
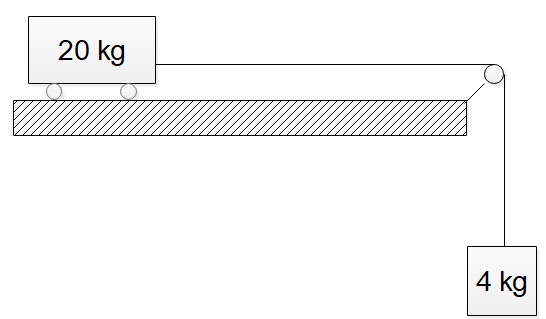
A trolley of mass 20 kg is attached to a block of mass 4 kg by a massless string passing over a frictionless pulley as shown in the figure. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the trolley and the surface is $ 0.02 $ , then the acceleration of the trolley and block system is:
$ \left( {{\text{Take }}g{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}10\;m{s^{ - 2}}} \right) $
A) $ 1\,m/{s^2} $
B) $ 2\,m/{s^2} $
C) $ 1.5\,m/{s^2} $
D) $ 2.5\,m/{s^2} $

Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: In this solution, we will first calculate the tension in the string on the left side and below the pulley. Since the pulley is smooth, the tension in the string will be the same on both sides of the pulley.
Formula used
In this solution, we will use the following formula:
- Friction force: $ {F_k} = \mu N $ where $ \mu $ is the coefficient of friction and $ N $ is the normal force.
Complete step by step answer:
In the situation given to us, the string is extensible, massless and the pulley is also smooth. Then the tension in the string will be constant and both the blocks will also have the same acceleration. For the block that is floating, the equation of motion will be
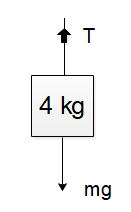
$ 4g - T = 4a $
Similarly, for the trolley, the equation of motion will be
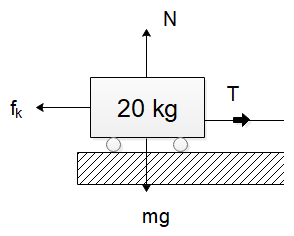
$ T - {f_k} = 20a $
Here $ {f_k} = \mu N $ . The normal force will be equal to $ N = mg $ . Since there is no other force in the vertical direction for the trolley, the normal force will be balanced by the weight of the trolley
Equating the tension in equation (1) and (2), we get
$ 4g - 4a = 20a + \mu N $
Substituting the value of $ N = 20g $ and $ g = 10\,m/{s^2} $ , we get the acceleration as
$ a = 1.5\,m/{s^2} $
This will be the acceleration of the trolley as well as the block that is falling down. Hence the correct choice is option (C).
Note:
The friction force acting, in this case, will be kinetic friction as the object will be accelerating. We should be careful to take the direction of the pseudo force in the direction opposite to the direction of the acceleration of the blocks. The weight of the hanging block must be greater than the static friction of the trolley for the trolley and the block to accelerate.
Formula used
In this solution, we will use the following formula:
- Friction force: $ {F_k} = \mu N $ where $ \mu $ is the coefficient of friction and $ N $ is the normal force.
Complete step by step answer:
In the situation given to us, the string is extensible, massless and the pulley is also smooth. Then the tension in the string will be constant and both the blocks will also have the same acceleration. For the block that is floating, the equation of motion will be

$ 4g - T = 4a $
Similarly, for the trolley, the equation of motion will be

$ T - {f_k} = 20a $
Here $ {f_k} = \mu N $ . The normal force will be equal to $ N = mg $ . Since there is no other force in the vertical direction for the trolley, the normal force will be balanced by the weight of the trolley
Equating the tension in equation (1) and (2), we get
$ 4g - 4a = 20a + \mu N $
Substituting the value of $ N = 20g $ and $ g = 10\,m/{s^2} $ , we get the acceleration as
$ a = 1.5\,m/{s^2} $
This will be the acceleration of the trolley as well as the block that is falling down. Hence the correct choice is option (C).
Note:
The friction force acting, in this case, will be kinetic friction as the object will be accelerating. We should be careful to take the direction of the pseudo force in the direction opposite to the direction of the acceleration of the blocks. The weight of the hanging block must be greater than the static friction of the trolley for the trolley and the block to accelerate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




