
A stick of mass $m$ and length $l$ is pivoted at the one end and is displaced through an angle $\theta $.The increase in potential energy is ?
Answer
477k+ views
Hint:The "center of mass" of any object can be considered as the average location of all of the mass in that object. To balance an object, all we need to do is make sure that the center of gravity of the object is either directly above or directly below the pivot point.
Formula used:
$V = mgl$ ………. (1)
Where $V$ is potential energy, $m$ is mass and $l$ is the length.
Complete step by step answer:
Potential energy can be defined as mechanical energy, stored energy, or energy caused by position. The term potential energy was introduced by Scottish engineer and Physicist William Rankine in the 19th century. Potential energy is a function of a field, when there is a field of force of any kind then any object interacts with the force to gain energy For example In nature around a mass we have a gravitational field. Any mass in that field experiences a force thus we can find energy associated with that mass and that energy will be Potential energy.
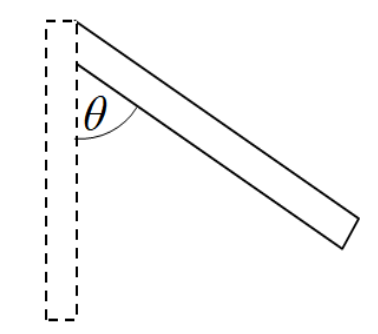
In the beginning, the height of the center of mass from the ground is $\dfrac{l}{2}$. So the initial potential energy is,
$V_i = - mg\dfrac{l}{2}$
When the stick is displaced at an angle $\theta $. The height of the center of mass from the ground is $\dfrac{l}{2}\sin \theta $.So the final potential energy is,
$V_f = - mg\dfrac{{l\sin \theta }}{2}$
The increase in potential energy
$V$ = $Vf - Vi$
\[V = - mg\dfrac{l}{2}\sin \theta + mg\dfrac{l}{2}\]
$ \Rightarrow V = - mg\dfrac{l}{2}(\sin \theta - 1)$
$ \therefore V = mg\dfrac{l}{2}(1 - \sin \theta )$
Therefore, the increase in potential energy is $mg\dfrac{l}{2}(1 - \sin \theta )$.
Note:There are three types of potential energy, (1) Elastic Potential energy: Any object that behaves as an elastic or spring contains elastic potential energy. (2)Gravitational potential energy: The earth has a gravitational force that pulls any object with mass towards the surface and so the object has energy associated with it called Gravitational Potential energy. (3) Chemical Potential Energy: The attractive forces between two atoms create chemical bonds and that bond between atoms and molecules leads to storage of energy in the form of Chemical Potential energy.
Formula used:
$V = mgl$ ………. (1)
Where $V$ is potential energy, $m$ is mass and $l$ is the length.
Complete step by step answer:
Potential energy can be defined as mechanical energy, stored energy, or energy caused by position. The term potential energy was introduced by Scottish engineer and Physicist William Rankine in the 19th century. Potential energy is a function of a field, when there is a field of force of any kind then any object interacts with the force to gain energy For example In nature around a mass we have a gravitational field. Any mass in that field experiences a force thus we can find energy associated with that mass and that energy will be Potential energy.

In the beginning, the height of the center of mass from the ground is $\dfrac{l}{2}$. So the initial potential energy is,
$V_i = - mg\dfrac{l}{2}$
When the stick is displaced at an angle $\theta $. The height of the center of mass from the ground is $\dfrac{l}{2}\sin \theta $.So the final potential energy is,
$V_f = - mg\dfrac{{l\sin \theta }}{2}$
The increase in potential energy
$V$ = $Vf - Vi$
\[V = - mg\dfrac{l}{2}\sin \theta + mg\dfrac{l}{2}\]
$ \Rightarrow V = - mg\dfrac{l}{2}(\sin \theta - 1)$
$ \therefore V = mg\dfrac{l}{2}(1 - \sin \theta )$
Therefore, the increase in potential energy is $mg\dfrac{l}{2}(1 - \sin \theta )$.
Note:There are three types of potential energy, (1) Elastic Potential energy: Any object that behaves as an elastic or spring contains elastic potential energy. (2)Gravitational potential energy: The earth has a gravitational force that pulls any object with mass towards the surface and so the object has energy associated with it called Gravitational Potential energy. (3) Chemical Potential Energy: The attractive forces between two atoms create chemical bonds and that bond between atoms and molecules leads to storage of energy in the form of Chemical Potential energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




