
A regular hexagon & a regular dodecagon are inscribed in the same circle. If the side of the dodecagon is \[(\sqrt 3 - 1)\], then the side of the hexagon is ________________
Answer
582k+ views
Hint: Hexagon is a six sided polygon & a dodecagon is a twelve sided polygon.
The angle made at centre by the sides of a hexagon is \[\dfrac{{360^\circ }}{6} = 60^\circ \]
Similarly the angle made at centre by the sides of a regular dodecagon is \[\dfrac{{360^\circ }}{{12}} = 30^\circ \]
Formula used: $\sin (A - B) = \sin (A)\cos (B) - \cos (B)\sin (A)$
Values of sine and cosine
\[\sin ({0^ \circ }) = 0{\text{ }}\cos ({0^ \circ }) = 1\]
\[\sin ({30^ \circ }) = \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{ }}\cos ({30^ \circ }) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\]
\[\sin ({45^ \circ }) = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}{\text{ }}\cos ({30^ \circ }) = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[\sin ({60^ \circ }) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}{\text{ }}\cos ({30^ \circ }) = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[\sin ({90^ \circ }) = 1{\text{ }}\cos ({90^ \circ }) = 0\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that a regular hexagon & a regular dodecagon are inscribed in the same circle.
Also given that, the side of the dodecagon is \[(\sqrt 3 - 1)\].
We need to find out the side of the hexagon.
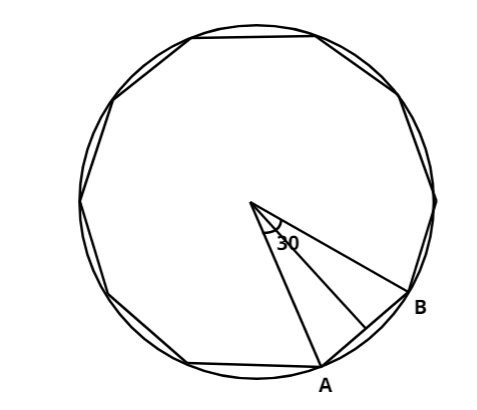
Let, \[AB = \left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right)\]
We know the angle made at centre by the sides of a regular dodecagon is \[\dfrac{{360^\circ }}{{12}} = 30^\circ \]
We draw a perpendicular on the side AB from O.
We get a right angle triangle whose angle at center is \[\dfrac{{30}}{2} = 15^\circ \] and one side of the triangle is
$\dfrac{{AB}}{2}$ =\[\dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{2}\]
Then,
$\Rightarrow$\[\sin 15^\circ = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{2}}}{{\dfrac{r}{1}}}\]
\[ =\dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{2} \times \dfrac{1}{r}\]
To find the value of $\sin ({15^ \circ })$ convert into,
$\Rightarrow$\[\sin (45^\circ - 30^\circ ) = \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{{2r}}\]
Using the formula we have mentioned in hint,
$\Rightarrow$\[\sin 45^\circ \cos 30^\circ - \cos 45^\circ \sin 30^\circ = \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{{2r}}\]
Putting the values of sine and cosine functions,
$\Rightarrow$\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \times \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{{2r}}\]
Simplifying that,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{2\sqrt 2 }} - \dfrac{1}{{2\sqrt 2 }} = \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{{2r}}\]
Rearranging the terms,
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{{2\sqrt 2 }} = \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{{2r}} \\
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt 2 \\
\]
So, the radius of the circle is \[\sqrt 2 \]
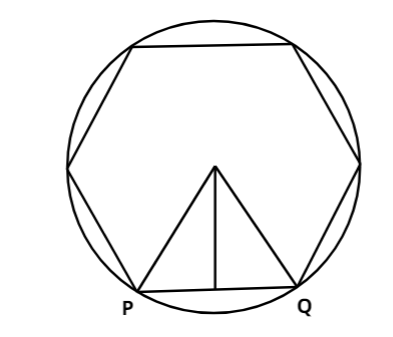
The side of the hexagon is \[PQ\].
The angle made at centre by the sides of a hexagon is \[\dfrac{{360^\circ }}{6} = 60^\circ \]
Again similar as dodecagon,
We draw a perpendicular on the side \[PQ\] from \[O\].
We get a right angle triangle whose angle at centre is \[\dfrac{{60^\circ }}{2} = 30^\circ \]and one side of the triangle is r.
Then,
\[\sin 30^\circ = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{PQ}}{2}}}{{\dfrac{r}{1}}}\]
Substitute the values of \[\sin 30^\circ \] and \[r\],
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{PQ}}{2}}}{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{1}}}\]
Simplifying we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{{PQ}}{2} \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
Solving for \[PQ\],
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{PQ}}{{2\sqrt 2 }} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow PQ = \sqrt 2 \]
Hence, the side of the hexagon is \[\sqrt 2 \]unit.
Note: The value of sine at 30° is \[\sin 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{2}\]. Here since it is given a regular hexagon the angle used in the problem is \[30^\circ \]. Since the sum of angles of any polygon is \[180^\circ \] and there are 6 sides in the hexagon we get an angle of \[30^\circ \].
The angle made at centre by the sides of a hexagon is \[\dfrac{{360^\circ }}{6} = 60^\circ \]
Similarly the angle made at centre by the sides of a regular dodecagon is \[\dfrac{{360^\circ }}{{12}} = 30^\circ \]


Formula used: $\sin (A - B) = \sin (A)\cos (B) - \cos (B)\sin (A)$
Values of sine and cosine
\[\sin ({0^ \circ }) = 0{\text{ }}\cos ({0^ \circ }) = 1\]
\[\sin ({30^ \circ }) = \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{ }}\cos ({30^ \circ }) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\]
\[\sin ({45^ \circ }) = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}{\text{ }}\cos ({30^ \circ }) = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[\sin ({60^ \circ }) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}{\text{ }}\cos ({30^ \circ }) = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[\sin ({90^ \circ }) = 1{\text{ }}\cos ({90^ \circ }) = 0\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that a regular hexagon & a regular dodecagon are inscribed in the same circle.
Also given that, the side of the dodecagon is \[(\sqrt 3 - 1)\].
We need to find out the side of the hexagon.
Let, \[AB = \left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right)\]
We know the angle made at centre by the sides of a regular dodecagon is \[\dfrac{{360^\circ }}{{12}} = 30^\circ \]
We draw a perpendicular on the side AB from O.
We get a right angle triangle whose angle at center is \[\dfrac{{30}}{2} = 15^\circ \] and one side of the triangle is
$\dfrac{{AB}}{2}$ =\[\dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{2}\]
Then,
$\Rightarrow$\[\sin 15^\circ = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{2}}}{{\dfrac{r}{1}}}\]
\[ =\dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{2} \times \dfrac{1}{r}\]
To find the value of $\sin ({15^ \circ })$ convert into,
$\Rightarrow$\[\sin (45^\circ - 30^\circ ) = \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{{2r}}\]
Using the formula we have mentioned in hint,
$\Rightarrow$\[\sin 45^\circ \cos 30^\circ - \cos 45^\circ \sin 30^\circ = \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{{2r}}\]
Putting the values of sine and cosine functions,
$\Rightarrow$\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \times \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{{2r}}\]
Simplifying that,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{2\sqrt 2 }} - \dfrac{1}{{2\sqrt 2 }} = \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{{2r}}\]
Rearranging the terms,
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{{2\sqrt 2 }} = \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 - 1)}}{{2r}} \\
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt 2 \\
\]
So, the radius of the circle is \[\sqrt 2 \]
The side of the hexagon is \[PQ\].
The angle made at centre by the sides of a hexagon is \[\dfrac{{360^\circ }}{6} = 60^\circ \]
Again similar as dodecagon,
We draw a perpendicular on the side \[PQ\] from \[O\].
We get a right angle triangle whose angle at centre is \[\dfrac{{60^\circ }}{2} = 30^\circ \]and one side of the triangle is r.
Then,
\[\sin 30^\circ = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{PQ}}{2}}}{{\dfrac{r}{1}}}\]
Substitute the values of \[\sin 30^\circ \] and \[r\],
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{PQ}}{2}}}{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{1}}}\]
Simplifying we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{{PQ}}{2} \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
Solving for \[PQ\],
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{PQ}}{{2\sqrt 2 }} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow PQ = \sqrt 2 \]
Hence, the side of the hexagon is \[\sqrt 2 \]unit.
Note: The value of sine at 30° is \[\sin 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{2}\]. Here since it is given a regular hexagon the angle used in the problem is \[30^\circ \]. Since the sum of angles of any polygon is \[180^\circ \] and there are 6 sides in the hexagon we get an angle of \[30^\circ \].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





