
A sequence of 3 bases on tRNA which binds to mRNA codon is
A. Triplet
B. Nonsense codon
C. Anticodon
D. Termination codon
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: tRNA is a type of RNA that carries and transfers an amino acid to the polypeptide chain which is being assembled by the ribosome. The anticodon is complementary to the three nucleotides in the corresponding codon on the mRNA.
Complete step by step answer: tRNA is a special type of RNA which plays an important role in translation. It is a specific three-dimensional folded structure which transfers an amino acid to the polypeptide chain by reading the codon sequence on the mRNA. At one end of the tRNA, there is a sequence of three nucleotides that is complementary to the three nucleotides in the corresponding codon on the mRNA, called the anticodon. Each anticodon is specific to one and only one codon of the mRNA. The tRNA acts as an adapter, while binding its anticodon to the complementary mRNA codon.
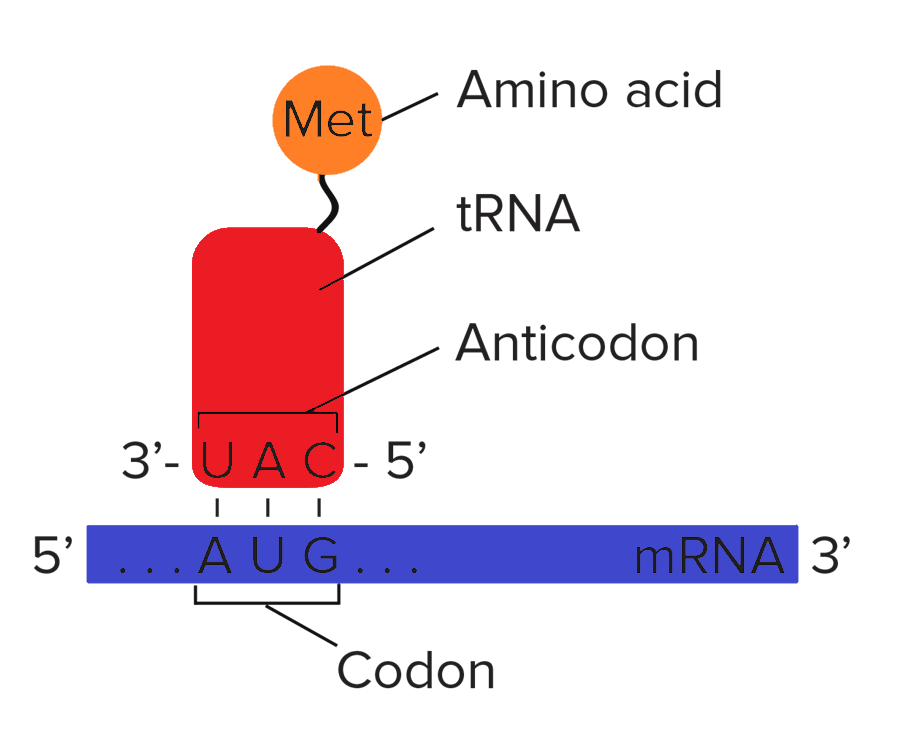
As the tRNA binds to the codon and the ribosomal unit, it brings into position the correct amino acid that is needed for the polypeptide chain formation. There are 61 different tRNAs, one for each functional codon which can be read from the mRNA.
Hydrogen bonds hold the complementary bases on the codon and anticodon. The ribosomal subunit allows the tRNA to bind to the mRNA only if it is carrying an amino acid. Once the codon has been read the amino acid is transferred from the tRNA to the polypeptide chain and the bonds between the codon and the anticodon dissociate.
A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on an mRNA strand which is also known as the triplet codon. Each codon encodes a specific amino acid. Sixty-four different type of triplet codons can be made using the four nucleotides (AUGC) in the mRNA. Out of the 64 types, three codons are called stop codons, as the terminate the translation process. There also exists a start codon which initiates translation.
Therefore, the correct answer is option is C.
Note: The triple nucleotide sequence on the mRNA is the codon and the one on the tRNA is the anticodon. It is important to remember the distinction between the two. Since the codon is a nucleotide sequence it is possible to determine the polypeptide sequence even from knowing the DNA. Another key aspect of the codon is that it is redundant, which means several codes for the same amino acid. As there are only 20 amino acids within the human body which can be coded by 62 codons. The start codon codes for methionine.
Complete step by step answer: tRNA is a special type of RNA which plays an important role in translation. It is a specific three-dimensional folded structure which transfers an amino acid to the polypeptide chain by reading the codon sequence on the mRNA. At one end of the tRNA, there is a sequence of three nucleotides that is complementary to the three nucleotides in the corresponding codon on the mRNA, called the anticodon. Each anticodon is specific to one and only one codon of the mRNA. The tRNA acts as an adapter, while binding its anticodon to the complementary mRNA codon.

As the tRNA binds to the codon and the ribosomal unit, it brings into position the correct amino acid that is needed for the polypeptide chain formation. There are 61 different tRNAs, one for each functional codon which can be read from the mRNA.
Hydrogen bonds hold the complementary bases on the codon and anticodon. The ribosomal subunit allows the tRNA to bind to the mRNA only if it is carrying an amino acid. Once the codon has been read the amino acid is transferred from the tRNA to the polypeptide chain and the bonds between the codon and the anticodon dissociate.
A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on an mRNA strand which is also known as the triplet codon. Each codon encodes a specific amino acid. Sixty-four different type of triplet codons can be made using the four nucleotides (AUGC) in the mRNA. Out of the 64 types, three codons are called stop codons, as the terminate the translation process. There also exists a start codon which initiates translation.
Therefore, the correct answer is option is C.
Note: The triple nucleotide sequence on the mRNA is the codon and the one on the tRNA is the anticodon. It is important to remember the distinction between the two. Since the codon is a nucleotide sequence it is possible to determine the polypeptide sequence even from knowing the DNA. Another key aspect of the codon is that it is redundant, which means several codes for the same amino acid. As there are only 20 amino acids within the human body which can be coded by 62 codons. The start codon codes for methionine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




