
What is a more substituted carbon from a less substituted carbon? What does substituted mean?
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: A carbon atom that is further substituted forms more bonds with other carbon atoms. There are less carbon atoms forming bonds to a less substituted carbon. A three-degree carbon atom, for example, has more substituted carbon atoms than a two-degree carbon atom.
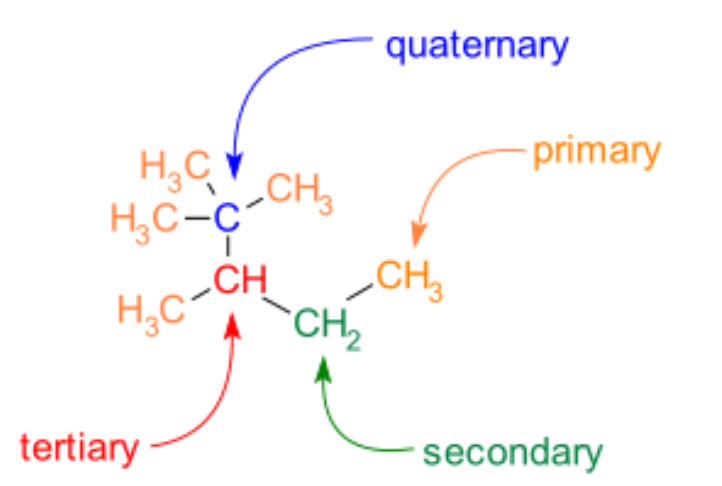
Complete answer: Primary carbon: (Less substituted)
A primary carbon atom is one that is only linked to one other carbon atom. As a result, it is found at the end of a carbon chain. Three hydrogen atoms are bound to a primary carbon of an alkane. A hydroxy group may also be substituted for a hydrogen atom, making the molecule a main alcohol.
Secondary carbon:
A carbon atom that is bound to two other carbon atoms is known as a secondary carbon. As a result, all hydrocarbons with at least three carbon atoms have secondary carbon atoms. The inner carbon atoms in unbranched alkanes are still secondary carbon atoms.
Tertiary Carbon:
A carbon atom that is bound to three other carbon atoms is known as a tertiary carbon atom. As a result, tertiary carbon atoms can only be present in hydrocarbons with at least four carbon atoms. In branched alkanes, for example, tertiary carbon atoms can be found, but not in linear alkanes.
Quaternary carbon:
A quaternary carbon atom is one that has four other carbon atoms bound to it. As a result, only hydrocarbons with at least five carbon atoms contain quaternary carbon atoms. In branched alkanes, quaternary carbon atoms can be found, but not in linear alkanes.
Note:
A chemical reaction involving the exchange of electron pairs between atoms is known as a covalent bond. Shared pairs or bonding pairs are the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they exchange electrons, and covalent bonding is the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons.
Complete answer: Primary carbon: (Less substituted)
A primary carbon atom is one that is only linked to one other carbon atom. As a result, it is found at the end of a carbon chain. Three hydrogen atoms are bound to a primary carbon of an alkane. A hydroxy group may also be substituted for a hydrogen atom, making the molecule a main alcohol.
Secondary carbon:
A carbon atom that is bound to two other carbon atoms is known as a secondary carbon. As a result, all hydrocarbons with at least three carbon atoms have secondary carbon atoms. The inner carbon atoms in unbranched alkanes are still secondary carbon atoms.
Tertiary Carbon:
A carbon atom that is bound to three other carbon atoms is known as a tertiary carbon atom. As a result, tertiary carbon atoms can only be present in hydrocarbons with at least four carbon atoms. In branched alkanes, for example, tertiary carbon atoms can be found, but not in linear alkanes.
Quaternary carbon:
A quaternary carbon atom is one that has four other carbon atoms bound to it. As a result, only hydrocarbons with at least five carbon atoms contain quaternary carbon atoms. In branched alkanes, quaternary carbon atoms can be found, but not in linear alkanes.

Note:
A chemical reaction involving the exchange of electron pairs between atoms is known as a covalent bond. Shared pairs or bonding pairs are the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they exchange electrons, and covalent bonding is the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




