
A thin rod of length L and mass M is bent at its midpoint into two halves so that the angle between them is ${90^0}$. The moment of inertia of the bent rod about an axis passing through the bending point and perpendicular to the plane defined by the two halves of the rod is:
$\left( A \right)\dfrac{{M{L^2}}}{2}$
$\left( B \right)\dfrac{{\sqrt 2 M{L^2}}}{{24}}$
$\left( C \right)\dfrac{{M{L^2}}}{{24}}$
$\left( D \right)\dfrac{{M{L^2}}}{{12}}$
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: In rotational motion, the property of the rigid body of which opposes any change in state of rest or of uniform circular motion is the rotational inertia. In rotational inertia the body rotates about the axis of rotation. Hence calculate the moment of inertia of the rod that is bent in two equal halves.
Formula used:
$I = m{r^2}$, Where $I$ is the moment of inertia and $m$ is the mass of the body.
Complete step by step answer:
In translator motion, the property that opposes the change in the state of a body from its state of rest or from uniform motion is inertia. In translator inertia the body moves linearly. In rotational motion, the property of the rigid body of which opposes any change in state of rest or of uniform circular motion is the rotational inertia. In rotational inertia the body rotates about the axis of rotation. In Rotatory motion, moment of inertia does the same role as the mass in linear motion. In rotational inertia the body rotates about the axis of rotation.
Bending a rod of mass M and length L into two halves will change the length to $\dfrac{L}{2}$ and mass $\dfrac{M}{2}$.
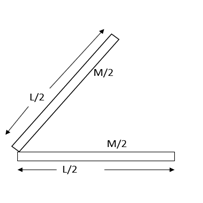
Moment of inertia of each part at one end is given by $\dfrac{1}{3}\left( {\dfrac{M}{2}} \right){\left( {\dfrac{L}{2}} \right)^2}$
Then the net moment of inertia at the point O
$I = \dfrac{1}{3}\left[ {\dfrac{{M{L^2}}}{8} + \dfrac{{M{L^2}}}{8}} \right] = \dfrac{{M{L^2}}}{{12}}$
Hence, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: Moment of inertia depends on mass and also on the distance from the axis of rotation. Moment of inertia also depends on the size and shape of the body. Larger moments of inertia will help the body to maintain uniform motion. In rotational inertia the body rotates about the axis of rotation.
Formula used:
$I = m{r^2}$, Where $I$ is the moment of inertia and $m$ is the mass of the body.
Complete step by step answer:
In translator motion, the property that opposes the change in the state of a body from its state of rest or from uniform motion is inertia. In translator inertia the body moves linearly. In rotational motion, the property of the rigid body of which opposes any change in state of rest or of uniform circular motion is the rotational inertia. In rotational inertia the body rotates about the axis of rotation. In Rotatory motion, moment of inertia does the same role as the mass in linear motion. In rotational inertia the body rotates about the axis of rotation.
Bending a rod of mass M and length L into two halves will change the length to $\dfrac{L}{2}$ and mass $\dfrac{M}{2}$.

Moment of inertia of each part at one end is given by $\dfrac{1}{3}\left( {\dfrac{M}{2}} \right){\left( {\dfrac{L}{2}} \right)^2}$
Then the net moment of inertia at the point O
$I = \dfrac{1}{3}\left[ {\dfrac{{M{L^2}}}{8} + \dfrac{{M{L^2}}}{8}} \right] = \dfrac{{M{L^2}}}{{12}}$
Hence, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: Moment of inertia depends on mass and also on the distance from the axis of rotation. Moment of inertia also depends on the size and shape of the body. Larger moments of inertia will help the body to maintain uniform motion. In rotational inertia the body rotates about the axis of rotation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




