
What is a Taxonomic hierarchy? Explain in detail.
Answer
500.7k+ views
Hint: It's the method of composing numerous organisms into sequential levels of the biological classification either associate degree exceedingly decreasing or an increasing order from kingdom to species and the other way around. In this system of classification, the kingdom is usually the highest followed by division.
Complete answer
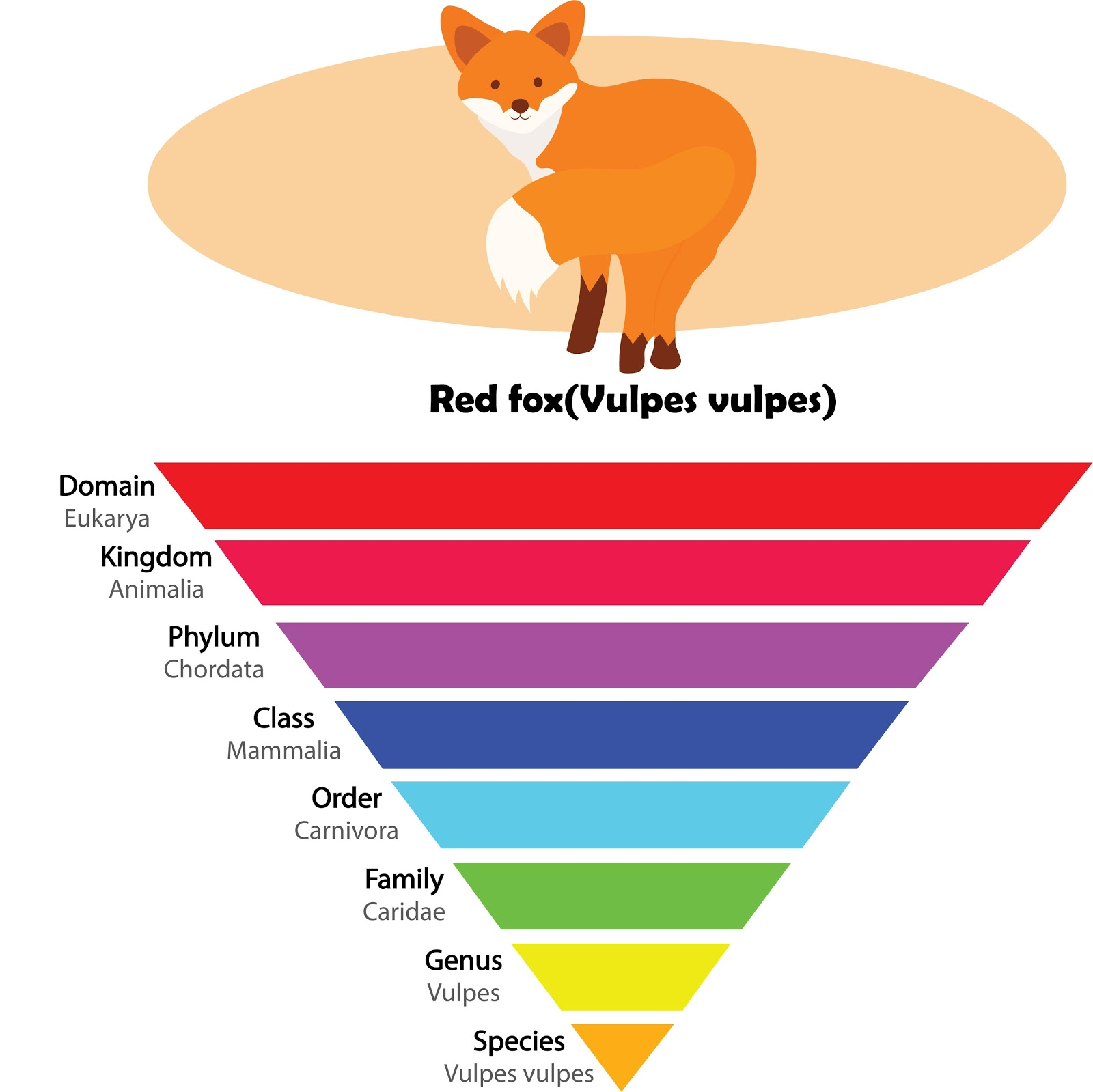
Linnaeus has been introduced to the taxonomic hierarchy. That’s why it is also called a Linnaean hierarchy. It's utilized to classify organisms into completely different classes. It includes the sequence of classes in an exceedingly decreasing or increasing order from kingdom to species and vice-versa. The domain is the top rank within the hierarchy and it is followed by division of the kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Species is the lowest rank within the hierarchy.
Additional information:
Taxonomic Hierarchy classes
Following are vital taxonomic hierarchies during which completely different organisms are classified:
Kingdom:
The kingdom is the highest level of classification, which is split into subgroups at numerous levels. There are five kingdoms in which the living organisms are classified, namely, Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, and Monera.
Phylum:
This is a successive level of classification and is more species than the kingdom. There are thirty-five phyla in the Animalia kingdom. Like as – phylum, Chordata, Arthropoda, etc.
Class:
The class was the foremost general rank within the taxonomic hierarchy till phyla weren't introduced. Animalia kingdom includes 108 categories as well as class, reptilia, aves, etc. However, the categories used these days are completely different from those projected by Linnaeus and don't seem to be used often.
Order:
The order could be a lot more specific than class. The order constitutes one or over one similar families. There are around twenty-six orders at school class Mammalia like primates, Carnivora, etc.
Family:
This class of taxonomical hierarchy includes numerous genera that share a number of similarities. For eg., the families within the order Carnivora include Canidae, Felidae, Ursidae, etc.
Genus:
A group of comparable species forms a genus. Some genera have only 1 species and are known as monotypic, whereas, some have over one species and are understood as polytypic. For eg., the lion and tiger are placed beneath the genus Panthera.
Species:
It is the lowest bottom level of the taxonomic hierarchy. There are 8.7 million various species on earth. It refers to a group of organisms that are similar in shape, form, generative options. Species may be more divided into subspecies.
Note:
A taxon is typically appointed a rank once it's given its formal name. The fundamental ranks are species and genus. Once an associate degree organism is given a species name it's appointed to a genus, and also the genus name is an element of the species name.
The species name is additionally known as a binomial, that is, a two-term name. As an example, the zoological name for the human species is Homo sapiens.
Complete answer
Linnaeus has been introduced to the taxonomic hierarchy. That’s why it is also called a Linnaean hierarchy. It's utilized to classify organisms into completely different classes. It includes the sequence of classes in an exceedingly decreasing or increasing order from kingdom to species and vice-versa. The domain is the top rank within the hierarchy and it is followed by division of the kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Species is the lowest rank within the hierarchy.
Additional information:
Taxonomic Hierarchy classes
Following are vital taxonomic hierarchies during which completely different organisms are classified:
Kingdom:
The kingdom is the highest level of classification, which is split into subgroups at numerous levels. There are five kingdoms in which the living organisms are classified, namely, Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, and Monera.
Phylum:
This is a successive level of classification and is more species than the kingdom. There are thirty-five phyla in the Animalia kingdom. Like as – phylum, Chordata, Arthropoda, etc.
Class:
The class was the foremost general rank within the taxonomic hierarchy till phyla weren't introduced. Animalia kingdom includes 108 categories as well as class, reptilia, aves, etc. However, the categories used these days are completely different from those projected by Linnaeus and don't seem to be used often.
Order:
The order could be a lot more specific than class. The order constitutes one or over one similar families. There are around twenty-six orders at school class Mammalia like primates, Carnivora, etc.
Family:
This class of taxonomical hierarchy includes numerous genera that share a number of similarities. For eg., the families within the order Carnivora include Canidae, Felidae, Ursidae, etc.
Genus:
A group of comparable species forms a genus. Some genera have only 1 species and are known as monotypic, whereas, some have over one species and are understood as polytypic. For eg., the lion and tiger are placed beneath the genus Panthera.
Species:
It is the lowest bottom level of the taxonomic hierarchy. There are 8.7 million various species on earth. It refers to a group of organisms that are similar in shape, form, generative options. Species may be more divided into subspecies.
Note:
A taxon is typically appointed a rank once it's given its formal name. The fundamental ranks are species and genus. Once an associate degree organism is given a species name it's appointed to a genus, and also the genus name is an element of the species name.
The species name is additionally known as a binomial, that is, a two-term name. As an example, the zoological name for the human species is Homo sapiens.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




