
A spinner has four colours as shown in the figure. When we spin it once, find
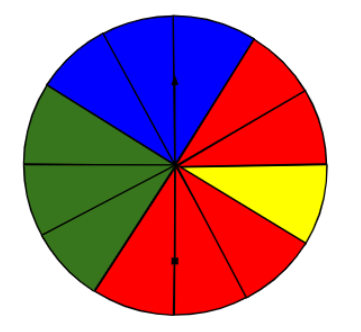
(a) At which colour, is the pointer more likely to stop?
(b) At which colour, is the pointer less likely to stop?
(c) At which colour, is the pointer equally likely to stop?
(d) What is the chance the pointer will stop on white?
(e) Is there any colour at which the pointer certainly stops?

Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: Firstly find the possible number of outcomes P(Y) that is the total number of sections in the spinner and wanted number of outcomes P(X) that are the colour at which the pointer stops. Calculate the probability by using the formula, probability of an event P(E) is given as \[P\left( E \right)=\dfrac{P\left( X \right)}{P\left( Y \right)}\]. Similarly calculate the probability for each case.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know the probability of any event P(E) is the ratio of number of wanted outcome P(X) to the number of possible outcomes P(Y) and is given by the formula \[P\left( E \right)=\dfrac{P\left( X \right)}{P\left( Y \right)}\].
We know the spinner has 12 sections, therefore we can say that the possible number of outcomes P(Y) is 12.
Out of the 12 sections 5 are of RED colour, 3 are of BLUE colour, 3 are of GREEN colour and one is of yellow colour.
For the spinner to be stopped at RED colour, the wanted number of outcomes P(X) is 5.
For the spinner to be stopped at BLUE colour, the wanted number of outcomes P(X) is 3.
For the spinner to be stopped at GREEN colour, the wanted number of outcomes P(X) is 3.
For the spinner to be stopped at YELLOW colour, the wanted number of outcomes P(X) is 1.
Finding the probability for the spinner to be stopped at RED colour P(R) using the above mentioned formula,
\[P\left( R \right)=\dfrac{5}{12}\]
Finding the probability for the spinner to be stopped at BLUE colour P(B) using the above mentioned formula,
\[P\left( B \right)=\dfrac{3}{12}\]
Finding the probability for the spinner to be stopped at GREEN colour P(G) using the above mentioned formula,
\[P\left( G \right)=\dfrac{3}{12}\]
Finding the probability for the spinner to be stopped at YELLOW colour P(Y) using the above mentioned formula,
\[P\left( Y \right)=\dfrac{1}{12}\]
By comparing all the probabilities we conclude that probability for the spinner to be stopped at RED colour P(R) is the greatest.
Hence at RED colour the pointer is more likely to stop.
By comparing all the probabilities we conclude that probability for the spinner to be stopped at YELLOW colour P(Y) is the greatest.
Hence at YELLOW colour the pointer is less likely to stop.
By comparing all the probabilities we conclude that probability for the spinner to be stopped at BLUE and GREEN colour is equal.
Hence the pointer is equally likely to stop at BLUE and GREEN colour.
As there is no WHITE colour in the spinner, we conclude the probability for the spinner to be stopped at WHITE colour is null.
Hence the pointer has 0 chance of stopping on WHITE.
NO, there is no colour at which the pointer stops certainly. Instead the position of pointer and at which colour it will stop depends on the probability of getting a specific colour.
Note: The possible mistake that you may encounter could be the negligence of any colour from the spinner. Also this question can also be attempted visually by simply observing the figure and answering the asked questions. But using probability offers a much more credible answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know the probability of any event P(E) is the ratio of number of wanted outcome P(X) to the number of possible outcomes P(Y) and is given by the formula \[P\left( E \right)=\dfrac{P\left( X \right)}{P\left( Y \right)}\].
We know the spinner has 12 sections, therefore we can say that the possible number of outcomes P(Y) is 12.
Out of the 12 sections 5 are of RED colour, 3 are of BLUE colour, 3 are of GREEN colour and one is of yellow colour.
For the spinner to be stopped at RED colour, the wanted number of outcomes P(X) is 5.
For the spinner to be stopped at BLUE colour, the wanted number of outcomes P(X) is 3.
For the spinner to be stopped at GREEN colour, the wanted number of outcomes P(X) is 3.
For the spinner to be stopped at YELLOW colour, the wanted number of outcomes P(X) is 1.
Finding the probability for the spinner to be stopped at RED colour P(R) using the above mentioned formula,
\[P\left( R \right)=\dfrac{5}{12}\]
Finding the probability for the spinner to be stopped at BLUE colour P(B) using the above mentioned formula,
\[P\left( B \right)=\dfrac{3}{12}\]
Finding the probability for the spinner to be stopped at GREEN colour P(G) using the above mentioned formula,
\[P\left( G \right)=\dfrac{3}{12}\]
Finding the probability for the spinner to be stopped at YELLOW colour P(Y) using the above mentioned formula,
\[P\left( Y \right)=\dfrac{1}{12}\]
By comparing all the probabilities we conclude that probability for the spinner to be stopped at RED colour P(R) is the greatest.
Hence at RED colour the pointer is more likely to stop.
By comparing all the probabilities we conclude that probability for the spinner to be stopped at YELLOW colour P(Y) is the greatest.
Hence at YELLOW colour the pointer is less likely to stop.
By comparing all the probabilities we conclude that probability for the spinner to be stopped at BLUE and GREEN colour is equal.
Hence the pointer is equally likely to stop at BLUE and GREEN colour.
As there is no WHITE colour in the spinner, we conclude the probability for the spinner to be stopped at WHITE colour is null.
Hence the pointer has 0 chance of stopping on WHITE.
NO, there is no colour at which the pointer stops certainly. Instead the position of pointer and at which colour it will stop depends on the probability of getting a specific colour.
Note: The possible mistake that you may encounter could be the negligence of any colour from the spinner. Also this question can also be attempted visually by simply observing the figure and answering the asked questions. But using probability offers a much more credible answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




