
A particle moving along a circular path of radius 6 meter with uniform speed of 8 meter per second. The average acceleration when the particle completes one half of the revolution is-
A. \[\dfrac{{16}}{{3\pi }}{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]
B. \[\dfrac{{32}}{{3\pi }}{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]
C. \[\dfrac{{64}}{{3\pi }}{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]
D. None of these
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: Particle has velocity tangential to the circle all the time when particle complete half of the circle then it changes its direction opposite to each other therefore initial velocity be $ - 8\mathop {\text{i}}\limits^ \wedge $ and final velocity be $8\mathop {\text{i}}\limits^ \wedge $.
Formula used:
${\text{Time}} = \dfrac{{{\text{distance}}}}{{{\text{speed}}}}$ and ${\text{Acceleration}} = \dfrac{{{\text{change in velocity}}}}{{{\text{total time taken}}}}$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
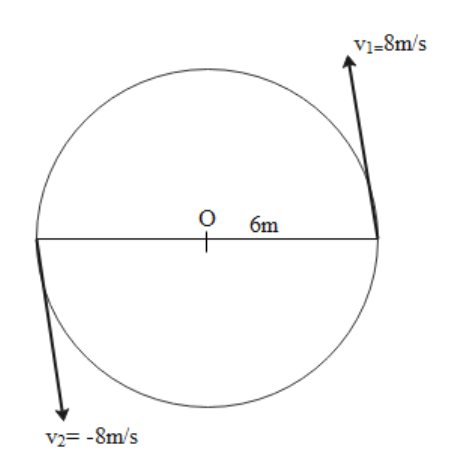
Given that,
Particle moves on a circular path with speed $ = 8{\text{m/s}}$
Radius of circular path i.e. ${\text{R = 6m}}$
We know that the particle has velocity tangential to the circle all the time when particle complete half of the circle than it change its direction opposite to each other,
Let the initial velocity be ${{\text{v}}_1}$ and final velocity be ${{\text{v}}_2}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{v}}_1} = - 8\mathop {\text{i}}\limits^ \wedge $
$\Rightarrow {{\text{v}}_2} = 8\mathop {\text{i}}\limits^ \wedge $
Particle completes one half revolution therefore distance travelled by particle is perimeter of circle divided by two $ = \dfrac{{2\pi {\text{R}}}}{2} = \pi {\text{R}}$
Therefore time taken $ = \dfrac{{{\text{distance}}}}{{{\text{speed}}}} = \dfrac{{\pi {\text{R}}}}{8} = \dfrac{{6\pi }}{8}{\text{sec}}$
And we know that acceleration $ = \dfrac{{{\text{change in velocity}}}}{{{\text{total time taken}}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{{{\text{v}}_2} - {{\text{v}}_1}}}{{\text{t}}} \\
= \dfrac{{8 - \left( { - 8} \right)}}{{\dfrac{{6\pi }}{8}}} \\
= \dfrac{{64}}{{3\pi }}{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2} \\ $
Hence the correct option is C.
Note: In this question, the particle moves on a circular path and completing one-half revolution therefore the distance traveled by the particle is one half of the perimeter of the circle and as speed is given so we calculated the time taken, after that, we applied the acceleration formula and the found the value of average acceleration to be $\dfrac{{64}}{{3\pi }}{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}$.
Formula used:
${\text{Time}} = \dfrac{{{\text{distance}}}}{{{\text{speed}}}}$ and ${\text{Acceleration}} = \dfrac{{{\text{change in velocity}}}}{{{\text{total time taken}}}}$.
Complete step-by-step solution:

Given that,
Particle moves on a circular path with speed $ = 8{\text{m/s}}$
Radius of circular path i.e. ${\text{R = 6m}}$
We know that the particle has velocity tangential to the circle all the time when particle complete half of the circle than it change its direction opposite to each other,
Let the initial velocity be ${{\text{v}}_1}$ and final velocity be ${{\text{v}}_2}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{v}}_1} = - 8\mathop {\text{i}}\limits^ \wedge $
$\Rightarrow {{\text{v}}_2} = 8\mathop {\text{i}}\limits^ \wedge $
Particle completes one half revolution therefore distance travelled by particle is perimeter of circle divided by two $ = \dfrac{{2\pi {\text{R}}}}{2} = \pi {\text{R}}$
Therefore time taken $ = \dfrac{{{\text{distance}}}}{{{\text{speed}}}} = \dfrac{{\pi {\text{R}}}}{8} = \dfrac{{6\pi }}{8}{\text{sec}}$
And we know that acceleration $ = \dfrac{{{\text{change in velocity}}}}{{{\text{total time taken}}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{{{\text{v}}_2} - {{\text{v}}_1}}}{{\text{t}}} \\
= \dfrac{{8 - \left( { - 8} \right)}}{{\dfrac{{6\pi }}{8}}} \\
= \dfrac{{64}}{{3\pi }}{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2} \\ $
Hence the correct option is C.
Note: In this question, the particle moves on a circular path and completing one-half revolution therefore the distance traveled by the particle is one half of the perimeter of the circle and as speed is given so we calculated the time taken, after that, we applied the acceleration formula and the found the value of average acceleration to be $\dfrac{{64}}{{3\pi }}{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




