
A pea plant which is homozygous for green pods which are inflated(GGII) is crossed with a homozygous plant for yellow pods which are considered (ggii).Answer the following question.State Mendel’s law of ‘Segregation of Gametes’.
Answer
528.9k+ views
Hint: A lifelong learner, teacher, scientist, and man of faith, Johann Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) provided the local natural history community with the results of his experiments with nearly 30,000 pea plants. He showed that traits in particular patterns are faithfully transmitted from parents to offspring.
Complete answer:
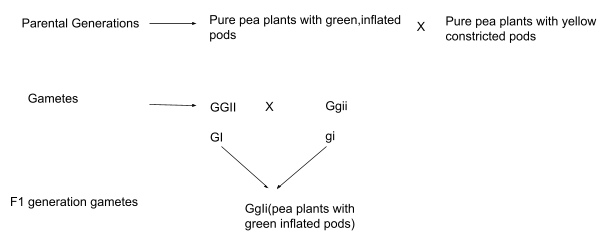
The first law of Mendel or the Law of Gametes Segregation states that "the alleles of a given locus segregate into separate gametes." Clarification - During meiosis, the two alleles of a gene pair segregate or separate from each other and each gamete has an equal chance of receiving either gene allele. A parent pea plant is homozygous for the dominant green and inflated pods [GGII].
Another parent pea plant is homozygous for recessive yellow and deflated pods[ggii]. Both the homozygous parent plants are crossed. GI and gi (alleles have separated) are the gametes acquired. The resulting progeny is heterozygous GgIii (with dominant traits).
To each gamete (egg or sperm cell) that it produces, only one of the two gene copies found in an organism is transmitted. The distribution of the copies of the genes is random. A new organism, whose genotype consists of the alleles present in the gametes, develops when an egg and a sperm participate in fertilisation.
Note: Due to the various distinct varieties, the ease of culture and control of pollination, and the high proportion of active seed germinations, Mendel preferred to conduct his studies with the edible pea (Pisum sativum).
Complete answer:
The first law of Mendel or the Law of Gametes Segregation states that "the alleles of a given locus segregate into separate gametes." Clarification - During meiosis, the two alleles of a gene pair segregate or separate from each other and each gamete has an equal chance of receiving either gene allele. A parent pea plant is homozygous for the dominant green and inflated pods [GGII].
Another parent pea plant is homozygous for recessive yellow and deflated pods[ggii]. Both the homozygous parent plants are crossed. GI and gi (alleles have separated) are the gametes acquired. The resulting progeny is heterozygous GgIii (with dominant traits).
To each gamete (egg or sperm cell) that it produces, only one of the two gene copies found in an organism is transmitted. The distribution of the copies of the genes is random. A new organism, whose genotype consists of the alleles present in the gametes, develops when an egg and a sperm participate in fertilisation.

| Gametes | GI | Gi | gI | gi |
| GI | GGII | GGIi | GgII | GgIi |
| Gi | GGIi | GGii | GgIi | Ggii |
| gI | GgII | GgIi | ggII | ggIi |
| gi | GgIi | Ggii | ggIi | ggii |
Note: Due to the various distinct varieties, the ease of culture and control of pollination, and the high proportion of active seed germinations, Mendel preferred to conduct his studies with the edible pea (Pisum sativum).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




