
A spring balance together with a suspended weight of 2.5 kg is dropped from a height of 30 metres. What is the reading of the weight on the spring balance while falling?
A. 2.5 kg
B. 1.25 kg
C. 0 kg
D. 25 kg
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Here, we will proceed by discussing the basics of the spring balance and how exactly it measures the weight. Then, we will write down the factor on which the reading of any spring balance depends.
Complete answer:
Wight of the object = 2.5 kg
Height of falling = 30 m
As, weight of any object is equal to the product of the mass of the object and the acceleration due to gravity i.e., g m/${{\text{s}}^2}$
i.e., Weight of the object = Mass of the object$ \times $Acceleration due to gravity
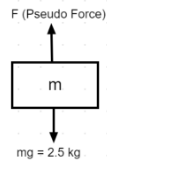
Spring balance is basically a weight measuring device which finds out the weight of the object by using the relation between the forces applied (or load applied) and the deformation in the spring.
Since, the external force applied to the spring is always directly proportional to the amount of the deformation occurred in the spring. This linear relationship is the principle on which the spring balance actually works. The deformation occurred in the spring can be either a compression or expansion depending on the direction of the force applied.
The net force acting on a spring balance by a suspended object. The acceleration due to gravity having a value of g m/${{\text{s}}^2}$ will be acting on the object. A pseudo force will be acting on the object having a magnitude equal to the product of mass and acceleration due to gravity (mg). This pseudo force acts in a direction opposite to the direction in which the weight of the body acts i.e., pseudo force will be acting upwards because on a free falling object, the weight (mg) will be acting downwards where m represents the mass of the object. This pseudo force acting on the object balances the weight acting on the object because both are of the same magnitude. Apart from these two forces (i.e., pseudo force and weight) acting on the object, no other force acts on the object. Also, the two forces are equal in magnitude and opposite so that means there is no net force which is acting on the spring balance.
Therefore, the reading of the weight on the spring balance while falling will be zero i.e., Weight on the spring balance = 0 kg
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The spring balance can also be used for the calibration regarding the accurate measurement of the mass. Spring balances can be used as the basics of the accelerometers. Heavy loads such as trucks, material carried on a conveyor belt, etc are used for weight measurement.
Complete answer:
Wight of the object = 2.5 kg
Height of falling = 30 m
As, weight of any object is equal to the product of the mass of the object and the acceleration due to gravity i.e., g m/${{\text{s}}^2}$
i.e., Weight of the object = Mass of the object$ \times $Acceleration due to gravity

Spring balance is basically a weight measuring device which finds out the weight of the object by using the relation between the forces applied (or load applied) and the deformation in the spring.
Since, the external force applied to the spring is always directly proportional to the amount of the deformation occurred in the spring. This linear relationship is the principle on which the spring balance actually works. The deformation occurred in the spring can be either a compression or expansion depending on the direction of the force applied.
The net force acting on a spring balance by a suspended object. The acceleration due to gravity having a value of g m/${{\text{s}}^2}$ will be acting on the object. A pseudo force will be acting on the object having a magnitude equal to the product of mass and acceleration due to gravity (mg). This pseudo force acts in a direction opposite to the direction in which the weight of the body acts i.e., pseudo force will be acting upwards because on a free falling object, the weight (mg) will be acting downwards where m represents the mass of the object. This pseudo force acting on the object balances the weight acting on the object because both are of the same magnitude. Apart from these two forces (i.e., pseudo force and weight) acting on the object, no other force acts on the object. Also, the two forces are equal in magnitude and opposite so that means there is no net force which is acting on the spring balance.
Therefore, the reading of the weight on the spring balance while falling will be zero i.e., Weight on the spring balance = 0 kg
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The spring balance can also be used for the calibration regarding the accurate measurement of the mass. Spring balances can be used as the basics of the accelerometers. Heavy loads such as trucks, material carried on a conveyor belt, etc are used for weight measurement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




