
A rectangular park is to be designed whose breadth is 3m less than its length. Its area is to be \[4\] square meter more than the area of a park that has already been made in the shape of an isosceles triangle with its base as the breadth of the rectangular park and altitude \[12m\]. Find the length and breadth of the rectangular park.
Answer
516.3k+ views
Hint: Some of the formulas that we need to know before getting into the problem.
Area of a rectangle \[ = l \times b\], where \[l\] is the length of a rectangle and \[b\] is the breadth of a rectangle.
Area of a triangle \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h\], where \[b\] is the base of the triangle and \[h\] is the height of the triangle.
An isosceles triangle is a triangle in which two of the angles of a triangle are equal and two of its sides are equal.
Complete step-by-step solution:
It is given that there is a rectangular park whose breadth is \[3m\] less than its length. Let us take the breadth of the given rectangular park to be \[x\](i.e., \[b = x\]). Therefore, from the given hypothesis, the length of the rectangular park will be \[l = x + 3\].
Also, it is given that the area of this rectangular park is \[4{m^2}\] more than the area of the triangular park whose base is as same as the breadth of the rectangular park and its altitude is \[12m\].
Therefore, the base of the triangular park\[ = x\] and the height of the triangular park \[ = 12\].
Let us draw a diagram using this hypothesis to get a clear idea.
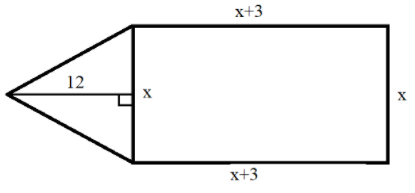
We know the area of a triangle \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h\], where \[b\] is the base of the triangle and \[h\] is the height of the triangle.
Thus, the area of a triangular park \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times x \times 12 = 6x\]
We know the area of a rectangle \[ = l \times b\], where \[l\] is the length of a rectangle and \[b\] is the breadth of a rectangle.
Thus, the area of a rectangular park \[ = (x + 3) \times x = {x^2} + 3x\]
It is given that, area of the rectangular park is \[4{m^2}\] more than the area of the triangular park.
Thus, we get the area of the rectangular park\[ = \] (area of a triangular park)\[ + 4\]
\[
\Rightarrow {x^2} + 3x = 6x + 4 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + 3x - 6x - 4 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} - 3x - 4 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} - 4x+x - 4 = 0 \]
On simplifying the above equation, we get \[x = 4\] and \[x = - 1\].
Since measure cannot be negative \[x = 4\]. Thus, the breadth of the rectangular park is \[4m\]and the length of the rectangular park is \[l = x + 3 = 4 + 3 = 7m\].
Note: Before we start solving this type of problem, we need to make a rough diagram. That will give us a clear idea to solve the problem. Pictorial representation is far better than the description. Thus, always try to make a rough figure of the given word problem if it is possible.
Area of a rectangle \[ = l \times b\], where \[l\] is the length of a rectangle and \[b\] is the breadth of a rectangle.
Area of a triangle \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h\], where \[b\] is the base of the triangle and \[h\] is the height of the triangle.
An isosceles triangle is a triangle in which two of the angles of a triangle are equal and two of its sides are equal.
Complete step-by-step solution:
It is given that there is a rectangular park whose breadth is \[3m\] less than its length. Let us take the breadth of the given rectangular park to be \[x\](i.e., \[b = x\]). Therefore, from the given hypothesis, the length of the rectangular park will be \[l = x + 3\].
Also, it is given that the area of this rectangular park is \[4{m^2}\] more than the area of the triangular park whose base is as same as the breadth of the rectangular park and its altitude is \[12m\].
Therefore, the base of the triangular park\[ = x\] and the height of the triangular park \[ = 12\].
Let us draw a diagram using this hypothesis to get a clear idea.

We know the area of a triangle \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h\], where \[b\] is the base of the triangle and \[h\] is the height of the triangle.
Thus, the area of a triangular park \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times x \times 12 = 6x\]
We know the area of a rectangle \[ = l \times b\], where \[l\] is the length of a rectangle and \[b\] is the breadth of a rectangle.
Thus, the area of a rectangular park \[ = (x + 3) \times x = {x^2} + 3x\]
It is given that, area of the rectangular park is \[4{m^2}\] more than the area of the triangular park.
Thus, we get the area of the rectangular park\[ = \] (area of a triangular park)\[ + 4\]
\[
\Rightarrow {x^2} + 3x = 6x + 4 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + 3x - 6x - 4 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} - 3x - 4 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} - 4x+x - 4 = 0 \]
On simplifying the above equation, we get \[x = 4\] and \[x = - 1\].
Since measure cannot be negative \[x = 4\]. Thus, the breadth of the rectangular park is \[4m\]and the length of the rectangular park is \[l = x + 3 = 4 + 3 = 7m\].
Note: Before we start solving this type of problem, we need to make a rough diagram. That will give us a clear idea to solve the problem. Pictorial representation is far better than the description. Thus, always try to make a rough figure of the given word problem if it is possible.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




