
A swimmer swims in still water at a speed of $5\text{km/hr}$. He enters a 200 m wide river, flowing at a speed of $4\text{km/hr}$at point A and proceeds to swim at an angle of ${{127}^{\circ }}$with the river flow direction. Another point B is located directly across A on the other side of the river. The swimmer lands on the other bank at a point C, from which he walks a distance CB with speed equal to $3\text{km/hr}$. The total time in which he reaches from A to B is
A.5 minutes
B.4 minutes
C.3 minutes
D.None
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: When the person starts swimming at a particular angle with the flow of the lake, there is a vertical component of velocity which is the velocity of the man in still water, and there is a horizontal component of velocity which is the velocity of the river. So resultant velocity will be the vector sum of these two velocities. The time taken to swim across the river can be found out by using the resultant velocity. Also, the Distance between point C and B can be calculated if we know the angle between resultant velocity and any of the two velocities.
Complete step by step answer:
So, we have a river which is 200m wide($d=200m$), the velocity of the man w.r.t the river can be represented by ${{v}_{sr}}$, which is equal to $5\text{km/hr}$. The velocity of the river is given by ${{v}_{r}}=4\text{km/hr}$. The angle made by the swimmer with the direction of river flow is $\theta ={{127}^{\circ }}$.
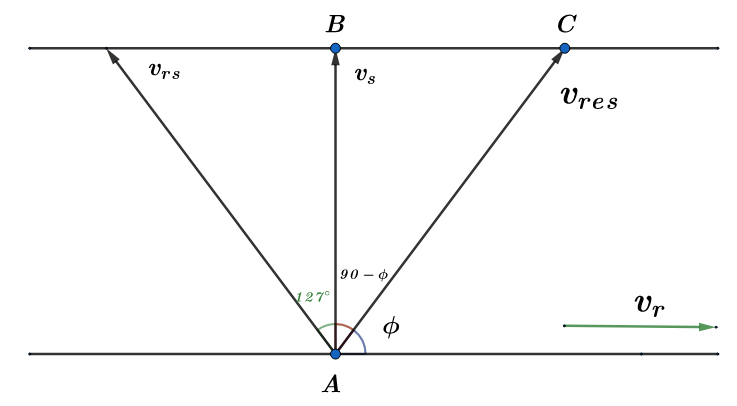
We can calculate the resultant velocity between the velocity of the man w.r.t to the river and the velocity of the river by making use of the formula:
${{v}_{res}}=\sqrt{{{v}_{s}}^{2}+{{v}_{r}}^{2}+2{{v}_{s}}{{v}_{r}}\cos \theta }$
Substituting the corresponding values in the equation above, we get
${{v}_{res}}=\sqrt{{{\left( 5\text{km/hr} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{4km/hr} \right)}^{2}}+2\left( 5\text{km/hr} \right)\left( \text{4km/hr} \right)\cos \left( {{127}^{\circ }} \right)}$
${{v}_{res}}=\sqrt{25+16+2\times 20\times (-0.602)}$
${{v}_{res}}=4.11\text{ km/hr}$ ….. equation (1)
So, the angle made by the resultant velocity $\left( {{v}_{res}} \right)$ with the velocity of the river $\left( {{v}_{r}} \right)$ is given by,
$\tan \phi =\dfrac{{{v}_{rs}}\sin \theta }{{{v}_{r}}+{{v}_{rs}}\cos \theta }=\dfrac{5\times \sin \left( {{127}^{\circ }} \right)}{4+\left( 5\times \cos ({{127}^{\circ }}) \right)}$
$\Rightarrow \phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{4}{1} \right)$
$\therefore \phi \approx {{76}^{\circ }}$
So the angle made with normal or the velocity of the man w.r.t to the ground will be $90-\phi $,
So the velocity of the man w.r.t the ground is given by,
${{v}_{s}}={{v}_{res}}\cos (90-\phi )$
${{v}_{s}}={{v}_{res}}\cos (14)$
$\therefore {{v}_{s}}=4\text{ km/hr}$
Velocity in the horizontal direction is,
${{v}_{h}}={{v}_{res}}\sin \left( 90-\phi \right)$
$\therefore {{v}_{h}}=1\text{ km/hr}$
So the time taken by the man to cover a distance of 200 m in the vertical direction is,
$t=\dfrac{d}{{{v}_{s}}}=\dfrac{0.2km}{4\text{km/hr}}$
$\therefore t=0.05hrs=3\text{ minutes}$
So the distance CB the man has drifted can be found out by taking the product of the horizontal velocity ${{v}_{h}}$ with the time taken to reach the other bank.
$CB={{v}_{h}}\times t$
$CB=1\text{ km/hr}\times 0.05hrs$
$\therefore CB=0.05km$
We know that the man runs from C to B at a speed of $3\text{km/hr}$, so, the time taken to cover this distance is,
$t'=\dfrac{CB}{3km/hr}$
$t'=\dfrac{0.05km}{3km/hr}$
$\therefore t'=1\text{ minute}$
So, the total time taken by the man is the sum of the time to reach the other bank and the time to reach point B from point C.
$\text{Total Time}=t+t'$
$\text{Total Time}=4\text{ minutes}$
So, answer to the question is option (B)- 4 minutes
Note:
Relative velocity is the velocity of an object or a person in another person’s rest frame. In one dimensional condition, it is the difference between the velocities of the two bodies. While in a higher dimension like in 2D and 3D, the velocities of the objects are split into components along various axes, and the relative velocity is found about each axis.
It can be used in the relativistic case, where the velocities are very small compared to the velocity of light. Galilean transformation is the principle used in these cases.
In an accelerated frame of reference, when a frame of reference is accelerated with respect to the other, the Galilean transformation does not hold.
In special relativity (non-relativistic case), the Galilean transformation is replaced by the Lorentz transformation.
Complete step by step answer:
So, we have a river which is 200m wide($d=200m$), the velocity of the man w.r.t the river can be represented by ${{v}_{sr}}$, which is equal to $5\text{km/hr}$. The velocity of the river is given by ${{v}_{r}}=4\text{km/hr}$. The angle made by the swimmer with the direction of river flow is $\theta ={{127}^{\circ }}$.

We can calculate the resultant velocity between the velocity of the man w.r.t to the river and the velocity of the river by making use of the formula:
${{v}_{res}}=\sqrt{{{v}_{s}}^{2}+{{v}_{r}}^{2}+2{{v}_{s}}{{v}_{r}}\cos \theta }$
Substituting the corresponding values in the equation above, we get
${{v}_{res}}=\sqrt{{{\left( 5\text{km/hr} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{4km/hr} \right)}^{2}}+2\left( 5\text{km/hr} \right)\left( \text{4km/hr} \right)\cos \left( {{127}^{\circ }} \right)}$
${{v}_{res}}=\sqrt{25+16+2\times 20\times (-0.602)}$
${{v}_{res}}=4.11\text{ km/hr}$ ….. equation (1)
So, the angle made by the resultant velocity $\left( {{v}_{res}} \right)$ with the velocity of the river $\left( {{v}_{r}} \right)$ is given by,
$\tan \phi =\dfrac{{{v}_{rs}}\sin \theta }{{{v}_{r}}+{{v}_{rs}}\cos \theta }=\dfrac{5\times \sin \left( {{127}^{\circ }} \right)}{4+\left( 5\times \cos ({{127}^{\circ }}) \right)}$
$\Rightarrow \phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{4}{1} \right)$
$\therefore \phi \approx {{76}^{\circ }}$
So the angle made with normal or the velocity of the man w.r.t to the ground will be $90-\phi $,
So the velocity of the man w.r.t the ground is given by,
${{v}_{s}}={{v}_{res}}\cos (90-\phi )$
${{v}_{s}}={{v}_{res}}\cos (14)$
$\therefore {{v}_{s}}=4\text{ km/hr}$
Velocity in the horizontal direction is,
${{v}_{h}}={{v}_{res}}\sin \left( 90-\phi \right)$
$\therefore {{v}_{h}}=1\text{ km/hr}$
So the time taken by the man to cover a distance of 200 m in the vertical direction is,
$t=\dfrac{d}{{{v}_{s}}}=\dfrac{0.2km}{4\text{km/hr}}$
$\therefore t=0.05hrs=3\text{ minutes}$
So the distance CB the man has drifted can be found out by taking the product of the horizontal velocity ${{v}_{h}}$ with the time taken to reach the other bank.
$CB={{v}_{h}}\times t$
$CB=1\text{ km/hr}\times 0.05hrs$
$\therefore CB=0.05km$
We know that the man runs from C to B at a speed of $3\text{km/hr}$, so, the time taken to cover this distance is,
$t'=\dfrac{CB}{3km/hr}$
$t'=\dfrac{0.05km}{3km/hr}$
$\therefore t'=1\text{ minute}$
So, the total time taken by the man is the sum of the time to reach the other bank and the time to reach point B from point C.
$\text{Total Time}=t+t'$
$\text{Total Time}=4\text{ minutes}$
So, answer to the question is option (B)- 4 minutes
Note:
Relative velocity is the velocity of an object or a person in another person’s rest frame. In one dimensional condition, it is the difference between the velocities of the two bodies. While in a higher dimension like in 2D and 3D, the velocities of the objects are split into components along various axes, and the relative velocity is found about each axis.
It can be used in the relativistic case, where the velocities are very small compared to the velocity of light. Galilean transformation is the principle used in these cases.
In an accelerated frame of reference, when a frame of reference is accelerated with respect to the other, the Galilean transformation does not hold.
In special relativity (non-relativistic case), the Galilean transformation is replaced by the Lorentz transformation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




