
A small disk placed on a frictionless horizontal floor is attached at one end of a light inextensible cord, the other end of which is attached on a vertical cylinder fixed on the floor. The disc is projected with a certain velocity perpendicular to the cord and along the floor. How will the tensile force in the cord and speed of the disc change during the ensuing motion?
A. Both will increase.
B. Both will remain constant.
C. Tensile force will increase and speed will decrease.
D. Tensile force will increase and the force will remain constant.

Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: The key concepts to be considered here are frictionless, inextensible string and velocity perpendicular to the cord. The disc will perform circular motion on the floor which has no friction with regards to the disc.
Complete step by step answer:
First things first, the table is frictionless so if we provide a velocity to the disc, it should not decrease. If disc is given perpendicular velocity (w.r.t. cord), it will perform circular motion; as we know in circular motion the velocity is perpendicular to the radius. Here, the length of the cord will serve as the radius for circular motion and the velocity we provided will be the velocity of its circular motion.
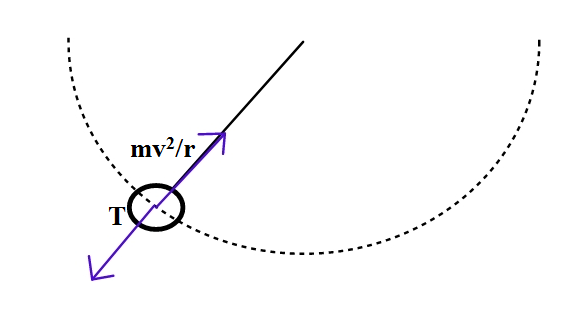
For a body performing circular motion horizontally, the tension will be due to the centripetal force keeping the disc in circular motion.
Initially, the disc was resting and as the string was inextensible, there was no tension in the string. As there was circular motion, the tension was due to the centripetal force acting on the body. So, the string went from a state of zero tension to some finite tension.
Therefore, the correct answer should be option (D). The tensile force will increase and speed will remain constant.
Note:
The direction of centripetal force for a body performing circular motion is towards the centre and direction of the centrifugal force experienced by the body will be outwards from the centre. The disc will experience a centrifugal force (pseudo force) equal in magnitude to centripetal force outwards which will create a tension in the string. Notice the use of word velocity in question and feed in to answer the velocity for the disc will change direction but the magnitude of that velocity will be constant so speed will be constant.
Complete step by step answer:
First things first, the table is frictionless so if we provide a velocity to the disc, it should not decrease. If disc is given perpendicular velocity (w.r.t. cord), it will perform circular motion; as we know in circular motion the velocity is perpendicular to the radius. Here, the length of the cord will serve as the radius for circular motion and the velocity we provided will be the velocity of its circular motion.

For a body performing circular motion horizontally, the tension will be due to the centripetal force keeping the disc in circular motion.
Initially, the disc was resting and as the string was inextensible, there was no tension in the string. As there was circular motion, the tension was due to the centripetal force acting on the body. So, the string went from a state of zero tension to some finite tension.
Therefore, the correct answer should be option (D). The tensile force will increase and speed will remain constant.
Note:
The direction of centripetal force for a body performing circular motion is towards the centre and direction of the centrifugal force experienced by the body will be outwards from the centre. The disc will experience a centrifugal force (pseudo force) equal in magnitude to centripetal force outwards which will create a tension in the string. Notice the use of word velocity in question and feed in to answer the velocity for the disc will change direction but the magnitude of that velocity will be constant so speed will be constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




