
How is a proton gradient established across the thylakoid membrane?
Answer
529.8k+ views
Hint: The production of a proton gradient across the thylakoid layer is an aftereffect of the gathering of protons on the internal side of the lumen and a lessening of protons in the stroma. It likewise results because of the change in pH on the lumen side of the thylakoid layer.
Complete answer:
A thylakoid is a sheet-like film-which is the site of the light-dependent photosynthesis present in chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. The site contains the chlorophyll used to retain light and use it for biochemical responses.
The pigment called chlorophyll is present in the thylakoid membrane. It is the main pigment which absorbs the sunlight and photolysis of water takes place. As a result of photolysis, the electrons are generated and are passed to a series of electron carriers within the thylakoid membrane. This leads to release of energy. This energy is used to pump protons from the thylakoid membrane to thylakoid space which generates proton gradient.
The figure below shows the proton gradient across the thylakoid.
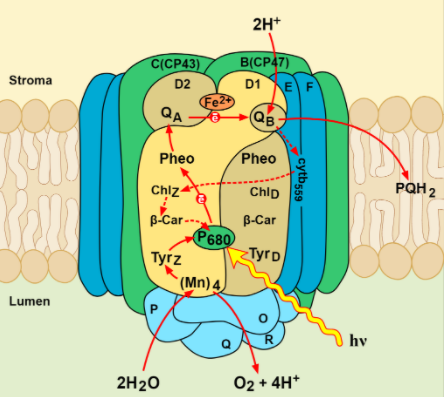
Additional Information: Structure of chloroplast: A chloroplast contains grana. Higher plants have exceptionally coordinated thylakoids in which every chloroplast has 10–100 grana that are associated with one another by stroma thylakoids. The stroma thylakoids might be considered as passages that interface the grana. The grana thylakoids and stroma thylakoids contain various proteins.
Note: The proton gradient is important in photosystem II of photosynthesis as it leads to the formation of ATP. It serves as an intermediate source of harvesting light energy into chemical energy. If the proton gradient gets disrupted, ATP is not produced which disturbs kreb’s cycle.
Complete answer:
A thylakoid is a sheet-like film-which is the site of the light-dependent photosynthesis present in chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. The site contains the chlorophyll used to retain light and use it for biochemical responses.
The pigment called chlorophyll is present in the thylakoid membrane. It is the main pigment which absorbs the sunlight and photolysis of water takes place. As a result of photolysis, the electrons are generated and are passed to a series of electron carriers within the thylakoid membrane. This leads to release of energy. This energy is used to pump protons from the thylakoid membrane to thylakoid space which generates proton gradient.
The figure below shows the proton gradient across the thylakoid.

Additional Information: Structure of chloroplast: A chloroplast contains grana. Higher plants have exceptionally coordinated thylakoids in which every chloroplast has 10–100 grana that are associated with one another by stroma thylakoids. The stroma thylakoids might be considered as passages that interface the grana. The grana thylakoids and stroma thylakoids contain various proteins.
Note: The proton gradient is important in photosystem II of photosynthesis as it leads to the formation of ATP. It serves as an intermediate source of harvesting light energy into chemical energy. If the proton gradient gets disrupted, ATP is not produced which disturbs kreb’s cycle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




