
What is a two-dimensional coordination number in a square close packing layer of a molecule?
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: In two dimensional square packing structure, the constituent particles are arranged in rows. These rows are arranged one on top of each other so that the particles from adjacent rows perfectly line up with each other.
Complete step by step answer:
As mentioned, if we considered an atom A and this atom is used to make a two dimensional square packing structure then we get a structure that looks like a sheet of repeating A atoms. This can be demonstrated in the picture below:
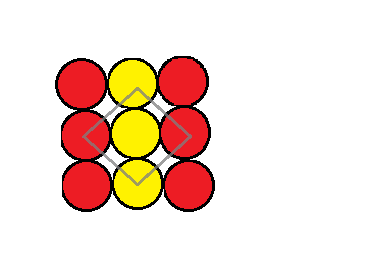
The coordination number can be defined as the number of atoms that are closest to one particular atom. This is demonstrated in the image above where you can see that the grey outline around the yellow atom represents or includes all the atoms that are closest to it. Looking at it closely we can see that it is closest to only four of the atoms. This means that the coordination number of an atom in the square closed packing in two dimensions is $4$.
We can also see that due to the arrangement of the particles in identical rows stacked upon each other. There is the appearance of voids or interstitial spaces.
We can also find the packing fraction that is, the percentage of area that is occupied by particles in the lattice. This can be found by taking the ratio of the area of a single atom to the area of the unit cell. The packing fraction of this two dimensional structure is $74%$. This means that $74%$of the lattice is occupied by the atoms. The remaining $26%$is made of interstitial sites or voids.
Therefore, the answer to this question is finally $4$.
Note: There is also another two dimensional close packing structure in which the particles are arranged in such a way that alternate rows of the particles are identical. This is called Hexagonal two dimensional closed packing. Make sure that you do not get confused with the two structures.
Complete step by step answer:
As mentioned, if we considered an atom A and this atom is used to make a two dimensional square packing structure then we get a structure that looks like a sheet of repeating A atoms. This can be demonstrated in the picture below:

The coordination number can be defined as the number of atoms that are closest to one particular atom. This is demonstrated in the image above where you can see that the grey outline around the yellow atom represents or includes all the atoms that are closest to it. Looking at it closely we can see that it is closest to only four of the atoms. This means that the coordination number of an atom in the square closed packing in two dimensions is $4$.
We can also see that due to the arrangement of the particles in identical rows stacked upon each other. There is the appearance of voids or interstitial spaces.
We can also find the packing fraction that is, the percentage of area that is occupied by particles in the lattice. This can be found by taking the ratio of the area of a single atom to the area of the unit cell. The packing fraction of this two dimensional structure is $74%$. This means that $74%$of the lattice is occupied by the atoms. The remaining $26%$is made of interstitial sites or voids.
Therefore, the answer to this question is finally $4$.
Note: There is also another two dimensional close packing structure in which the particles are arranged in such a way that alternate rows of the particles are identical. This is called Hexagonal two dimensional closed packing. Make sure that you do not get confused with the two structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




