
(a) State Ohm’s law
(b) Describe an experiment to verify this law.
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Ohm’s law relates the potential difference between the two ends of a conductor with the current flowing through the conductor. Ohm’s law is valid at constant temperature. The graph between the potential difference and current flowing through the conductor will be a straight line for conductors obeying Ohm’s law.
Formulas used:
\[V\propto I\Rightarrow V=IR\]
Complete answer:
At constant temperature, the potential difference$V$, across the ends of a given metallic wire in an electric circuit is proportional to the current flowing through it. This is known as Ohm’s law.i.e.
\[\begin{align}
& V\propto I \\
& or, \dfrac{V}{I}=\text{ constant=}R \\
& or, V=IR \\
\end{align}\]
The constant R is constant for a given metallic wire and at a given temperature and is known as resistance.
Experimental verification of Ohm’s law:
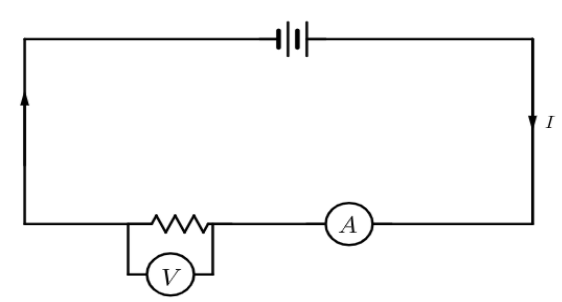
Setup a circuit as shown in figure. Connect a voltmeter parallel with a resistance R and connect the ammeter in series with the circuit. First note the reading on voltmeter and ammeter For 5 Volt source battery. Then increase the value of the source battery from 5 Volts to 10 Volts and note down the readings on the voltmeter and ammeter. Increase the source battery volt by 5Volt and repeat the experiment for ten times.
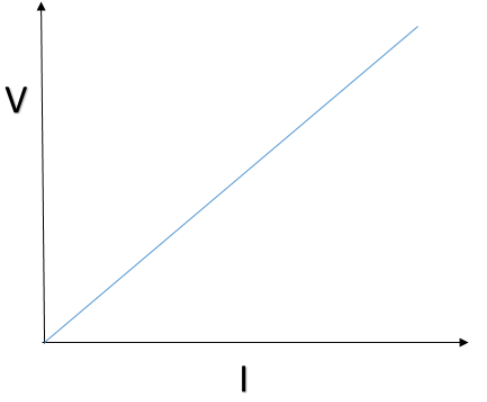
Plot a graph between the voltmeter reading (y-axis) and ammeter reading (x-axis). The graph will be a straight line verifying the Ohm’s law. The slope of the graph will give the resistance.
Note:
The resistance of a conductor is proportional to the temperature. The resistance in a conductor arises due to the collision of electrons inside the conductor. So if the temperature increases the velocity of electrons inside the conductor will increase and they will collide more with themselves due to which the resistance will increase. So Ohm’s law is only valid at constant temperature.
Formulas used:
\[V\propto I\Rightarrow V=IR\]
Complete answer:
At constant temperature, the potential difference$V$, across the ends of a given metallic wire in an electric circuit is proportional to the current flowing through it. This is known as Ohm’s law.i.e.
\[\begin{align}
& V\propto I \\
& or, \dfrac{V}{I}=\text{ constant=}R \\
& or, V=IR \\
\end{align}\]
The constant R is constant for a given metallic wire and at a given temperature and is known as resistance.
Experimental verification of Ohm’s law:

Setup a circuit as shown in figure. Connect a voltmeter parallel with a resistance R and connect the ammeter in series with the circuit. First note the reading on voltmeter and ammeter For 5 Volt source battery. Then increase the value of the source battery from 5 Volts to 10 Volts and note down the readings on the voltmeter and ammeter. Increase the source battery volt by 5Volt and repeat the experiment for ten times.
Plot a graph between the voltmeter reading (y-axis) and ammeter reading (x-axis). The graph will be a straight line verifying the Ohm’s law. The slope of the graph will give the resistance.

Note:
The resistance of a conductor is proportional to the temperature. The resistance in a conductor arises due to the collision of electrons inside the conductor. So if the temperature increases the velocity of electrons inside the conductor will increase and they will collide more with themselves due to which the resistance will increase. So Ohm’s law is only valid at constant temperature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




