
What is a particle that rapidly moves around the outside of the nucleus and carries a negative charge?
Answer
507.3k+ views
Hint :We know that the charge atoms are neutral. Atom is made up of particles such as protons, electrons and neutrons. As we know that the opposite charges attract each other. In the same way, the positively charged nucleus holds the negatively charged electrons in an atom.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As we know, the nucleus of an atom is positively charged. Protons are positively charged; electrons are negatively charged whereas neutrons are chargeless species. Most of the mass is due to the presence of these two subatomic particles. Since the protons are positively charged and neutrons are chargeless species, they together combine to form a positively charged nucleus. Protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged and they together when combined will result in a neutral nucleus, which is contradictory to the fact that nucleus is positively charged.
The nucleus is held together by the strong force, one of the four basic forces in nature. Electrons are the subatomic particles which revolve around the nucleus of the atom. These electrons can be lost from or gained by an atom to form the ions. Electrons of several different atoms come together to participate in the chemical bonding.
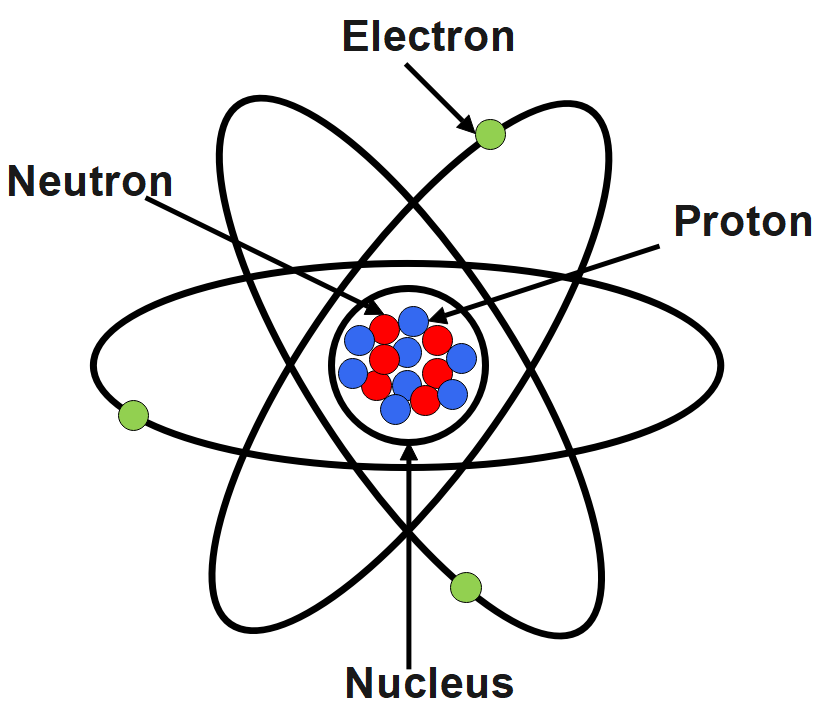
Electrons are called to be the negatively charged subatomic particles. Equal number of both the electrons and protons constitute in the atoms of all the elements. J. Thompson is known to be related to the discovery of electrons because he was the first person to accurately calculate the mass and the charge of an electron. The electrons have the same amount of charge of the Protons of the nucleus but negative.
Therefore, a particle that rapidly moves around the outside of the nucleus and carries a negative charge is an electron.
Note :
Remember that the force between the protons and neutrons overcomes the repulsive electrical force that would otherwise push the protons apart, according to the rules of electricity. Some atomic nuclei are unstable because the binding force varies for different atoms based on the size of the nucleus.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As we know, the nucleus of an atom is positively charged. Protons are positively charged; electrons are negatively charged whereas neutrons are chargeless species. Most of the mass is due to the presence of these two subatomic particles. Since the protons are positively charged and neutrons are chargeless species, they together combine to form a positively charged nucleus. Protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged and they together when combined will result in a neutral nucleus, which is contradictory to the fact that nucleus is positively charged.
The nucleus is held together by the strong force, one of the four basic forces in nature. Electrons are the subatomic particles which revolve around the nucleus of the atom. These electrons can be lost from or gained by an atom to form the ions. Electrons of several different atoms come together to participate in the chemical bonding.

Electrons are called to be the negatively charged subatomic particles. Equal number of both the electrons and protons constitute in the atoms of all the elements. J. Thompson is known to be related to the discovery of electrons because he was the first person to accurately calculate the mass and the charge of an electron. The electrons have the same amount of charge of the Protons of the nucleus but negative.
Therefore, a particle that rapidly moves around the outside of the nucleus and carries a negative charge is an electron.
Note :
Remember that the force between the protons and neutrons overcomes the repulsive electrical force that would otherwise push the protons apart, according to the rules of electricity. Some atomic nuclei are unstable because the binding force varies for different atoms based on the size of the nucleus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




