
A ring has mass $M$ ,radius $R$. A point mass $m$ is placed at a distance $x$ on the axial line as shown in the figure. Find $x$ so that force experienced is maximum.
A. $\dfrac{R}{{3\varepsilon }}$
B.$\dfrac{R}{2}$
C. $\dfrac{R}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
D. $\dfrac{R}{{\sqrt 3 }}$

Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: One of the masses is a ring. Consider a small element $dm$ which makes an angle $\theta $ with the center of the ring.
$dm = \dfrac{M}{{2\pi }}d\theta $
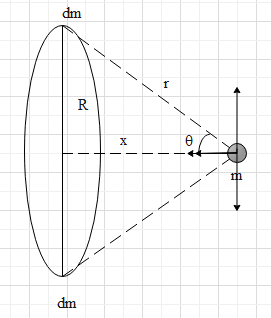
Because of symmetry if we consider two diametrically opposite points. Then the vertical component of forces of both these points on the point mass $m$ will cancel out and the horizontal component gets added up.
The horizontal component is $\cos \theta $.
Since, $\cos \theta $ is equal to adjacent side by hypotenuse,
Here using Pythagoras theorem
Hypotenuse, $r = \sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} $
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} }}$
Therefore,
$dF = \dfrac{{G\dfrac{M}{{2\pi }}d\theta m}}{{{r^2}}} \times 2 \times \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} }}$
On integrating we can find $F$.
When, $F$ is maximum
$\dfrac{{dF}}{{dx}} = 0$
Complete step by step answer:
According to the law of gravitation force of gravity is directly proportional to the product of the mass of the bodies and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
In equation form it is given as
$F = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{{r^2}}}$
This is for the case of a point mass.
Here one of the masses is a ring. Let us consider a small element $dm$ which makes an angle $\theta $ with the center of the Ring.

$dm = \dfrac{M}{{2\pi }}d\theta $
Because of symmetry if we consider two diametrically opposite points. Then the vertical component of forces of both these points on the point mass $m$ will cancel out and the horizontal component gets added up.
The horizontal component is $\cos \theta $.
Since, $\cos \theta $ is equal to adjacent side by hypotenuse,
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} }}$
Here using Pythagoras theorem
Hypotenuse, $r = \sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} $
Therefore,
$dF = \dfrac{{G\dfrac{M}{{2\pi }}d\theta m}}{{{r^2}}} \times 2 \times \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} }}$
Thus,
$F = \int\limits_0^{2\pi } {\dfrac{{G\dfrac{M}{{2\pi }}d\theta m}}{{{r^2}}}} = \dfrac{{GM2\pi m}}{{2\pi ({R^2} + {X^2})}}\dfrac{{2x}}{{\sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} }}$
$F = \dfrac{{GMmx}}{{{{\left( {{R^2} + {x^2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}$
When, $F$ is maximum
$
\dfrac{{dF}}{{dx}} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow x \times \dfrac{{ - 3}}{2}{\left( {{R^2} + {x^2}} \right)^{\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}}} \times 2x + {\left( {{R^2} + {x^2}} \right)^{\dfrac{{ - 3}}{2}}} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 2{x^2} = {R^2} \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{R}{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
$
So, the correct option is option C.
Note:
- Remember that the equation $F = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{{r^2}}}$ is used when both the masses are point masses.
- In this case, one of the masses is a distributed mass. So, we need to modify the equation according to the situation.
- Also, remember that due to the symmetry of the ring if we consider two diametrically opposite points. Then the vertical component of forces of both these points on the point mass $m$ will cancel out and the horizontal component gets added up.
$dm = \dfrac{M}{{2\pi }}d\theta $

Because of symmetry if we consider two diametrically opposite points. Then the vertical component of forces of both these points on the point mass $m$ will cancel out and the horizontal component gets added up.
The horizontal component is $\cos \theta $.
Since, $\cos \theta $ is equal to adjacent side by hypotenuse,
Here using Pythagoras theorem
Hypotenuse, $r = \sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} $
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} }}$
Therefore,
$dF = \dfrac{{G\dfrac{M}{{2\pi }}d\theta m}}{{{r^2}}} \times 2 \times \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} }}$
On integrating we can find $F$.
When, $F$ is maximum
$\dfrac{{dF}}{{dx}} = 0$
Complete step by step answer:
According to the law of gravitation force of gravity is directly proportional to the product of the mass of the bodies and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
In equation form it is given as
$F = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{{r^2}}}$
This is for the case of a point mass.
Here one of the masses is a ring. Let us consider a small element $dm$ which makes an angle $\theta $ with the center of the Ring.

$dm = \dfrac{M}{{2\pi }}d\theta $
Because of symmetry if we consider two diametrically opposite points. Then the vertical component of forces of both these points on the point mass $m$ will cancel out and the horizontal component gets added up.
The horizontal component is $\cos \theta $.
Since, $\cos \theta $ is equal to adjacent side by hypotenuse,
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} }}$
Here using Pythagoras theorem
Hypotenuse, $r = \sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} $
Therefore,
$dF = \dfrac{{G\dfrac{M}{{2\pi }}d\theta m}}{{{r^2}}} \times 2 \times \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} }}$
Thus,
$F = \int\limits_0^{2\pi } {\dfrac{{G\dfrac{M}{{2\pi }}d\theta m}}{{{r^2}}}} = \dfrac{{GM2\pi m}}{{2\pi ({R^2} + {X^2})}}\dfrac{{2x}}{{\sqrt {{R^2} + {x^2}} }}$
$F = \dfrac{{GMmx}}{{{{\left( {{R^2} + {x^2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}$
When, $F$ is maximum
$
\dfrac{{dF}}{{dx}} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow x \times \dfrac{{ - 3}}{2}{\left( {{R^2} + {x^2}} \right)^{\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}}} \times 2x + {\left( {{R^2} + {x^2}} \right)^{\dfrac{{ - 3}}{2}}} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 2{x^2} = {R^2} \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{R}{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
$
So, the correct option is option C.
Note:
- Remember that the equation $F = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{{r^2}}}$ is used when both the masses are point masses.
- In this case, one of the masses is a distributed mass. So, we need to modify the equation according to the situation.
- Also, remember that due to the symmetry of the ring if we consider two diametrically opposite points. Then the vertical component of forces of both these points on the point mass $m$ will cancel out and the horizontal component gets added up.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




