
A neutron travelling with a velocity v and kinetic energy E collides elastically head on with the nucleus of an atom of mass number A at rest. The fraction of total energy retained by the neutron is:
$\begin{align}
& A){{\left( \dfrac{A-1}{A+1} \right)}^{2}} \\
& B){{\left( \dfrac{A+1}{A-1} \right)}^{2}} \\
& C){{\left( \dfrac{A-1}{A} \right)}^{2}} \\
& D){{\left( \dfrac{A+1}{A} \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we need to have a basic idea of a neutron and its nature. Draw a figure of before and after collision movement of two bodies to understand the situation better. Then, we will apply the law of conservation of momentum as the given collision is an elastic collision and hence find the final velocity for the neutron. We know that the coefficient of restitution for an elastic collision is 1 and it is given by the velocity of separation after collision to velocity of approach before collision.
Formula used:
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{1}}{{u}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{u}_{2}}={{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}} \\
& e=\dfrac{\text{velocity of separation after collision}}{\text{velocity of approach before collision}} \\
& K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Complete answer:
We know that a neutron is colliding elastically head on with the nucleus of an atom.
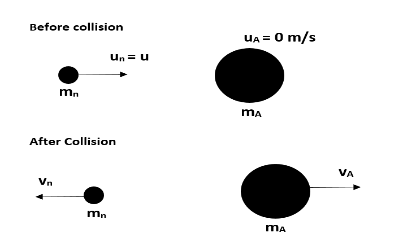
Let us consider the mass of the neutron as ${{m}_{n}}$ and the mass of the nucleus as ${{m}_{A}}$. We know that nucleus consists of both neutrons and protons and neutrons and protons have the same mass. i.e. ${{m}_{n}}={{m}_{p}}=m$. Also, mass number is given as the sum of the number of protons and neutrons. Let us take x as number of neutrons and y as number of protons.
Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{A}}=x{{m}_{n}}+y{{m}_{p}} \\
& {{m}_{A}}=\left( x+y \right)m \\
& {{m}_{A}}=Am \\
\end{align}$
Here, A is the mass number and m is the mass of either neutron or proton. Let us take ${{m}_{n}}$ for the sake of easy calculations.
Now, law of conservation of momentum states that total momentum of a body will be always conserved. While applying law of conservation of momentum to these two bodies,
\[\begin{align}
& {{m}_{1}}{{u}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{u}_{2}}={{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}} \\
& {{m}_{n}}u+A{{m}_{n}}\times 0={{m}_{n}}\left( -{{v}_{1}} \right)+A{{m}_{n}}{{v}_{2}} \\
& {{m}_{n}}u=-{{m}_{n}}{{v}_{1}}+A{{m}_{n}}{{v}_{2}} \\
& u=A{{v}_{2}}-{{v}_{1}}\text{ --- (1)} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we know that, coefficient of restitution for an elastic collision is 1. That is,
$e=\dfrac{\text{velocity of separation after collision}}{\text{velocity of approach before collision}}=1$
Here,
Velocity of separation after collision = Relative velocity of neutron and nucleus after collision
That is, ${{v}_{1}}+{{v}_{2}}$ .
Velocity of approach before collision is $u$.
Therefore,
\[\begin{align}
& e=\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}+{{v}_{2}}}{u}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow u={{v}_{1}}+{{v}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}_{2}}=u-{{v}_{1}}\text{ -- (2)} \\
\end{align}\]
Substituting (2) in (1),
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow u=A\left( u-{{v}_{1}} \right)-{{v}_{1}} \\
& \Rightarrow u=Au-A{{v}_{1}}-{{v}_{1}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}_{1}}(A+1)=u(A-1) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{(A-1)}{(A+1)} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the relation between initial and final velocity of the neutron is found to be \[\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{(A-1)}{(A+1)}\].
Now, we have to find the fraction of the kinetic energy as,
\[\begin{align}
& K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}} \\
& \dfrac{K.{{E}_{final}}}{K.{{E}_{initial}}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}m{{({{v}_{1}})}^{2}}}{\dfrac{1}{2}m{{(u)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{({{v}_{1}})}^{2}}}{{{(u)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{u} \right)={{\left( \dfrac{1-A}{1+A} \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the fraction of the total energy retained by the neutron is \[{{\left( \dfrac{1-A}{1+A} \right)}^{2}}\].
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
We need to keep in mind the law of conservation of energy which is a fundamental concept of physics. This states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed and the energy of a system is constant at any point of time. When elastic collision comes into play, we need to consider the momentum before and after the collision takes place. With these points in mind, we will be able to easily solve any question of this kind.
Formula used:
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{1}}{{u}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{u}_{2}}={{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}} \\
& e=\dfrac{\text{velocity of separation after collision}}{\text{velocity of approach before collision}} \\
& K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Complete answer:
We know that a neutron is colliding elastically head on with the nucleus of an atom.

Let us consider the mass of the neutron as ${{m}_{n}}$ and the mass of the nucleus as ${{m}_{A}}$. We know that nucleus consists of both neutrons and protons and neutrons and protons have the same mass. i.e. ${{m}_{n}}={{m}_{p}}=m$. Also, mass number is given as the sum of the number of protons and neutrons. Let us take x as number of neutrons and y as number of protons.
Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{A}}=x{{m}_{n}}+y{{m}_{p}} \\
& {{m}_{A}}=\left( x+y \right)m \\
& {{m}_{A}}=Am \\
\end{align}$
Here, A is the mass number and m is the mass of either neutron or proton. Let us take ${{m}_{n}}$ for the sake of easy calculations.
Now, law of conservation of momentum states that total momentum of a body will be always conserved. While applying law of conservation of momentum to these two bodies,
\[\begin{align}
& {{m}_{1}}{{u}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{u}_{2}}={{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}} \\
& {{m}_{n}}u+A{{m}_{n}}\times 0={{m}_{n}}\left( -{{v}_{1}} \right)+A{{m}_{n}}{{v}_{2}} \\
& {{m}_{n}}u=-{{m}_{n}}{{v}_{1}}+A{{m}_{n}}{{v}_{2}} \\
& u=A{{v}_{2}}-{{v}_{1}}\text{ --- (1)} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we know that, coefficient of restitution for an elastic collision is 1. That is,
$e=\dfrac{\text{velocity of separation after collision}}{\text{velocity of approach before collision}}=1$
Here,
Velocity of separation after collision = Relative velocity of neutron and nucleus after collision
That is, ${{v}_{1}}+{{v}_{2}}$ .
Velocity of approach before collision is $u$.
Therefore,
\[\begin{align}
& e=\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}+{{v}_{2}}}{u}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow u={{v}_{1}}+{{v}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}_{2}}=u-{{v}_{1}}\text{ -- (2)} \\
\end{align}\]
Substituting (2) in (1),
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow u=A\left( u-{{v}_{1}} \right)-{{v}_{1}} \\
& \Rightarrow u=Au-A{{v}_{1}}-{{v}_{1}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}_{1}}(A+1)=u(A-1) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{(A-1)}{(A+1)} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the relation between initial and final velocity of the neutron is found to be \[\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{(A-1)}{(A+1)}\].
Now, we have to find the fraction of the kinetic energy as,
\[\begin{align}
& K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}} \\
& \dfrac{K.{{E}_{final}}}{K.{{E}_{initial}}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}m{{({{v}_{1}})}^{2}}}{\dfrac{1}{2}m{{(u)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{({{v}_{1}})}^{2}}}{{{(u)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{u} \right)={{\left( \dfrac{1-A}{1+A} \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the fraction of the total energy retained by the neutron is \[{{\left( \dfrac{1-A}{1+A} \right)}^{2}}\].
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
We need to keep in mind the law of conservation of energy which is a fundamental concept of physics. This states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed and the energy of a system is constant at any point of time. When elastic collision comes into play, we need to consider the momentum before and after the collision takes place. With these points in mind, we will be able to easily solve any question of this kind.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




