
A right angles triangle whose sides are 3cm and 4 cm (other than hypotenuse) is made to revolve around its hypotenuse. Find the volume and the surface area of the double cone so formed. (Choose a value of $\pi $ as find appropriate).
Answer
614.7k+ views
Hint – Initially the perpendicular of the right angles triangle is 4cm and the base was 3cm. After the revolution the perpendicular will now be 3cm and the base of this right triangle will be 4cm. Use the direct formula for volume and curved surface area of the cone.
Complete step-by-step answer:
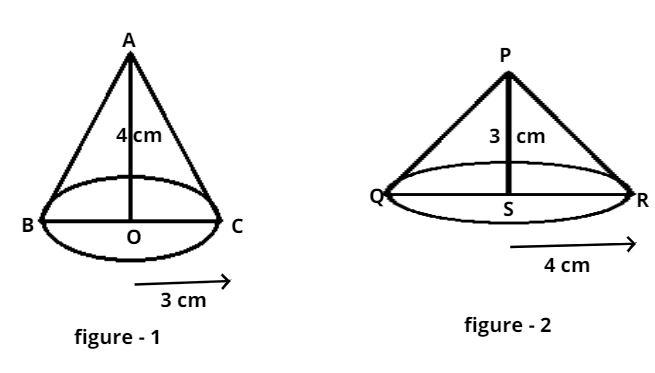
Consider the right angle triangles AOC and PSR respectively.
The base OC = 3 cm and SR = 4 cm.
And height AO = 4 cm and PS = 3cm.
So by Pythagoras theorem we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AO} \right)^2} + {\left( {OC} \right)^2}$ and ${\left( {PR} \right)^2} = {\left( {PS} \right)^2} + {\left( {SR} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {3^2} + {4^2} = 9 + 16 = 25 = {5^2}$ and ${\left( {PR} \right)^2} = {4^2} + {3^2} = 16 + 9 = 25 = {5^2}$
$ \Rightarrow AC = PR = 5$ cm.
So the hypotenuse = 5 cm.
Now when we revolve this right angle triangles about its hypotenuse it will form a cone as shown in figures. When base is 3 cm it will form a cone as shown in figure – 1 and when the base is 4 cm it will form a cone as shown in figure – 2.
Now as we know that the volume (V) of the cube is $\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {\left( r \right)^2}h$ cubic units.
Where (r) and (h) are the base radius and height of the cone respectively.
Now as we know that the surface area (S.A) of the cone is $\left( {\pi rl + \pi {r^2}} \right)$
Where (r) and (l) is base radius and slant height of the cone respectively.
So the slant height of the first and second cone is 5 cm.
So the volume (V1) and surface area (S.A)1 of the first cone is
$ \Rightarrow {V_1} = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times {\left( 3 \right)^2} \times 4 = 37.7{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$ $\left[ {\because \pi = \dfrac{{22}}{7}} \right]$
And
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {S.A} \right)_1} = \left( {\pi rl + \pi {r^2}} \right) = \pi r\left( {l + r} \right) = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 3\left( {5 + 3} \right) = 75.42{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
Now the volume (V2) and surface (S.A)2 area of the second cone is
$ \Rightarrow {V_2} = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times {\left( 4 \right)^2} \times 3 = 50.28{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$
And
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {S.A} \right)_2} = \left( {\pi rl + \pi {r^2}} \right) = \pi r\left( {l + r} \right) = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 4\left( {5 + 4} \right) = 113.14{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
So this is the required answer.
Note – When a triangle is revolved with a very high speed the observer observes its configuration as a cone that is why it is being asked to find the volume and surface area of the cone so formed. A cone is a three-dimensional shape in geometry that narrows smoothly from a flat base (usually circular base) to a point (which forms an axis to the center of the base) called the apex or the vertex.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Consider the right angle triangles AOC and PSR respectively.
The base OC = 3 cm and SR = 4 cm.
And height AO = 4 cm and PS = 3cm.
So by Pythagoras theorem we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AO} \right)^2} + {\left( {OC} \right)^2}$ and ${\left( {PR} \right)^2} = {\left( {PS} \right)^2} + {\left( {SR} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {3^2} + {4^2} = 9 + 16 = 25 = {5^2}$ and ${\left( {PR} \right)^2} = {4^2} + {3^2} = 16 + 9 = 25 = {5^2}$
$ \Rightarrow AC = PR = 5$ cm.
So the hypotenuse = 5 cm.
Now when we revolve this right angle triangles about its hypotenuse it will form a cone as shown in figures. When base is 3 cm it will form a cone as shown in figure – 1 and when the base is 4 cm it will form a cone as shown in figure – 2.
Now as we know that the volume (V) of the cube is $\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {\left( r \right)^2}h$ cubic units.
Where (r) and (h) are the base radius and height of the cone respectively.
Now as we know that the surface area (S.A) of the cone is $\left( {\pi rl + \pi {r^2}} \right)$
Where (r) and (l) is base radius and slant height of the cone respectively.
So the slant height of the first and second cone is 5 cm.
So the volume (V1) and surface area (S.A)1 of the first cone is
$ \Rightarrow {V_1} = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times {\left( 3 \right)^2} \times 4 = 37.7{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$ $\left[ {\because \pi = \dfrac{{22}}{7}} \right]$
And
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {S.A} \right)_1} = \left( {\pi rl + \pi {r^2}} \right) = \pi r\left( {l + r} \right) = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 3\left( {5 + 3} \right) = 75.42{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
Now the volume (V2) and surface (S.A)2 area of the second cone is
$ \Rightarrow {V_2} = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times {\left( 4 \right)^2} \times 3 = 50.28{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$
And
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {S.A} \right)_2} = \left( {\pi rl + \pi {r^2}} \right) = \pi r\left( {l + r} \right) = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 4\left( {5 + 4} \right) = 113.14{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
So this is the required answer.
Note – When a triangle is revolved with a very high speed the observer observes its configuration as a cone that is why it is being asked to find the volume and surface area of the cone so formed. A cone is a three-dimensional shape in geometry that narrows smoothly from a flat base (usually circular base) to a point (which forms an axis to the center of the base) called the apex or the vertex.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




