
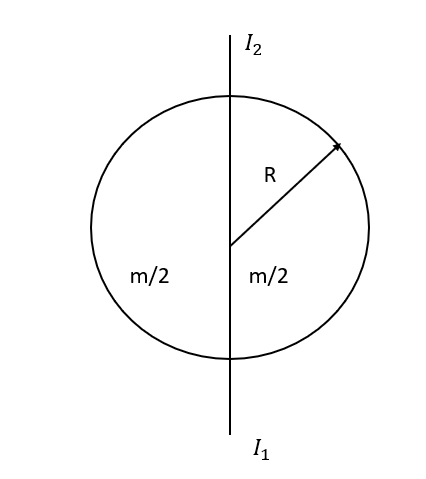
A solid hemisphere and a hemispherical shell are joined as shown. Both of them have $\dfrac{m}{2}$ individually. Find out the moment of inertia about axis $I_{1}$, $I_{2}$.

Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint: We have given the moment of inertia of a solid sphere and a hemispherical shell. Composite system is the combination of the solid sphere and hemispherical shell. The moment of inertia of the is the sum of the moment of inertia of the solid sphere and moment of inertia of the hollow sphere.
Complete step-by-step solution: -
Moment of inertia of the solid sphere, $I_{1} = \dfrac{2}{5} MR^{2}$.
Moment of inertia of the hollow sphere, $I_{2} = \dfrac{2}{3} MR^{2}$.
R is the radius.
The moment of inertia of a rigid composite system is the total moment of inertia of its component subsystems.
Moment of inertia,
$I = \dfrac{2}{3} MR^{2} + \dfrac{2}{5} MR^{2}$
$\implies I = \dfrac{16}{15} MR^{2}$
Given: $M = \dfrac{m}{2}$
$ I = \dfrac{16}{15} \times \dfrac{m}{2} \times R^{2}$
$\implies I = \dfrac{8}{15} MR^{2}$
Note: The moment of inertia is a quantity that defines the torque required for a desired angular acceleration around a rotational axis, how mass defines the force needed for the wanted acceleration. It depends on the body's mass configuration and the axis taken, with significant moments needing more torque to alter its rotation rate. It is an extensive property: the moment of inertia is just the mass times the perpendicular distance square to the pole of rotation. The moment of inertia of a complex composite system is the actual inertia of its component subsystems.
Complete step-by-step solution: -
Moment of inertia of the solid sphere, $I_{1} = \dfrac{2}{5} MR^{2}$.
Moment of inertia of the hollow sphere, $I_{2} = \dfrac{2}{3} MR^{2}$.
R is the radius.
The moment of inertia of a rigid composite system is the total moment of inertia of its component subsystems.
Moment of inertia,
$I = \dfrac{2}{3} MR^{2} + \dfrac{2}{5} MR^{2}$
$\implies I = \dfrac{16}{15} MR^{2}$
Given: $M = \dfrac{m}{2}$
$ I = \dfrac{16}{15} \times \dfrac{m}{2} \times R^{2}$
$\implies I = \dfrac{8}{15} MR^{2}$
Note: The moment of inertia is a quantity that defines the torque required for a desired angular acceleration around a rotational axis, how mass defines the force needed for the wanted acceleration. It depends on the body's mass configuration and the axis taken, with significant moments needing more torque to alter its rotation rate. It is an extensive property: the moment of inertia is just the mass times the perpendicular distance square to the pole of rotation. The moment of inertia of a complex composite system is the actual inertia of its component subsystems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




