
A stick is thrown in the air and lands on the ground at some distance from the thrower. The centre of mass of the stick will move along the parabolic path
A) in all cases
B) only if the stick is uniform
C) only if the stick has linear motion but not rotational motion
D) only if the stick has a shape such that its centre of mass is located at some point on it and not outside it.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Different bodies have a different distribution of mass but centre of mass is a point in the body where the whole mass is supposed to be concentrated.
We can trace the movement of the stick to observe the force acting and the centre of mass will be considered as a point mass.
Complete step by step answer:
Representation of the movement of the thrown stick:
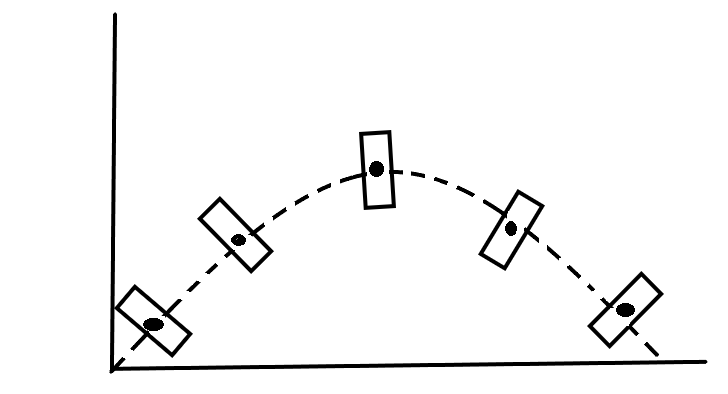
The mass of the thrown stick is supposed to be concentrated on its centre of mass.
At all the positions of the stick, only the force due to gravity [ acceleration due to gravity ( g ) ] is acting on it in the downward direction at its centre of mass and thus centre of mass tends to travel in a parabolic path throughout the motion like a point mass.
Therefore, in every condition, the centre of mass will be covering a parabolic path.
Checking the options:
Uniform stick: Uniformity of stick plays no role in the movement of centre of mass along the parabolic path as the force (g) depends upon where the mass is concentrated and not hoe I is distributed.
Linear motion but not rotational motion: The stick might also rotate in the air but then also the centre of mass will be moving along the parabolic path, so this option gets canceled.
Centre of mass is located at some point on it and not outside it: The motion of centre of mass does not depends on its location, so this option also gets canceled
Therefore, it can be concluded that if a stick is thrown in the air and lands on the ground at some distance from the thrower, the centre of mass of the stick will move along the parabolic path in all cases, and thus the correct option is A).
Note:The velocity of the centre of mass does not change throughout the motion.
We consider the centre of mass of a body a point mass so as to follow Newton’s Laws.
Generally, when an object is thrown in air (terms is referred to as projectile), its different parts can travel along different directions but the centre of mass will always be traveling a parabolic path.
We can trace the movement of the stick to observe the force acting and the centre of mass will be considered as a point mass.
Complete step by step answer:
Representation of the movement of the thrown stick:

The mass of the thrown stick is supposed to be concentrated on its centre of mass.
At all the positions of the stick, only the force due to gravity [ acceleration due to gravity ( g ) ] is acting on it in the downward direction at its centre of mass and thus centre of mass tends to travel in a parabolic path throughout the motion like a point mass.
Therefore, in every condition, the centre of mass will be covering a parabolic path.
Checking the options:
Uniform stick: Uniformity of stick plays no role in the movement of centre of mass along the parabolic path as the force (g) depends upon where the mass is concentrated and not hoe I is distributed.
Linear motion but not rotational motion: The stick might also rotate in the air but then also the centre of mass will be moving along the parabolic path, so this option gets canceled.
Centre of mass is located at some point on it and not outside it: The motion of centre of mass does not depends on its location, so this option also gets canceled
Therefore, it can be concluded that if a stick is thrown in the air and lands on the ground at some distance from the thrower, the centre of mass of the stick will move along the parabolic path in all cases, and thus the correct option is A).
Note:The velocity of the centre of mass does not change throughout the motion.
We consider the centre of mass of a body a point mass so as to follow Newton’s Laws.
Generally, when an object is thrown in air (terms is referred to as projectile), its different parts can travel along different directions but the centre of mass will always be traveling a parabolic path.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




