
What is a node? What is an antinode?
Answer
537.6k+ views
Hint: A standing wave pattern is an interference phenomenon. It's formed because of the superbly timed interference of two waves passing through identical mediums. A stationary wave pattern is not actually a wave but rather it's the pattern that is originated or formed when two waves of identical frequency and directions within a similar medium interfere with each other.
Complete step by step answer:
One of the most important and noticeable properties of stationary wave patterns is that there are points within the medium that appear to be at rest or standing still. These points, sometimes described as points of no displacement, are mentioned as nodes.
There are other points along the medium that undergo vibrations between an oversized positive and huge negative displacement. These points are the opposite of nodes, then they're called antinodes.
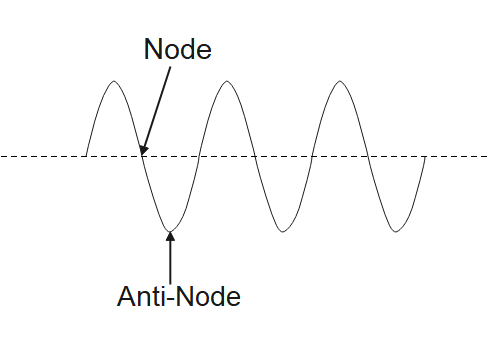
When a standing wave pattern is established during a medium, the nodes and therefore the antinodes are always located at identical positions along the medium; they're standing still. It's this characteristic that has earned the pattern the name standing wave.
The positioning of the nodes and antinodes during a standing wave pattern are often explained by focusing on the interference of the 2 waves. The nodes are produced at locations where destructive interference occurs. as an example, nodes form at locations where a crest of 1 wave meets a trough of a second wave; or a half-crest of 1 wave meets a half-trough of a second wave; or a quarter-crest of 1 wave meets a quarter-trough of a second wave; etc. Antinodes, on the opposite hand, are produced at locations where constructive interference occurs. For instance, if a crest of 1 wave meets a crest of a second wave, some extent of huge positive displacement results.
Note: Nodes and antinodes shouldn't be confused with crests and troughs. When the motion of a wave is discussed, it's customary to refer to some extent of huge maximum displacement as a crest and some extent of huge negative displacement as a trough. These represent points of the disturbance that travel from one location to a different through the medium. An antinode on the opposite hand is a point on the medium that's staying within the same location.
Complete step by step answer:
One of the most important and noticeable properties of stationary wave patterns is that there are points within the medium that appear to be at rest or standing still. These points, sometimes described as points of no displacement, are mentioned as nodes.
There are other points along the medium that undergo vibrations between an oversized positive and huge negative displacement. These points are the opposite of nodes, then they're called antinodes.

When a standing wave pattern is established during a medium, the nodes and therefore the antinodes are always located at identical positions along the medium; they're standing still. It's this characteristic that has earned the pattern the name standing wave.
The positioning of the nodes and antinodes during a standing wave pattern are often explained by focusing on the interference of the 2 waves. The nodes are produced at locations where destructive interference occurs. as an example, nodes form at locations where a crest of 1 wave meets a trough of a second wave; or a half-crest of 1 wave meets a half-trough of a second wave; or a quarter-crest of 1 wave meets a quarter-trough of a second wave; etc. Antinodes, on the opposite hand, are produced at locations where constructive interference occurs. For instance, if a crest of 1 wave meets a crest of a second wave, some extent of huge positive displacement results.
Note: Nodes and antinodes shouldn't be confused with crests and troughs. When the motion of a wave is discussed, it's customary to refer to some extent of huge maximum displacement as a crest and some extent of huge negative displacement as a trough. These represent points of the disturbance that travel from one location to a different through the medium. An antinode on the opposite hand is a point on the medium that's staying within the same location.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




