
A standing wave having \[3\] nodes and \[2\] antinodes is formed between two atoms having a distance \[1.21{A^o}\] between them. The wavelength of the standing wave is
A. \[1.21{A^o}\]
B. \[3.63{A^o}\]
C. \[4.84{A^o}\]
D. \[5.86{A^o}\]
Answer
496.2k+ views
Hint: We start by defining what standing waves are. We then move onto writing down the given data from the question. Then once we have done this, we define what wavelength, nodes and antinodes are. Then we see the number of nodes and antinodes in one wave and see if the number of nodes and antinodes match the number of nodes and antinodes in one wave. We can also draw a diagram to make sure what a wave having \[3\] nodes and \[2\] antinodes look like.
Complete answer:
Let us start by defining what a standing wave is. A standing wave or a stationary wave is a kind of wave whose peak amplitude does not change in space but oscillates in time and the oscillations at different times are in phase.
We are given a standing wave having \[3\] nodes and \[2\] antinodes. Moving onto defining what nodes and antinodes are. Nodes are the points in a standing wave that has minimum amplitude. Antinodes are the points in a standing wave that has maximum amplitude. Now that we have defined all the terms in the question, we can draw the diagram for the standing wave having \[3\] nodes and \[2\] antinodes. It will be as follows,
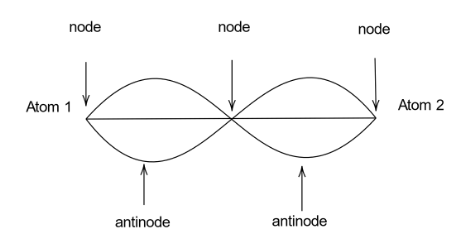
We can see that the number of nodes and antinodes formed is equal to the number of the same in one wavelength. Hence the wavelength of the wave will be the same as the distance between the two atoms
Therefore, the right answer is option A.
Note: Here, the wavelength of a standing wave is defined with respect to the number of nodes and antinodes present. This helps in solving the problem more efficiently and easily. Wavelength can also be defined as the distance between two consecutive crests or two consecutive troughs. Crests and antinodes are two completely different ideas as, crests meet a crest; and then one-half cycle later, a trough will meet a trough whereas; an antinode will continue to vibrate between the positive and negative maximum values.
Complete answer:
Let us start by defining what a standing wave is. A standing wave or a stationary wave is a kind of wave whose peak amplitude does not change in space but oscillates in time and the oscillations at different times are in phase.
We are given a standing wave having \[3\] nodes and \[2\] antinodes. Moving onto defining what nodes and antinodes are. Nodes are the points in a standing wave that has minimum amplitude. Antinodes are the points in a standing wave that has maximum amplitude. Now that we have defined all the terms in the question, we can draw the diagram for the standing wave having \[3\] nodes and \[2\] antinodes. It will be as follows,

We can see that the number of nodes and antinodes formed is equal to the number of the same in one wavelength. Hence the wavelength of the wave will be the same as the distance between the two atoms
Therefore, the right answer is option A.
Note: Here, the wavelength of a standing wave is defined with respect to the number of nodes and antinodes present. This helps in solving the problem more efficiently and easily. Wavelength can also be defined as the distance between two consecutive crests or two consecutive troughs. Crests and antinodes are two completely different ideas as, crests meet a crest; and then one-half cycle later, a trough will meet a trough whereas; an antinode will continue to vibrate between the positive and negative maximum values.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




