
A variable straight line drawn through the point of intersection of lines \[\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1\] and $\dfrac{x}{b} + \dfrac{y}{a} = 1$, meets the coordinate axes at A and B. Show that the locus of the midpoint of AB is $2(a + b) = ab(x + y)$
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: This problem deals with the concept of straight lines. Here two straight lines \[\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1\] and $\dfrac{x}{b} + \dfrac{y}{a} = 1$, are intersected at a point. A line passing through the point of intersection of these straight lines intersects the coordinate axes at two points. We have to find the locus of the midpoint of these two points on the coordinate axes.
If any two lines intersect each other, if the two lines are $a{x_1} + b{y_1} + {c_1} = 0$ and $a{x_2} + b{y_2} + {c_2} = 0$, then the equation of the line passing through the point of intersection of the above lines is :
$\left( {a{x_1} + b{y_1} + {c_1}} \right) + k\left( {a{x_2} + b{y_2} + {c_2}} \right) = 0$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that there are two lines \[\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1\] and $\dfrac{x}{b} + \dfrac{y}{a} = 1$, they intersect the axes as shown below in the figure.
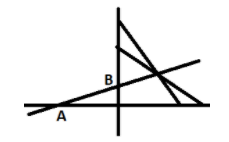
Now a line passes through the point of intersection of the lines \[\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1\] and $\dfrac{x}{b} + \dfrac{y}{a} = 1$, intersects the coordinate axes at two points A and B, as shown in the figure above.
We have to find the locus of the midpoint of the line segment AB.
Consider the equation \[\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1\], simplify the equation as given below:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{bx + ay}}{{ab}} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow bx + ay = ab$
$ \Rightarrow bx + ay - ab = 0$
Now consider the equation $\dfrac{x}{b} + \dfrac{y}{a} = 1$, simplify the equation as given below:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ax + by}}{{ab}} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow ax + by = ab$
$ \Rightarrow ax + by - ab = 0$
We know that as these lines intersect, the equation of the line passing through the point of intersection is given by:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {bx + ay - ab} \right) + k\left( {ax + by - ab} \right) = 0$
Simplifying the above equation:
$ \Rightarrow bx + ay - ab + kax + kby - kab = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {ak + b} \right)x + \left( {a + kb} \right)y - ab\left( {1 + k} \right) = 0$
Now this line intersects the coordinate axes, so finding the x- coordinate when intersects the x-axis:
Here $y = 0$,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {ak + b} \right)x + \left( {a + kb} \right)(0) - ab\left( {1 + k} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {ak + b} \right)x - ab\left( {1 + k} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {ak + b} \right)x = ab\left( {1 + k} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {ak + b} \right)}}$
So the coordinates of point A is $\left( {x,0} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {ak + b} \right)}},0} \right)$
This line also intersects the y- axis, so finding the y- coordinate:
Here $x = 0$,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {ak + b} \right)\left( 0 \right) + \left( {a + kb} \right)y - ab\left( {1 + k} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {a + kb} \right)y - ab\left( {1 + k} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {a + kb} \right)y = ab\left( {1 + k} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {a + kb} \right)}}$
So the coordinates of point B is $\left( {0,y} \right) = \left( {0,\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {a + kb} \right)}}} \right)$
We have the coordinates of both points A and B.
$A = \left( {\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {ak + b} \right)}},0} \right)$, $B = \left( {0,\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {a + kb} \right)}}} \right)$
Now the midpoint of AB is given by:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {ak + b} \right)}} + 0} \right)}}{2},\dfrac{{\left( {0 + \dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {a + kb} \right)}}} \right)}}{2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{2\left( {ak + b} \right)}},\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{2\left( {a + kb} \right)}}} \right)$
Let the coordinates of the midpoint of AB be $\left( {x,y} \right)$, so that we can eliminate $k$, and the locus of the midpoint AB can be found, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{2\left( {ak + b} \right)}},\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{2\left( {a + kb} \right)}}} \right) = \left( {x,y} \right)$
Equating x and y coordinates as given below:
First equating the x-coordinate:
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{2\left( {ak + b} \right)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2akx + 2bx = ab + abk\]
\[ \Rightarrow ak(2x - b) = b(a - 2x)\]
\[ \Rightarrow k = \dfrac{{b(a - 2x)}}{{a(2x - b)}}\]
Now equating y-coordinate:
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{2\left( {a + kb} \right)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2ay + 2kby = ab + abk\]
\[ \Rightarrow bk(2y - a) = a(b - 2y)\]
\[ \Rightarrow k = \dfrac{{a(b - 2y)}}{{b(2y - a)}}\]
Now equating both $k$ expressions as given below:
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{b(a - 2x)}}{{a(2x - b)}} = \dfrac{{a(b - 2y)}}{{b(2y - a)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {b^2}(a - 2x)(2y - a) = {a^2}(b - 2y)(2x - b)\]
On solving the above equation, gives:
$ \Rightarrow 2(a + b) = ab(x + y)$
Hence proved.
Note: While solving this problem please note that we used a formula for finding the midpoint of the line joining two points A and B. If the points \[A = \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[B = \left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\], then the midpoint of AB is given by: $\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$.
If any two lines intersect each other, if the two lines are $a{x_1} + b{y_1} + {c_1} = 0$ and $a{x_2} + b{y_2} + {c_2} = 0$, then the equation of the line passing through the point of intersection of the above lines is :
$\left( {a{x_1} + b{y_1} + {c_1}} \right) + k\left( {a{x_2} + b{y_2} + {c_2}} \right) = 0$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that there are two lines \[\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1\] and $\dfrac{x}{b} + \dfrac{y}{a} = 1$, they intersect the axes as shown below in the figure.

Now a line passes through the point of intersection of the lines \[\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1\] and $\dfrac{x}{b} + \dfrac{y}{a} = 1$, intersects the coordinate axes at two points A and B, as shown in the figure above.
We have to find the locus of the midpoint of the line segment AB.
Consider the equation \[\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1\], simplify the equation as given below:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{bx + ay}}{{ab}} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow bx + ay = ab$
$ \Rightarrow bx + ay - ab = 0$
Now consider the equation $\dfrac{x}{b} + \dfrac{y}{a} = 1$, simplify the equation as given below:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ax + by}}{{ab}} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow ax + by = ab$
$ \Rightarrow ax + by - ab = 0$
We know that as these lines intersect, the equation of the line passing through the point of intersection is given by:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {bx + ay - ab} \right) + k\left( {ax + by - ab} \right) = 0$
Simplifying the above equation:
$ \Rightarrow bx + ay - ab + kax + kby - kab = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {ak + b} \right)x + \left( {a + kb} \right)y - ab\left( {1 + k} \right) = 0$
Now this line intersects the coordinate axes, so finding the x- coordinate when intersects the x-axis:
Here $y = 0$,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {ak + b} \right)x + \left( {a + kb} \right)(0) - ab\left( {1 + k} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {ak + b} \right)x - ab\left( {1 + k} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {ak + b} \right)x = ab\left( {1 + k} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {ak + b} \right)}}$
So the coordinates of point A is $\left( {x,0} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {ak + b} \right)}},0} \right)$
This line also intersects the y- axis, so finding the y- coordinate:
Here $x = 0$,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {ak + b} \right)\left( 0 \right) + \left( {a + kb} \right)y - ab\left( {1 + k} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {a + kb} \right)y - ab\left( {1 + k} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {a + kb} \right)y = ab\left( {1 + k} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {a + kb} \right)}}$
So the coordinates of point B is $\left( {0,y} \right) = \left( {0,\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {a + kb} \right)}}} \right)$
We have the coordinates of both points A and B.
$A = \left( {\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {ak + b} \right)}},0} \right)$, $B = \left( {0,\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {a + kb} \right)}}} \right)$
Now the midpoint of AB is given by:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {ak + b} \right)}} + 0} \right)}}{2},\dfrac{{\left( {0 + \dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{\left( {a + kb} \right)}}} \right)}}{2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{2\left( {ak + b} \right)}},\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{2\left( {a + kb} \right)}}} \right)$
Let the coordinates of the midpoint of AB be $\left( {x,y} \right)$, so that we can eliminate $k$, and the locus of the midpoint AB can be found, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{2\left( {ak + b} \right)}},\dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{2\left( {a + kb} \right)}}} \right) = \left( {x,y} \right)$
Equating x and y coordinates as given below:
First equating the x-coordinate:
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{2\left( {ak + b} \right)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2akx + 2bx = ab + abk\]
\[ \Rightarrow ak(2x - b) = b(a - 2x)\]
\[ \Rightarrow k = \dfrac{{b(a - 2x)}}{{a(2x - b)}}\]
Now equating y-coordinate:
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{ab\left( {1 + k} \right)}}{{2\left( {a + kb} \right)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2ay + 2kby = ab + abk\]
\[ \Rightarrow bk(2y - a) = a(b - 2y)\]
\[ \Rightarrow k = \dfrac{{a(b - 2y)}}{{b(2y - a)}}\]
Now equating both $k$ expressions as given below:
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{b(a - 2x)}}{{a(2x - b)}} = \dfrac{{a(b - 2y)}}{{b(2y - a)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {b^2}(a - 2x)(2y - a) = {a^2}(b - 2y)(2x - b)\]
On solving the above equation, gives:
$ \Rightarrow 2(a + b) = ab(x + y)$
Hence proved.
Note: While solving this problem please note that we used a formula for finding the midpoint of the line joining two points A and B. If the points \[A = \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[B = \left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\], then the midpoint of AB is given by: $\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




