
A particle is released on a vertical smooth semicircular track from point X, so that OX makes an angle, \[\theta \], from the vertical (see figure). The normal reaction of the track on the particle vanishes at point Y, where OY makes an angle \[\phi \] with the horizontal. Then
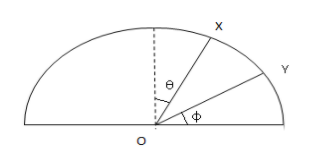
A. \[\sin \phi = \cos \theta \]
B. \[\sin \phi = \dfrac{1}{2}\cos \theta \]
C. \[\sin \phi = \dfrac{2}{3}\cos \theta \]
D. \[\sin \phi = \dfrac{3}{4}\cos \theta \]

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Find the distance the particle travels when it falls from point X to point Y. Use work-energy theorem to find the energy of the particle when it falls. Check for all the forces acting on the particle at point Y.
Complete Step by step answer: Let R be the radius of the semicircle and h be the distance between point X and point Y
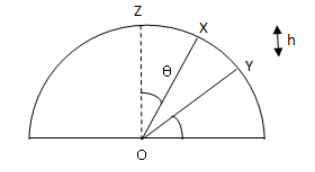
The component of OX along OZ is \[R\cos \theta \] and component of OY along OZ is \[R\sin \phi \]
Therefore, the distance travelled by the particle when it is released from X to Y is
\[h = R\cos \theta - R\sin \phi \]
Now, due to work done by gravity when the particle falls, it gains a velocity. Let \[v\] be the velocity of the particle. From work-energy theorem we have,
Work done by gravity \[ = \] gain in kinetic energy of the particle
\[ \Rightarrow mgh = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\]
Where \[mgh\] is the work done by the gravity and \[\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\] is the kinetic energy of the particle.
\[ \Rightarrow v = \sqrt {2gh} \]
Substituting the value of \[h\] we get,
\[v = \sqrt {2g\left( {R\cos \theta - R\sin \phi } \right)} \]
Now, we draw a free body diagram, showing all the forces acting on the particle
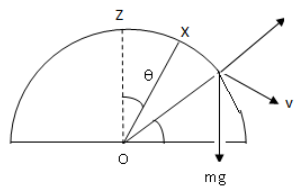
At point Y, we have along radial direction in circular motion ( in frame of particle)
\[N + \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} = mg\sin \phi \] (i)
Where \[N\] is the normal reaction and \[\phi \] is the angle between force \[mg\] and velocity \[v\]
Given, the normal reaction vanishes, \[N = 0\]
Therefore, equation (i) becomes,
\[\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} = mg\sin \phi \] (ii)
Putting the value of \[v\] in equation (ii), we get
\[\dfrac{{2mg\left( {R\cos \theta - R\sin \phi } \right)}}{R} = mg\sin \phi \\
\Rightarrow 2(\cos \theta - \sin \phi ) = \sin \phi \\
\Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{3}{2}\sin \phi \\
\Rightarrow \sin \phi = \dfrac{2}{3}\cos \theta \\ \]
Therefore, the correct answer is option (C) \[\sin \phi = \dfrac{2}{3}\cos \theta \]
Note: In this problem no other external forces were acting on the particle, so the problem was quite simple. But if there are other forces like external force or frictional forces acting on the particle then we should consider those forces in calculations too.
Complete Step by step answer: Let R be the radius of the semicircle and h be the distance between point X and point Y

The component of OX along OZ is \[R\cos \theta \] and component of OY along OZ is \[R\sin \phi \]
Therefore, the distance travelled by the particle when it is released from X to Y is
\[h = R\cos \theta - R\sin \phi \]
Now, due to work done by gravity when the particle falls, it gains a velocity. Let \[v\] be the velocity of the particle. From work-energy theorem we have,
Work done by gravity \[ = \] gain in kinetic energy of the particle
\[ \Rightarrow mgh = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\]
Where \[mgh\] is the work done by the gravity and \[\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\] is the kinetic energy of the particle.
\[ \Rightarrow v = \sqrt {2gh} \]
Substituting the value of \[h\] we get,
\[v = \sqrt {2g\left( {R\cos \theta - R\sin \phi } \right)} \]
Now, we draw a free body diagram, showing all the forces acting on the particle

At point Y, we have along radial direction in circular motion ( in frame of particle)
\[N + \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} = mg\sin \phi \] (i)
Where \[N\] is the normal reaction and \[\phi \] is the angle between force \[mg\] and velocity \[v\]
Given, the normal reaction vanishes, \[N = 0\]
Therefore, equation (i) becomes,
\[\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} = mg\sin \phi \] (ii)
Putting the value of \[v\] in equation (ii), we get
\[\dfrac{{2mg\left( {R\cos \theta - R\sin \phi } \right)}}{R} = mg\sin \phi \\
\Rightarrow 2(\cos \theta - \sin \phi ) = \sin \phi \\
\Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{3}{2}\sin \phi \\
\Rightarrow \sin \phi = \dfrac{2}{3}\cos \theta \\ \]
Therefore, the correct answer is option (C) \[\sin \phi = \dfrac{2}{3}\cos \theta \]
Note: In this problem no other external forces were acting on the particle, so the problem was quite simple. But if there are other forces like external force or frictional forces acting on the particle then we should consider those forces in calculations too.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




