
A moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter by:
A. Introducing the shunt resistance of large value in series
B. introducing the shunt resistance of small value in parallel
C. introducing the resistance of small value in series
D. introducing the resistance of large value in parallel
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: The opposition offered by the inductor in an A.C circuit to flow the A.C current is known as inductive reactance. The working principle of ammeter is that it should have low inductive reactance and resistivity.
Complete step by step answer:
We can convert a galvanometer to an ammeter by connecting the galvanometer in parallel to a low resistance, which is known as a shunt. The value of the shunt is adjusted so that the maximum current flow through the shunt. Thus, the galvanometer is converted to an ammeter and now can easily measure heavy currents without being fully deflected. And the conversion of the galvanometer into the ammeter is given in the circuit diagram.
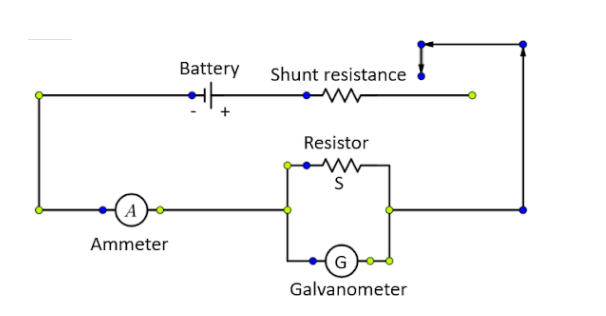
To find the current resistivity of the galvanometer:
$K = \dfrac{E}{{\left( {P + Q} \right).G}}\left( {\dfrac{P}{d}} \right)\dfrac{{Amp}}{{div}}$
Where, $K$is the current resistivity, $G$is the galvanometer, $P,Q$is the resistance boxes.
Thus, from the above explanation, we can conclude that option (B)- introducing a shunt resistance of small value in parallel, is the correct answer.
Additional information:
An ammeter is a device to measure current and has negligible resistance, that is connected in series with the test resistor. A galvanometer is a device that can determine the presence, direction, and strength of an electric current and voltage in a circuit.
A galvanometer is extremely sensitive to high currents and to measure heavy currents, a galvanometer is always converted into an ammeter. A resistor that has a small resistance connected in parallel with the coil in an ammeter. This resistor is called a shunt. A shunt allows electric current to move around another point of the circuit by breaking it and shifting it to another point in the circuit by creating a low resistance path. The sensitivity of a galvanometer can be expressed as a ratio of change in deflection of the galvanometer and change in value. To measure currents, we need to connect the galvanometer in series and since this setup will have large resistance, it will undoubtedly change the current in the circuit. So, to maintain the level of current a small resistance, is needed to be connected in parallel.
Note:
Remember that the small resistor, that is the shunt, needs to be connected in parallel with the galvanometer to reduce the resistance. This is because when resistances are connected in parallel their average resistance is low and when connected in series, the average resistance is higher.`B
Complete step by step answer:
We can convert a galvanometer to an ammeter by connecting the galvanometer in parallel to a low resistance, which is known as a shunt. The value of the shunt is adjusted so that the maximum current flow through the shunt. Thus, the galvanometer is converted to an ammeter and now can easily measure heavy currents without being fully deflected. And the conversion of the galvanometer into the ammeter is given in the circuit diagram.

To find the current resistivity of the galvanometer:
$K = \dfrac{E}{{\left( {P + Q} \right).G}}\left( {\dfrac{P}{d}} \right)\dfrac{{Amp}}{{div}}$
Where, $K$is the current resistivity, $G$is the galvanometer, $P,Q$is the resistance boxes.
Thus, from the above explanation, we can conclude that option (B)- introducing a shunt resistance of small value in parallel, is the correct answer.
Additional information:
An ammeter is a device to measure current and has negligible resistance, that is connected in series with the test resistor. A galvanometer is a device that can determine the presence, direction, and strength of an electric current and voltage in a circuit.
A galvanometer is extremely sensitive to high currents and to measure heavy currents, a galvanometer is always converted into an ammeter. A resistor that has a small resistance connected in parallel with the coil in an ammeter. This resistor is called a shunt. A shunt allows electric current to move around another point of the circuit by breaking it and shifting it to another point in the circuit by creating a low resistance path. The sensitivity of a galvanometer can be expressed as a ratio of change in deflection of the galvanometer and change in value. To measure currents, we need to connect the galvanometer in series and since this setup will have large resistance, it will undoubtedly change the current in the circuit. So, to maintain the level of current a small resistance, is needed to be connected in parallel.
Note:
Remember that the small resistor, that is the shunt, needs to be connected in parallel with the galvanometer to reduce the resistance. This is because when resistances are connected in parallel their average resistance is low and when connected in series, the average resistance is higher.`B
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




