
What is a vascular bundle? Name any two types of Vascular bundles.
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: In plants in order to transport the water and minerals, there is separate tissue called vascular tissue found in vascular plants, and it contains mainly xylem and phloem, and some other protective tissues.
Complete answer:
When coming to the types of vascular bundles, based on the relative position of the xylem and phloem they mainly classified into 3types
- Radial
- Conjoint
- Concentric vascular bundles
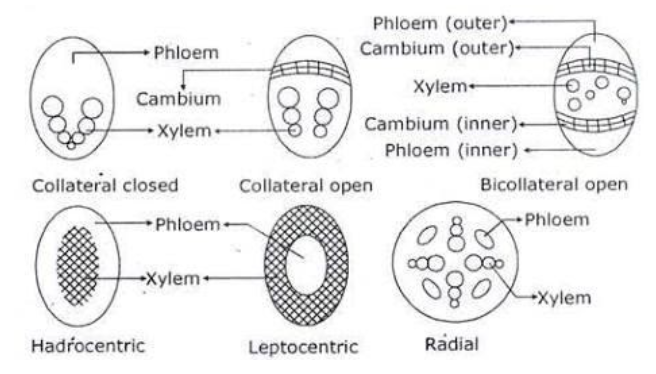
> Radial vascular bundle: In general this type of vascular bundles is seen in roots
- Where the xylem and the phsome are seen at various radial locations.
> Conjoint vascular bundle: In this conjoint vascular bundle, usually both xylem and phloem are present on the same radius, but they are located opposite to each other.
- We commonly observe conjoint vascular bundles in stems of dicots
- Based on the phloem this is again classified into two forms they are
- Collateral vascular bundle: This type of vascular bundles are commonly found in the dicot stems, except in some families of Cucurbitaceae and Convolvulaceae and at the same time on the presence of cambium, based on this they, in turn, are again classified into a closed or open type of vascular bundles
- Bicollateral vascular bundle: This type of vascular bundles mainly consists of phloem in two patches, which present on either side of the xylem. Where the outer remains periphery and inner remains to the middle, whereas they also contain 2 cambium, which outer cambium is more active than the inner one.
> Concentric vascular bundles: In this type mainly xylem surrounds the tissue of the phloem or vice versa
- Based on this they are again of two types
- Leptocentric type : where the xylem surrounds the phloem in all the sides
- Hadrocentric type: where phloem covers the xylem all over the tissue.
Note: In this type of questions, drawing diagrams adds extra strength to the answer and it becomes easy to understand. And it’s important to mention about the other names for example Lepto Centric is also called as amphivasal, while hadrocentric type is also called as amphicribral.
Complete answer:
When coming to the types of vascular bundles, based on the relative position of the xylem and phloem they mainly classified into 3types
- Radial
- Conjoint
- Concentric vascular bundles

> Radial vascular bundle: In general this type of vascular bundles is seen in roots
- Where the xylem and the phsome are seen at various radial locations.
> Conjoint vascular bundle: In this conjoint vascular bundle, usually both xylem and phloem are present on the same radius, but they are located opposite to each other.
- We commonly observe conjoint vascular bundles in stems of dicots
- Based on the phloem this is again classified into two forms they are
- Collateral vascular bundle: This type of vascular bundles are commonly found in the dicot stems, except in some families of Cucurbitaceae and Convolvulaceae and at the same time on the presence of cambium, based on this they, in turn, are again classified into a closed or open type of vascular bundles
- Bicollateral vascular bundle: This type of vascular bundles mainly consists of phloem in two patches, which present on either side of the xylem. Where the outer remains periphery and inner remains to the middle, whereas they also contain 2 cambium, which outer cambium is more active than the inner one.
> Concentric vascular bundles: In this type mainly xylem surrounds the tissue of the phloem or vice versa
- Based on this they are again of two types
- Leptocentric type : where the xylem surrounds the phloem in all the sides
- Hadrocentric type: where phloem covers the xylem all over the tissue.
Note: In this type of questions, drawing diagrams adds extra strength to the answer and it becomes easy to understand. And it’s important to mention about the other names for example Lepto Centric is also called as amphivasal, while hadrocentric type is also called as amphicribral.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




