
When a mixture of diborane and ammonia is heated, the final product is:
(A) $B{{H}_{3}}$
(B) $N{{H}_{4}}B{{H}_{4}}$
(C) $N{{H}_{2}}N{{H}_{2}}$
(D) ${{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Recollect the concept of bonding in boranes and their reactions. Boron will react with ammonia to form an intermediate which will decompose to give the final product. The final product might be similar to benzene.
Complete step by step answer:
-Boron is a non-metal having atomic number 5. Boron forms only covalent compounds. Boron hydride, $B{{H}_{3}}$ is quite stable in its dimeric form, also known as diborane, \[{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}\].
-Diborane is a boron hydride formed by dimerization of two borane molecules. It is the most stable form of borane.
-Diborane is highly reactive when exposed to air and catches fire spontaneously.
-When diborane reacts with ammonia, an addition product that is, an adduct is formed when further decomposes on heating at 473K to form a volatile compound called borazine or borazole.
\[3{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+6N{{H}_{3}}\to 3{{\left[ B{{H}_{2}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} \right]}^{+}}{{\left[ B{{H}_{4}} \right]}^{-}}\]
\[3{{\left[ B{{H}_{2}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} \right]}^{+}}{{\left[ B{{H}_{4}} \right]}^{-}}\xrightarrow{473K}2{{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}+12{{H}_{2}}\]
-Borazine is isostructural to benzene and hence, it is known as inorganic benzene.
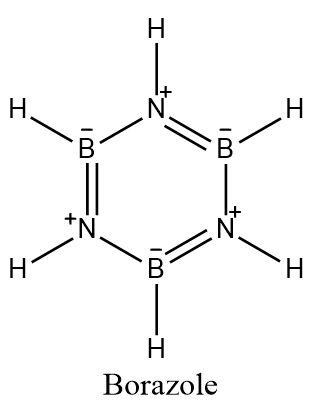
-Borazole consists of alternate boron and nitrogen atoms having alternate single and double bonds. It has three double bonds and has $6\pi $ electron system which is similar to benzene.
-Borazine has the molecular formula, ${{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information:
In diborane, there is presence of two 3-centre-2-electron bonds also known as banana bonding. This banana bond is formed during dimerization of $B{{H}_{3}}$. 1s orbital of one hydrogen having one electron overlaps with one 2p orbital having one electron of one boron atom and one vacant 2p orbital of another boron atom to form this type of bonding.
Note: Revise the concept of boron. Remember diborane is stable due to banana bonding and borazine or borazole is isostructural with benzene.
Complete step by step answer:
-Boron is a non-metal having atomic number 5. Boron forms only covalent compounds. Boron hydride, $B{{H}_{3}}$ is quite stable in its dimeric form, also known as diborane, \[{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}\].
-Diborane is a boron hydride formed by dimerization of two borane molecules. It is the most stable form of borane.
-Diborane is highly reactive when exposed to air and catches fire spontaneously.
-When diborane reacts with ammonia, an addition product that is, an adduct is formed when further decomposes on heating at 473K to form a volatile compound called borazine or borazole.
\[3{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+6N{{H}_{3}}\to 3{{\left[ B{{H}_{2}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} \right]}^{+}}{{\left[ B{{H}_{4}} \right]}^{-}}\]
\[3{{\left[ B{{H}_{2}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} \right]}^{+}}{{\left[ B{{H}_{4}} \right]}^{-}}\xrightarrow{473K}2{{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}+12{{H}_{2}}\]
-Borazine is isostructural to benzene and hence, it is known as inorganic benzene.

-Borazole consists of alternate boron and nitrogen atoms having alternate single and double bonds. It has three double bonds and has $6\pi $ electron system which is similar to benzene.
-Borazine has the molecular formula, ${{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information:
In diborane, there is presence of two 3-centre-2-electron bonds also known as banana bonding. This banana bond is formed during dimerization of $B{{H}_{3}}$. 1s orbital of one hydrogen having one electron overlaps with one 2p orbital having one electron of one boron atom and one vacant 2p orbital of another boron atom to form this type of bonding.
Note: Revise the concept of boron. Remember diborane is stable due to banana bonding and borazine or borazole is isostructural with benzene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




