sum{F}=0$
We know the forces that are acting on the body. They are: the restoring force of the spring and the gravity.
By Hooke’s law, we have,
Spring force ${{F}_{s}}$ is directly proportional to its displacement from the equilibrium position. That is,
${{F}_{s}}=-kx$ ………………. (1)
Where, k (spring constant) is the constant of proportionality.
Force due to gravity is its weight,
${{F}_{g}}=mg$ ……………….. (2)
At equilibrium, the sum of (1) and (2) is zero.
${{F}_{s}}+{{F}_{g}}=0$
$\Rightarrow mg+(-kx)=0$
$\Rightarrow mg=kx$ ……………….. (3)
We are given,
$m=0.2kg$
$k=200N{{m}^{-1}}$
$g=9.8m{{s}^{-2}}$
Substituting we get,
$x=\dfrac{0.2\times 9.8}{200}m$
$x=0.01m=1cm$
So, option A is true.
For the mass to be raised to the unstretched position work done is given by,
$W=mgx=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$ ………… (4)
Now the body is released, by law of conservation of energy, the total work now becomes,
$mgd=mgx+\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$
Where d is the distance at which it goes down when released.
From (4),
$mgd=2mgx$
$d=2x=2\times 1cm=2cm$
So, option B is also true.
Frequency of this system is given by,
$\nu =\dfrac{1}{2\pi }\sqrt{\dfrac{k}{m}}$ ……………… (5)
$\nu =\dfrac{1}{2\pi }\sqrt{\dfrac{200}{0.2}}$
$\nu =5.03Hz\sim 5Hz$
So, option C is also true.
Equation (4) clearly shows that, the frequency is independent of g, the acceleration due to gravity. So, the system will have the same frequency of oscillation if we take it to the moon. Hence option D is also true.
So, the correct answer is “Option A,B,C and D”.
Note:
We are given the question that there are multiple options that are true. So we should consider each and every option being true. Also, try to draw a free body diagram mentioning all the forces acting on the body in questions like this, so as to make it easier for you to solve the question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




