
A ray of light is incident at $ 60^\circ $ on a prism of refracting angle $ 30^\circ $ . The emerging ray is at an angle $ 30^\circ $ with the incident ray. The value of the refractive index of the prism is?
(A) $ \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4} $
(B) $ \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} $
(C) $ \sqrt 3 $
(D) $ \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }} $
Answer
539.7k+ views
Hint :In this question, we have to use the concept of refraction of light when it passes through a prism. The refractive index is a measure of comparing different materials. It tells how fast light can travel through a medium. Since $ {\delta _m} $ is not given so we cannot use the formula $ \mu = \dfrac{{\sin (A + \dfrac{{{\delta _m}}}{2})}}{{\sin (\dfrac{A}{2})}} $ . Instead find $ {r_1} $ and use the formula $ \mu = \dfrac{{\sin {i_1}}}{{\sin {r_1}}} $ , since $ {i_1} $ is given.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Given are the following information: Incident angle $ {i_1} = 60^\circ $ , Angle of prism $ A = 30^\circ $ , Angle of deviation(angle between incident ray and emergent ray) $ \delta = 30^\circ $ . Let the emergent angle be $ {i_2} $ , refractive angle at incident plane $ {r_1} $ and refractive angle at emergent plane $ {r_2} $ as shown in the figure-
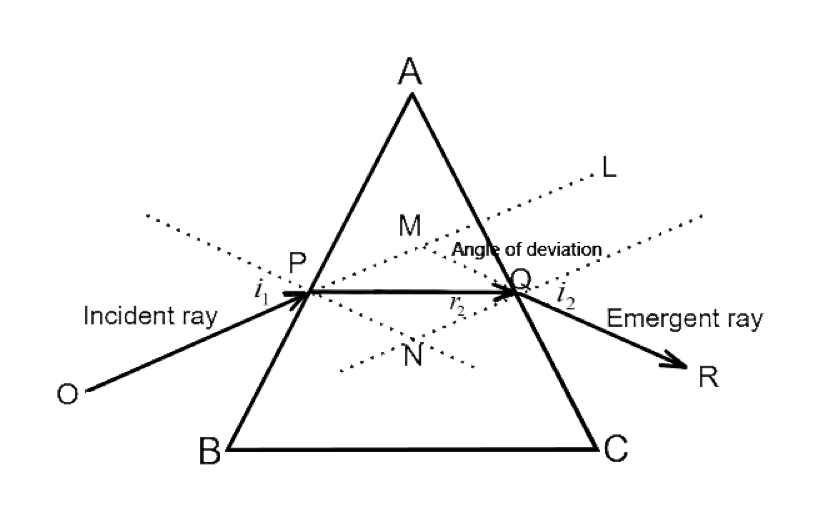
From the figure we note that $ {i_1} = {r_1} + {\delta _1} $ and $ {i_2} = {r_2} + {\delta _2} $ . Adding both equations we have
$ {i_1} + {i_2} = {r_1} + {r_2} + {\delta _1} + {\delta _2} $ (1)
From $ \vartriangle PMQ $ and $ \square APNA $ we see that $ \delta = {\delta _1} + {\delta _2} $ and $ A = {r_1} + {r_2} $ respectively
Substituting this and respective values of variables in equation 1, we get,
$ {i_1} + {i_2} = A + \delta \Rightarrow {i_2} = 0^\circ $
which further implies that
$ {r_2} = 0^\circ \Rightarrow {r_1} = A = 30^\circ $
Using Snell’s law $ \mu = \dfrac{{\sin {i_1}}}{{\sin {r_1}}} \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{\sin 60^\circ }}{{\sin 30^\circ }} \Rightarrow \mu = \sqrt 3 $
Therefore, the refractive index of the prism $ \mu = \sqrt 3 $ .
The answer is option (C).
Note :
Don’t get confused by the term refracting angle. It is not the refractive angle at the incident plane. The angle of prism A is also called refracting angle. Also, whenever it is mentioned the angle made by emergent ray with incident ray it means the total deviation $ \delta ( = {\delta _1} + {\delta _2}) $ .
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Given are the following information: Incident angle $ {i_1} = 60^\circ $ , Angle of prism $ A = 30^\circ $ , Angle of deviation(angle between incident ray and emergent ray) $ \delta = 30^\circ $ . Let the emergent angle be $ {i_2} $ , refractive angle at incident plane $ {r_1} $ and refractive angle at emergent plane $ {r_2} $ as shown in the figure-

From the figure we note that $ {i_1} = {r_1} + {\delta _1} $ and $ {i_2} = {r_2} + {\delta _2} $ . Adding both equations we have
$ {i_1} + {i_2} = {r_1} + {r_2} + {\delta _1} + {\delta _2} $ (1)
From $ \vartriangle PMQ $ and $ \square APNA $ we see that $ \delta = {\delta _1} + {\delta _2} $ and $ A = {r_1} + {r_2} $ respectively
Substituting this and respective values of variables in equation 1, we get,
$ {i_1} + {i_2} = A + \delta \Rightarrow {i_2} = 0^\circ $
which further implies that
$ {r_2} = 0^\circ \Rightarrow {r_1} = A = 30^\circ $
Using Snell’s law $ \mu = \dfrac{{\sin {i_1}}}{{\sin {r_1}}} \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{\sin 60^\circ }}{{\sin 30^\circ }} \Rightarrow \mu = \sqrt 3 $
Therefore, the refractive index of the prism $ \mu = \sqrt 3 $ .
The answer is option (C).
Note :
Don’t get confused by the term refracting angle. It is not the refractive angle at the incident plane. The angle of prism A is also called refracting angle. Also, whenever it is mentioned the angle made by emergent ray with incident ray it means the total deviation $ \delta ( = {\delta _1} + {\delta _2}) $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




