
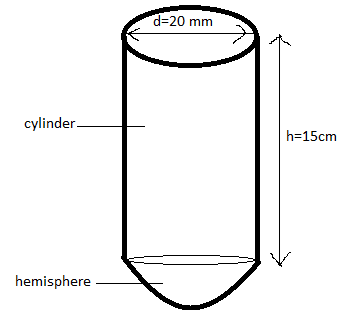
A test tube has a diameter 20 mm and height is 15 cm. The lower portion is a hemisphere. Find the capacity of the test tube. (π = 3.14)

Answer
617.1k+ views
Hint: Divide the test tube into a hemisphere and a cylinder. Find both the volumes and add them to find the capacity of the test tube. The capacity of the test tube is nothing but the volume of the test tube. Convert the measurements into the same units.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given Data
Diameter d = 20 mm = 2 cm (1 cm = 10 mm)
Radius r = 10 mm = 1 cm $\left( {{\text{r = }}\dfrac{{\text{d}}}{2}} \right)$
Let us consider the volume of the cylinder as $V_1$ and volume of the hemisphere as $V_2$.
Volume of a cylinder = 2πrh (where r – radius and h – height)
And, Volume of hemisphere = $\dfrac{2}{3}\pi {{\text{r}}^3}$(where r – radius)
Now $V_1$ = 2 × 3.14 × 1 × 15 = 94.2 ${\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$
$V_2$ = $\dfrac{2}{3} \times 3.14 \times {1^3} = {\text{2}}{\text{.093c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$
Now volume of test tube = $V_1$ + $V_2$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{V = 94}}{\text{.2 + 2}}{\text{.093 = 96}}{\text{.293c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$
The capacity of is the volume of the test tube which is ${\text{96}}{\text{.293c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$
Note: The pivotal part of the problem is to break down the given figure into known figures with known formulae. In this problem the volume of the test tube is unknown but when it is broken down into a cylinder and a hemisphere whose volumes are known the problem becomes pretty straight forward.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given Data
Diameter d = 20 mm = 2 cm (1 cm = 10 mm)
Radius r = 10 mm = 1 cm $\left( {{\text{r = }}\dfrac{{\text{d}}}{2}} \right)$
Let us consider the volume of the cylinder as $V_1$ and volume of the hemisphere as $V_2$.
Volume of a cylinder = 2πrh (where r – radius and h – height)
And, Volume of hemisphere = $\dfrac{2}{3}\pi {{\text{r}}^3}$(where r – radius)
Now $V_1$ = 2 × 3.14 × 1 × 15 = 94.2 ${\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$
$V_2$ = $\dfrac{2}{3} \times 3.14 \times {1^3} = {\text{2}}{\text{.093c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$
Now volume of test tube = $V_1$ + $V_2$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{V = 94}}{\text{.2 + 2}}{\text{.093 = 96}}{\text{.293c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$
The capacity of is the volume of the test tube which is ${\text{96}}{\text{.293c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$
Note: The pivotal part of the problem is to break down the given figure into known figures with known formulae. In this problem the volume of the test tube is unknown but when it is broken down into a cylinder and a hemisphere whose volumes are known the problem becomes pretty straight forward.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




