
A root grows in length, which region of the root is responsible for this growth?
(a) Root cap
(b) Region of meristematic activity
(c) Region of elongation
(d) Region of maturation
Answer
531.3k+ views
Hint: The root tips of a plant are divided into three different regions or zones. The region of the root which is responsible for growth in length is the middle region among them. The cells of this region lose the ability to divide gradually.
Complete answer:
Root growth begins right after seed germination. When the plant embryo emerges from a seed, the radicular part forms the root system. The zone of elongation or the region of elongation is the region of the root where newly-formed cells increase in length, thereby increasing the root length. The root tip of a plant is divided into three different zones or regions; a zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a zone of maturation.
The zone of cell division is present adjacent to the root tip and is composed of actively-dividing cells of the root meristem. They contain the undifferentiated cells of a germinating plant. Second is the zone of elongation, where newly-formed cells increase in length and thus increase the root length. At the first root hair, begins the zone of cell maturation where the root cells are differentiated into different specialized cell types. All the three zones or regions occur within approximately the first centimeter of the root tip.
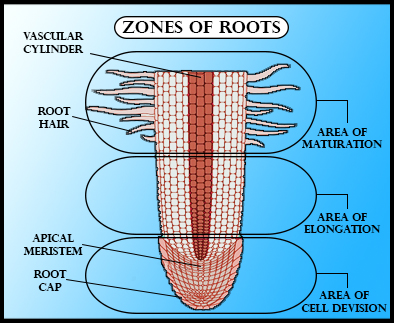
So, the answer is, ‘Region of elongation.’
Note: The tip of the root is protected by a root cap, which is a structure exclusive to the roots and is unlike any of the other plant structures. The root cap has to be replaced continuously because it gets easily damaged as the root pushes through the soil. All the zones lie just within 1cm of this root tip.
Complete answer:
Root growth begins right after seed germination. When the plant embryo emerges from a seed, the radicular part forms the root system. The zone of elongation or the region of elongation is the region of the root where newly-formed cells increase in length, thereby increasing the root length. The root tip of a plant is divided into three different zones or regions; a zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a zone of maturation.
The zone of cell division is present adjacent to the root tip and is composed of actively-dividing cells of the root meristem. They contain the undifferentiated cells of a germinating plant. Second is the zone of elongation, where newly-formed cells increase in length and thus increase the root length. At the first root hair, begins the zone of cell maturation where the root cells are differentiated into different specialized cell types. All the three zones or regions occur within approximately the first centimeter of the root tip.

So, the answer is, ‘Region of elongation.’
Note: The tip of the root is protected by a root cap, which is a structure exclusive to the roots and is unlike any of the other plant structures. The root cap has to be replaced continuously because it gets easily damaged as the root pushes through the soil. All the zones lie just within 1cm of this root tip.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




