
A ray of light is moving from a rare to a denser medium and strikes a plane mirror at ${90^ \circ }$ to the direction of the ray as shown in the diagram.
(i). Copy the diagram and mark the arrows to show the path of the ray of the light after it is reflected from the mirror.
(ii). Name the principle you have used to mark the arrow the direction of the ray.
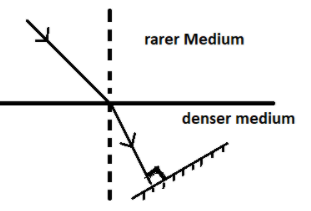

Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: Using the law of reflection, it is known that the ray will reflect at ${90^ \circ }$. So, the ray shall trace back the same path after reflecting from the mirror.
Complete step-by-step solution -
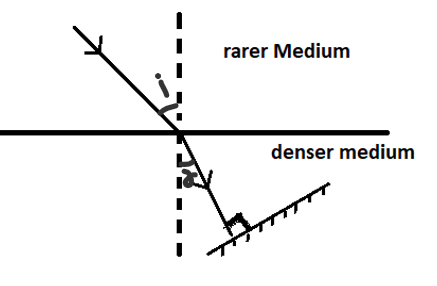
Refraction is a phenomenon that occurs when light changes its travelling medium. Different mediums have different optical densities. A denser medium has more optical density than a rarer medium.
It is observed that, when light goes from a rarer medium to a denser medium it bends towards the normal. When light goes from a denser medium to a rarer medium, it bends away from the normal.
The relation between the angles made as light changes its medium and the relative refractive index is given by the Snell’s law:
\[\mu = \dfrac{{\sin (i)}}{{\sin (r)}}\]
The principle of reversibility states that light retraces the same path if the direction of travel of light is reversed. There are no changes, losses or further bending if the path of light is just reversed, which can be achieved by placing a mirror in the path of the light just perpendicular to its passage. It can be concluded that reversibility principle is a simple deduction of Snell’s law.
So, here in the question, as the light strikes the mirror at perpendicular angles it retraces the exact path. So, the principle of reversibility has been used.
Note: From Snell’s law, it’s known that refracted and incident angles occur in pairs. So at the interface of the mediums, the incident angle in the return journey was the refracted angle before reflection. So, the ray traced back the same path after refraction too.
Complete step-by-step solution -

Refraction is a phenomenon that occurs when light changes its travelling medium. Different mediums have different optical densities. A denser medium has more optical density than a rarer medium.
It is observed that, when light goes from a rarer medium to a denser medium it bends towards the normal. When light goes from a denser medium to a rarer medium, it bends away from the normal.
The relation between the angles made as light changes its medium and the relative refractive index is given by the Snell’s law:
\[\mu = \dfrac{{\sin (i)}}{{\sin (r)}}\]
The principle of reversibility states that light retraces the same path if the direction of travel of light is reversed. There are no changes, losses or further bending if the path of light is just reversed, which can be achieved by placing a mirror in the path of the light just perpendicular to its passage. It can be concluded that reversibility principle is a simple deduction of Snell’s law.
So, here in the question, as the light strikes the mirror at perpendicular angles it retraces the exact path. So, the principle of reversibility has been used.
Note: From Snell’s law, it’s known that refracted and incident angles occur in pairs. So at the interface of the mediums, the incident angle in the return journey was the refracted angle before reflection. So, the ray traced back the same path after refraction too.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




