
What is a normal probability curve?
Answer
534k+ views
Hint: we first describe the importance of the normal distribution and the components of its PDF. Then we discuss the normal probability curve and the use of mean and the standard deviation for the formula makes it unique for real life implications.
Complete step by step solution:
There are two main parameters which impact a normal distribution and they are mean and the standard deviation of the sample
The normal curve shows the probability distribution for continuous random variable and the curve is bell-shaped. The graph of the probability density function of the normal distribution is symmetrical about the mean and it is called Normal Probability Curve.
Normal distributions become more perfect for finer level of measurement and larger sample.
The mean of the sample for the normal distribution creates the symmetry on its both sides so that the right side of the centre is a mirror image of the left side.
The probability density function of the normal distribution is $f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{1}{\sigma \sqrt{2\pi }}{{e}^{-\dfrac{1}{2}{{\left( \dfrac{x-\mu }{\sigma } \right)}^{2}}}}$ where $\mu $ is the mean and $\sigma $ is the standard deviation of the sample.
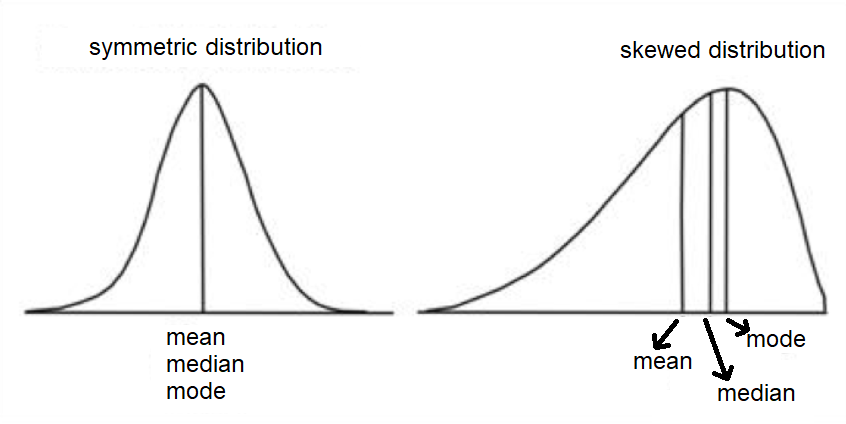
Note: Normal curve has great significance in social sciences and behavioural sciences. In behavioural measurement most of the aspects approximate to the normal distribution. The normal curve is unimodal.
Complete step by step solution:
There are two main parameters which impact a normal distribution and they are mean and the standard deviation of the sample
The normal curve shows the probability distribution for continuous random variable and the curve is bell-shaped. The graph of the probability density function of the normal distribution is symmetrical about the mean and it is called Normal Probability Curve.
Normal distributions become more perfect for finer level of measurement and larger sample.
The mean of the sample for the normal distribution creates the symmetry on its both sides so that the right side of the centre is a mirror image of the left side.
The probability density function of the normal distribution is $f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{1}{\sigma \sqrt{2\pi }}{{e}^{-\dfrac{1}{2}{{\left( \dfrac{x-\mu }{\sigma } \right)}^{2}}}}$ where $\mu $ is the mean and $\sigma $ is the standard deviation of the sample.

Note: Normal curve has great significance in social sciences and behavioural sciences. In behavioural measurement most of the aspects approximate to the normal distribution. The normal curve is unimodal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




