
A p-n junction ideal diode is in forward bias and a current of 20mA flows through the circuit. When it is in reverse bias, the magnitude of the current is-
(A). 20 mA
(B). infinity
(C). zero
(D). 30 mA
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: In forward bias the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the p-junction and negative terminal is connected to the n-junction. In reverse bias, the positive terminal is connected to the n-junction and the negative terminal is connected to the p-junction. So the flow of holes and electrons across the p-n junction is different for both types of biasing.
Complete answer:
A diode is a semiconductor device that allows the current to flow only in one direction. It is represented as –
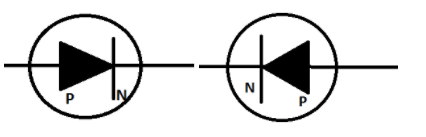
Diode has two parts; a p-junction where holes are in majority and an n-junction where the electrons are in majority
Diodes can either be forward-biased or reverse-biased.
In forward-bias, the positive terminal of the external voltage is connected to the p-junction of the diode and the negative terminal is connected to the n-junction.
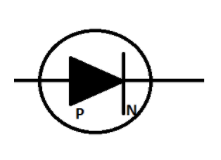
The above figure represents a forward bias.
In reverse-bias, the positive terminal of the external voltage is connected to the n-junction of the diode and the negative terminal is connected to the p-junction.
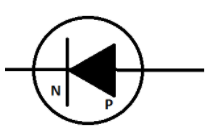
The above figure represents a reverse-bias.
When the diode is in forward bias, due to the flow of current, more holes are added to the p-junction to the point that some holes start moving to the n-junction. Similarly, more electrons are added to the n-junction to the point that some electrons move to the p-junction. So a movement of holes and electrons takes place across the junction of the diode. In this way, they are able to overcome the depletion region and combine in a continuous process which gives rise to a current flow. This current is large enough to be detected by an ammeter.
In-reverse-bias, electrons are added to p-junction which combine with the majority of the holes while holes are added to n-junction which combine with the majority of electrons. In this way more and more electrons and holes combine to neutralise and the depletion region increases in size and almost no current flow is observed across the junction. The current is almost negligible so it is not detected by the ammeter.
Therefore, in forward-bias current is large enough to be detected by the ammeter, i.e.20 mA but in reverse-bias the current flow is almost negligible, so the current observed is zero.
So, the correct option is (C).
Note:
In forward bias an electric field is generated across the p-n junction which breaks the depletion layer due to which a large amount of current suddenly flows in the circuit. Whereas in reverse bias, the electrons and holes neutralize each other due to which almost no flow of current takes place.
Complete answer:
A diode is a semiconductor device that allows the current to flow only in one direction. It is represented as –

Diode has two parts; a p-junction where holes are in majority and an n-junction where the electrons are in majority
Diodes can either be forward-biased or reverse-biased.
In forward-bias, the positive terminal of the external voltage is connected to the p-junction of the diode and the negative terminal is connected to the n-junction.

The above figure represents a forward bias.
In reverse-bias, the positive terminal of the external voltage is connected to the n-junction of the diode and the negative terminal is connected to the p-junction.

The above figure represents a reverse-bias.
When the diode is in forward bias, due to the flow of current, more holes are added to the p-junction to the point that some holes start moving to the n-junction. Similarly, more electrons are added to the n-junction to the point that some electrons move to the p-junction. So a movement of holes and electrons takes place across the junction of the diode. In this way, they are able to overcome the depletion region and combine in a continuous process which gives rise to a current flow. This current is large enough to be detected by an ammeter.
In-reverse-bias, electrons are added to p-junction which combine with the majority of the holes while holes are added to n-junction which combine with the majority of electrons. In this way more and more electrons and holes combine to neutralise and the depletion region increases in size and almost no current flow is observed across the junction. The current is almost negligible so it is not detected by the ammeter.
Therefore, in forward-bias current is large enough to be detected by the ammeter, i.e.20 mA but in reverse-bias the current flow is almost negligible, so the current observed is zero.
So, the correct option is (C).
Note:
In forward bias an electric field is generated across the p-n junction which breaks the depletion layer due to which a large amount of current suddenly flows in the circuit. Whereas in reverse bias, the electrons and holes neutralize each other due to which almost no flow of current takes place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




